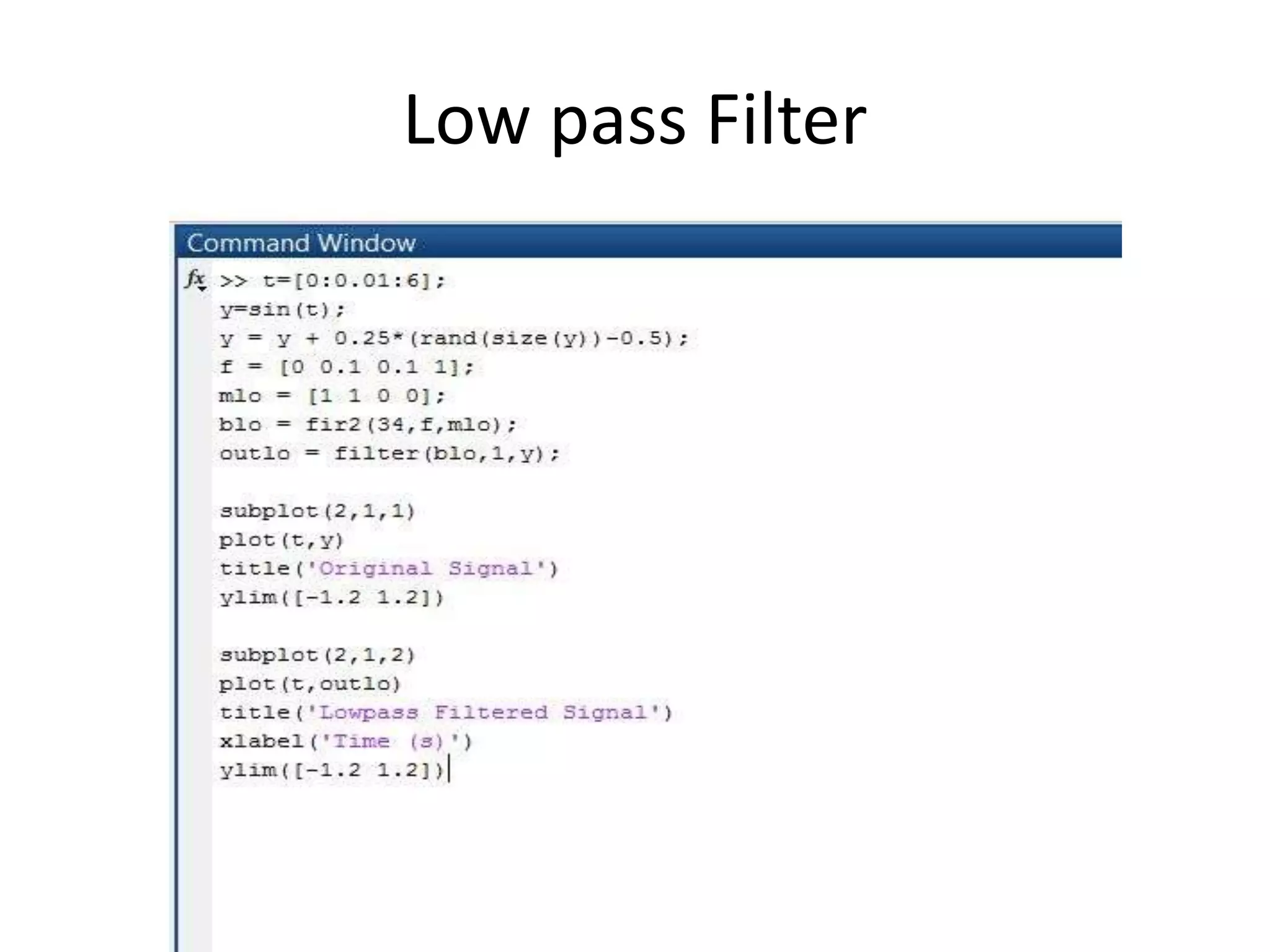
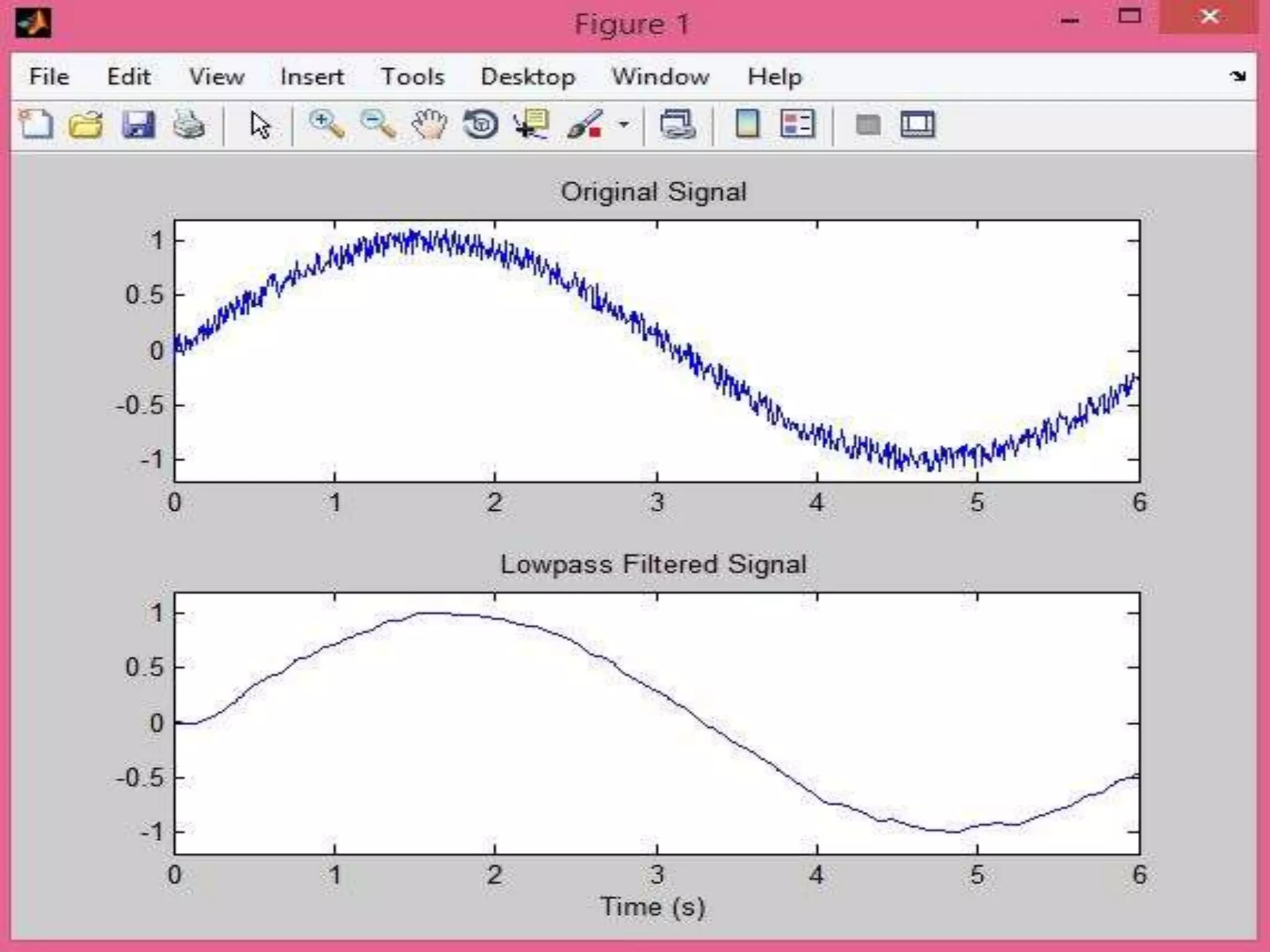
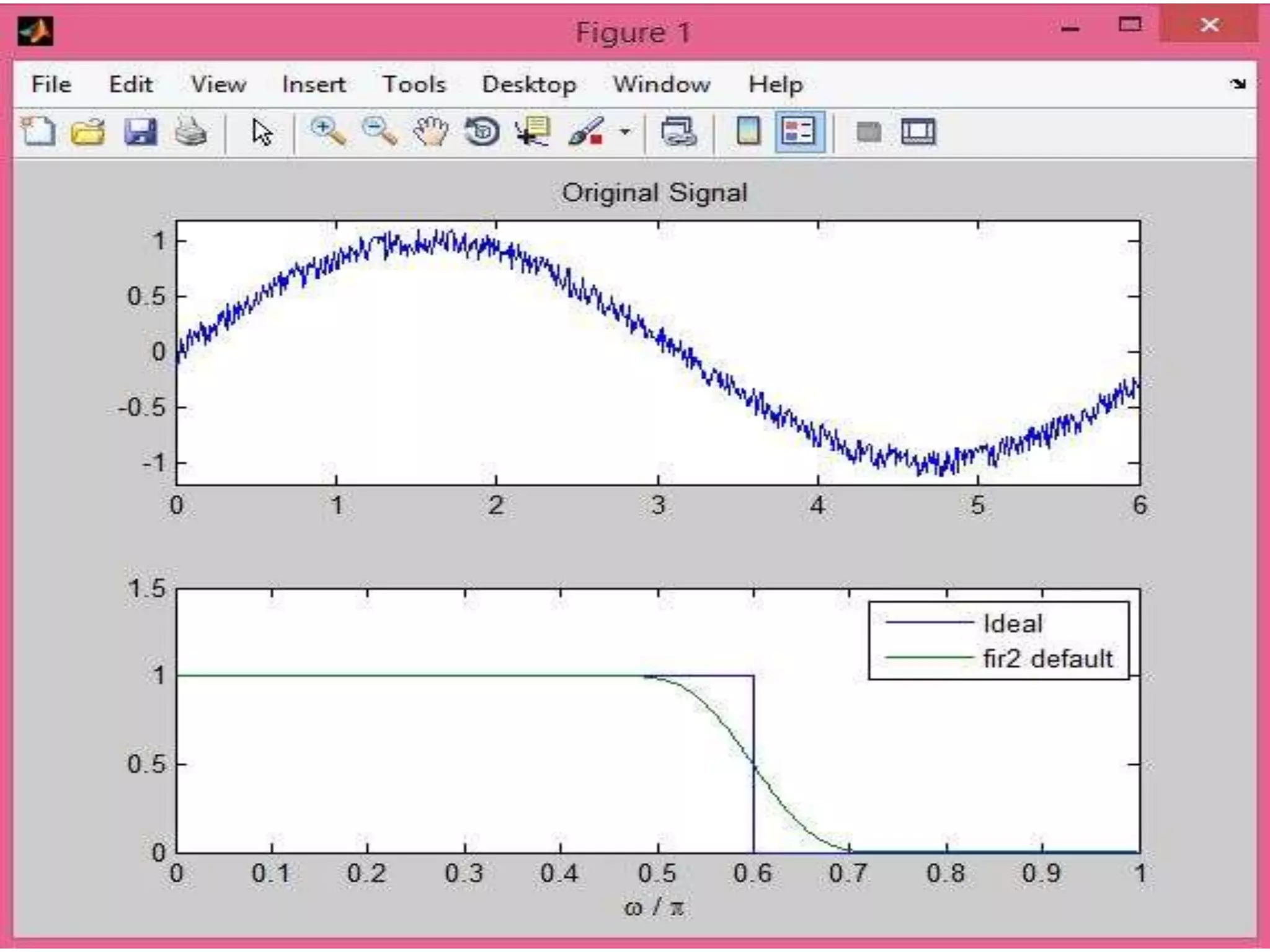
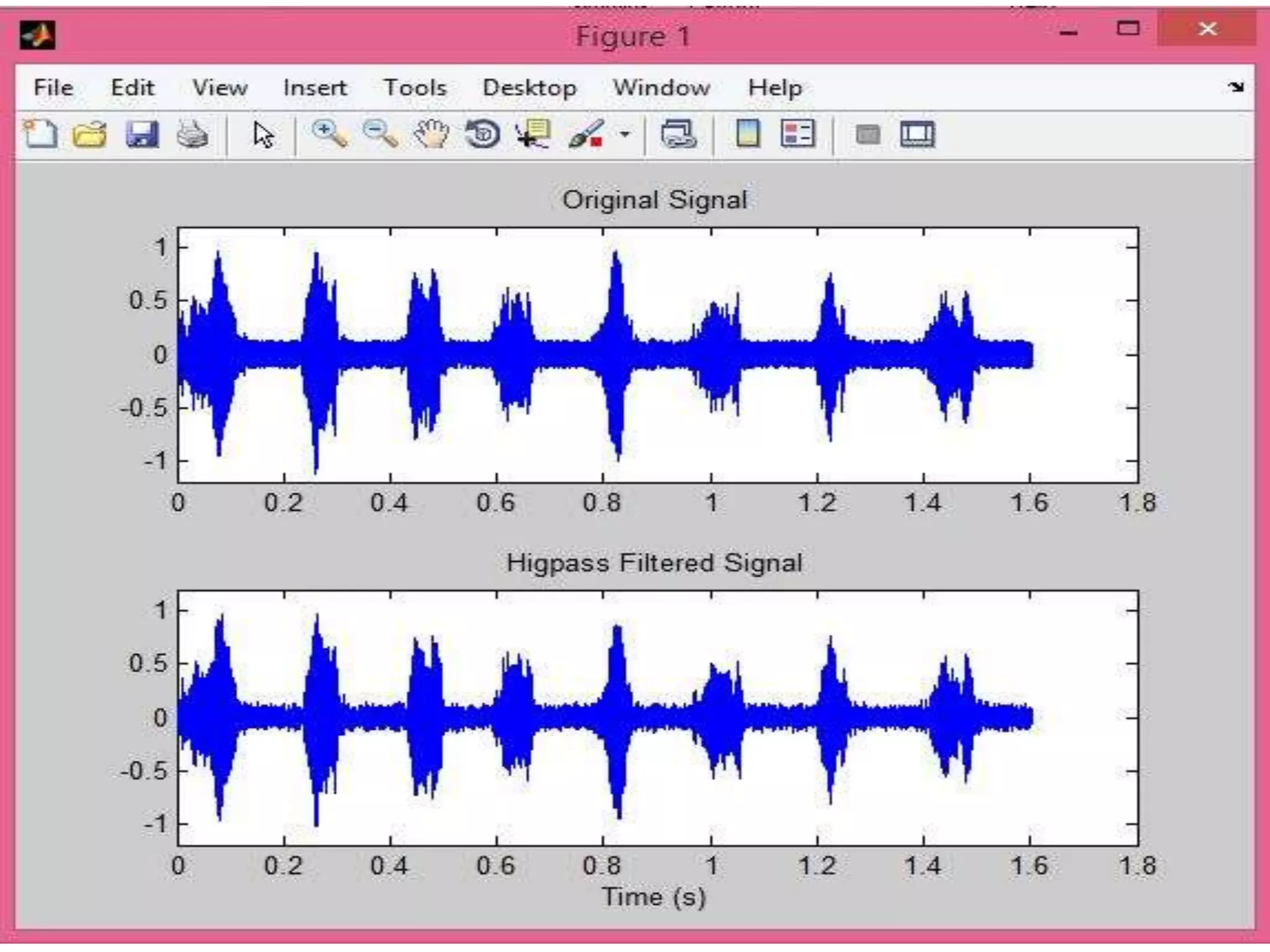
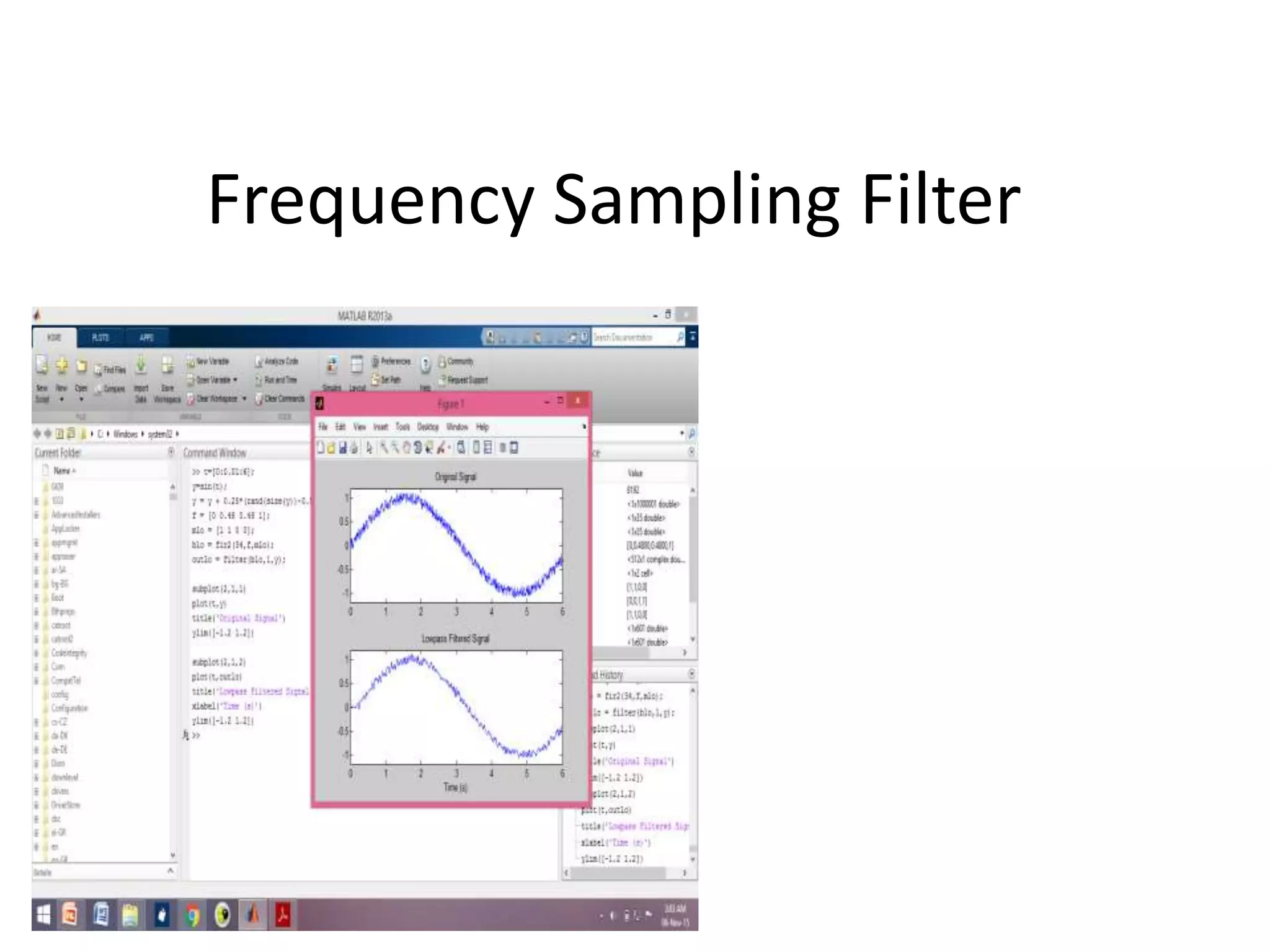
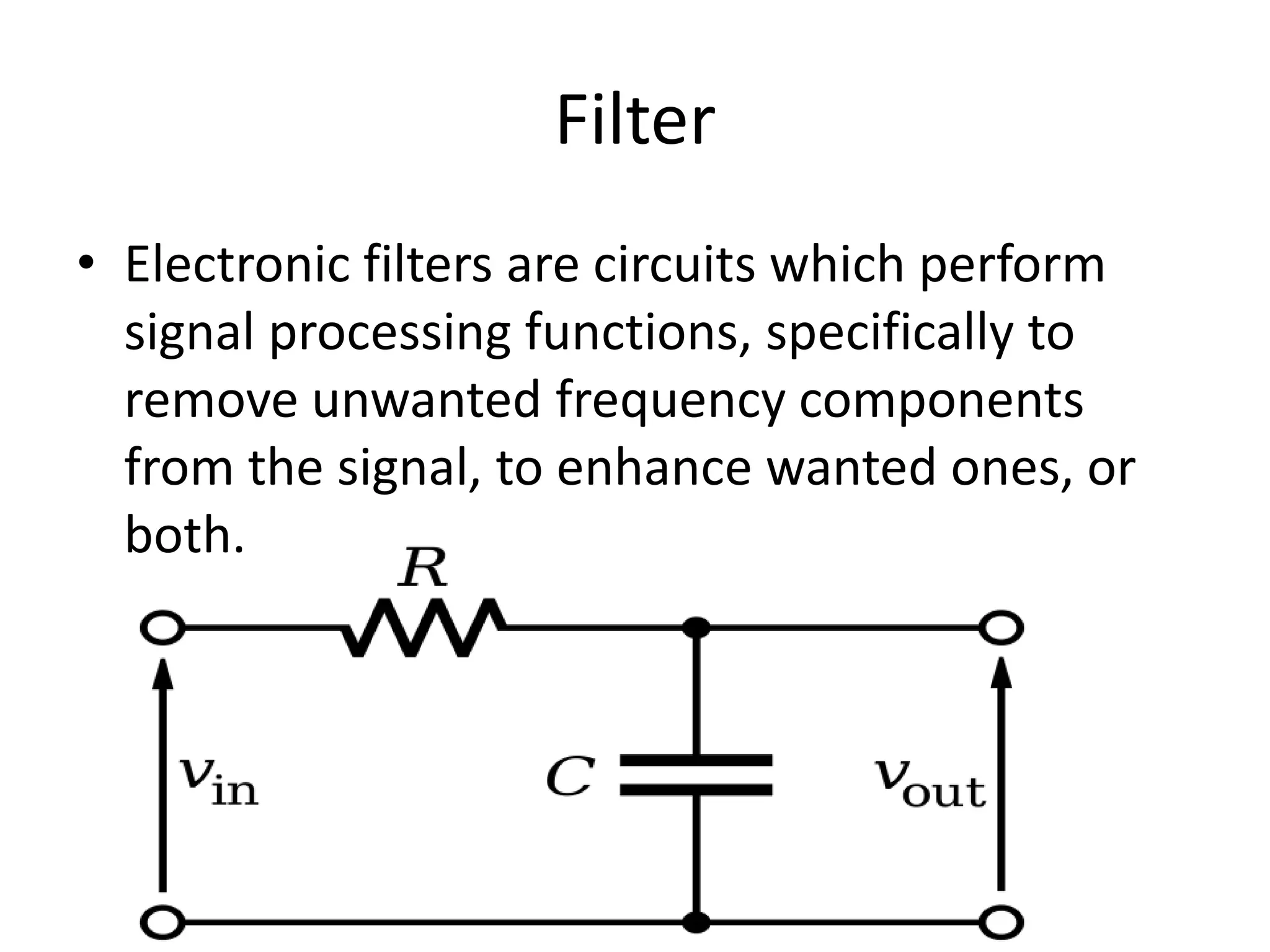
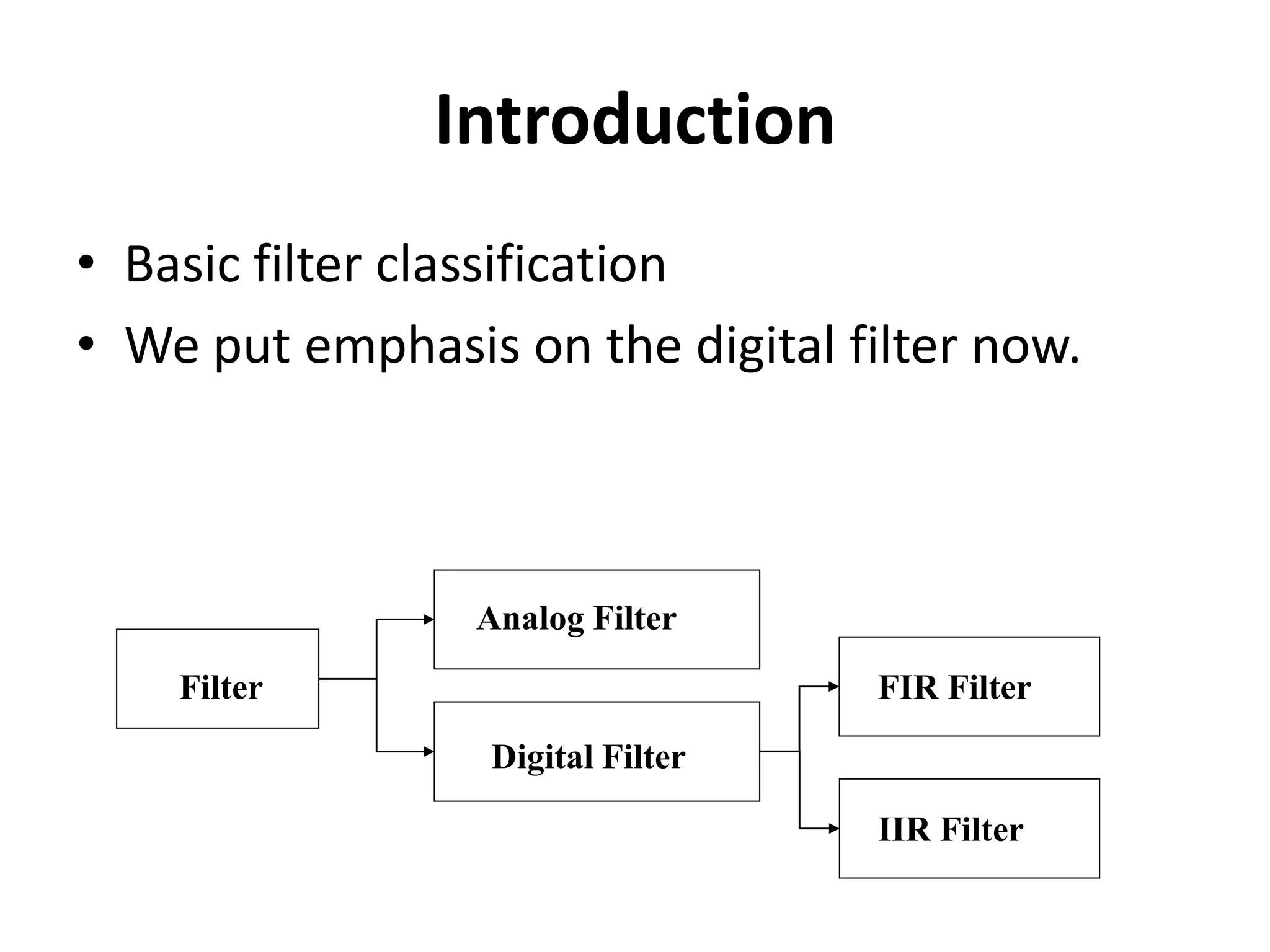
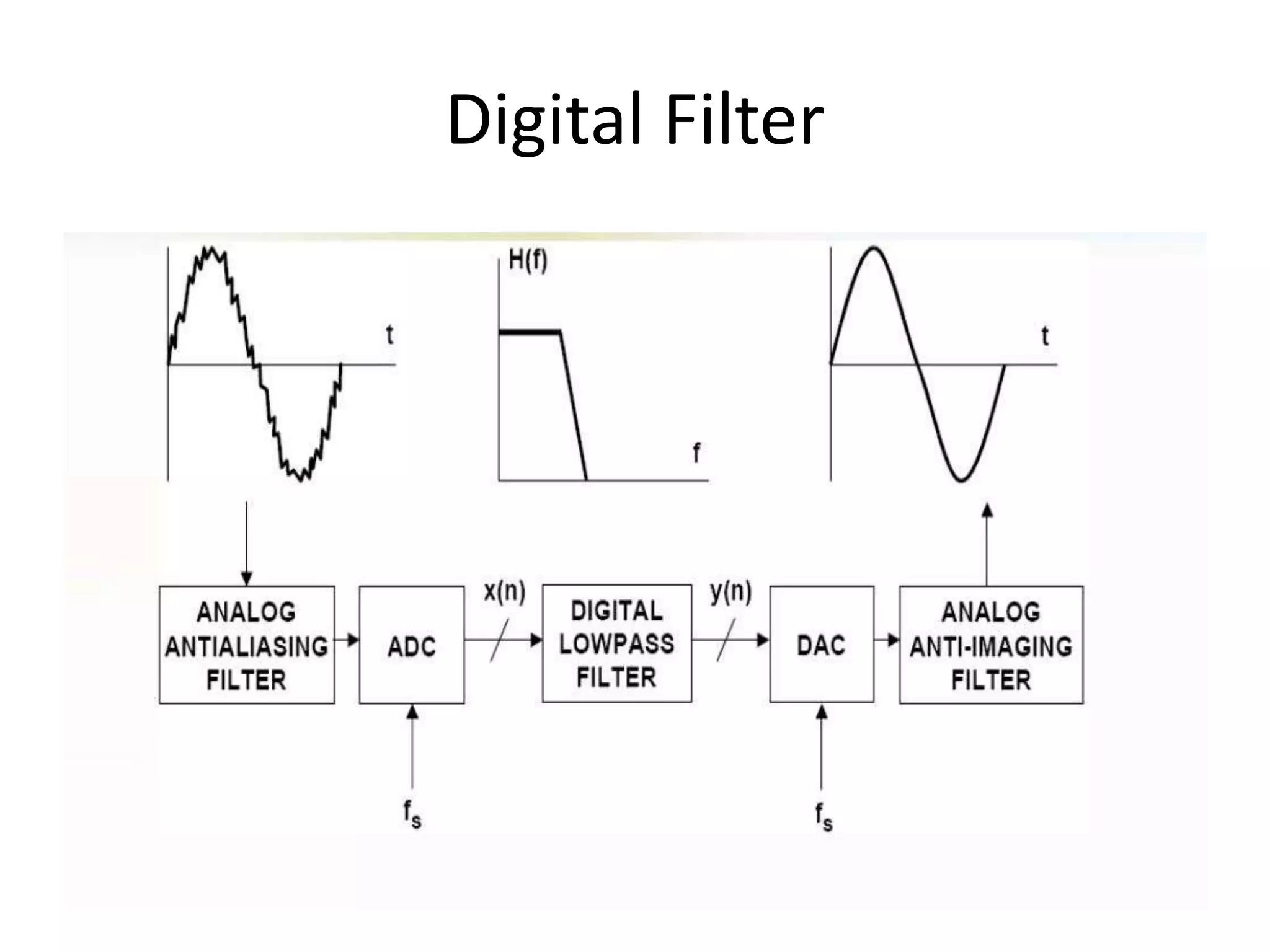
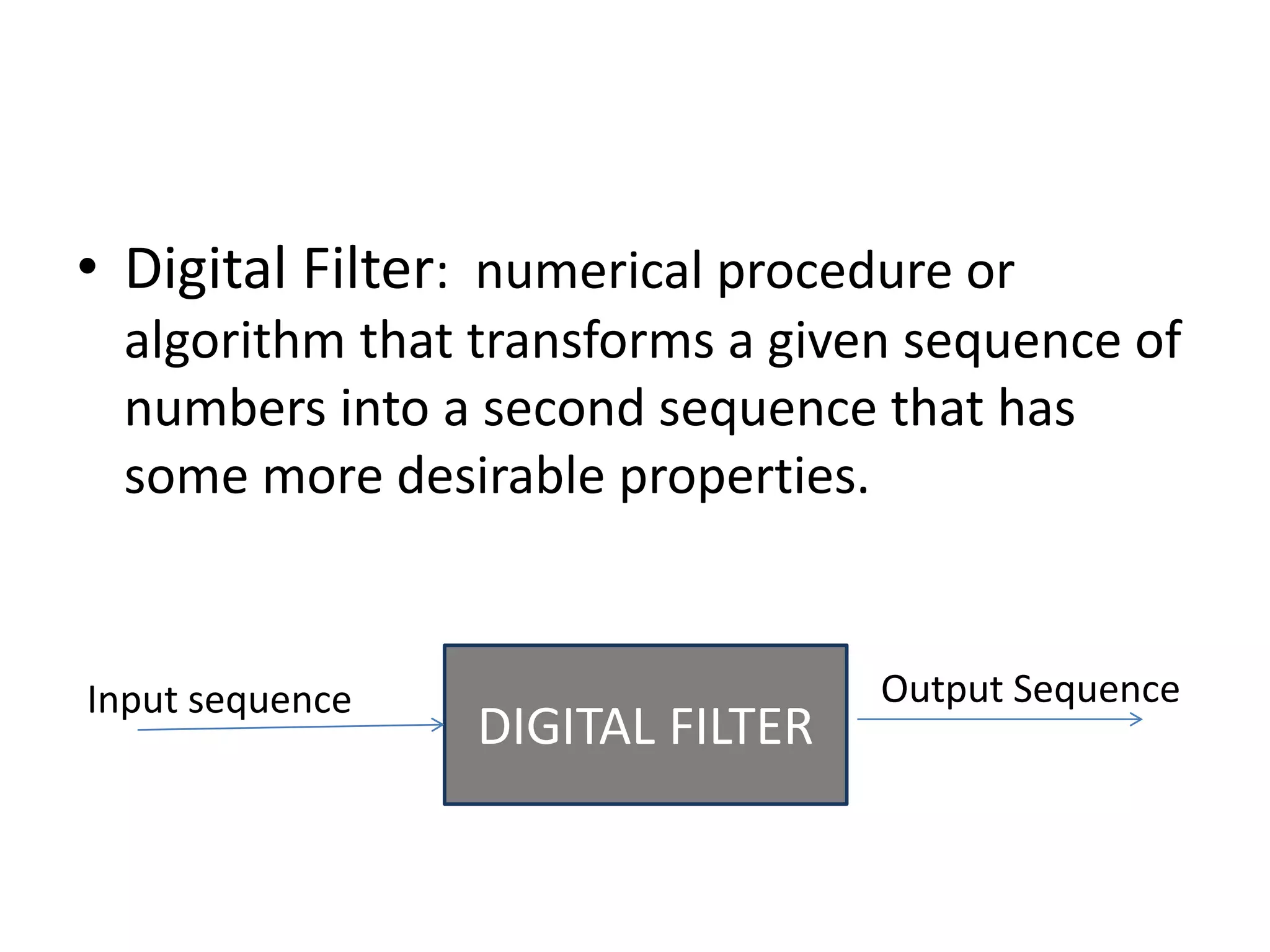
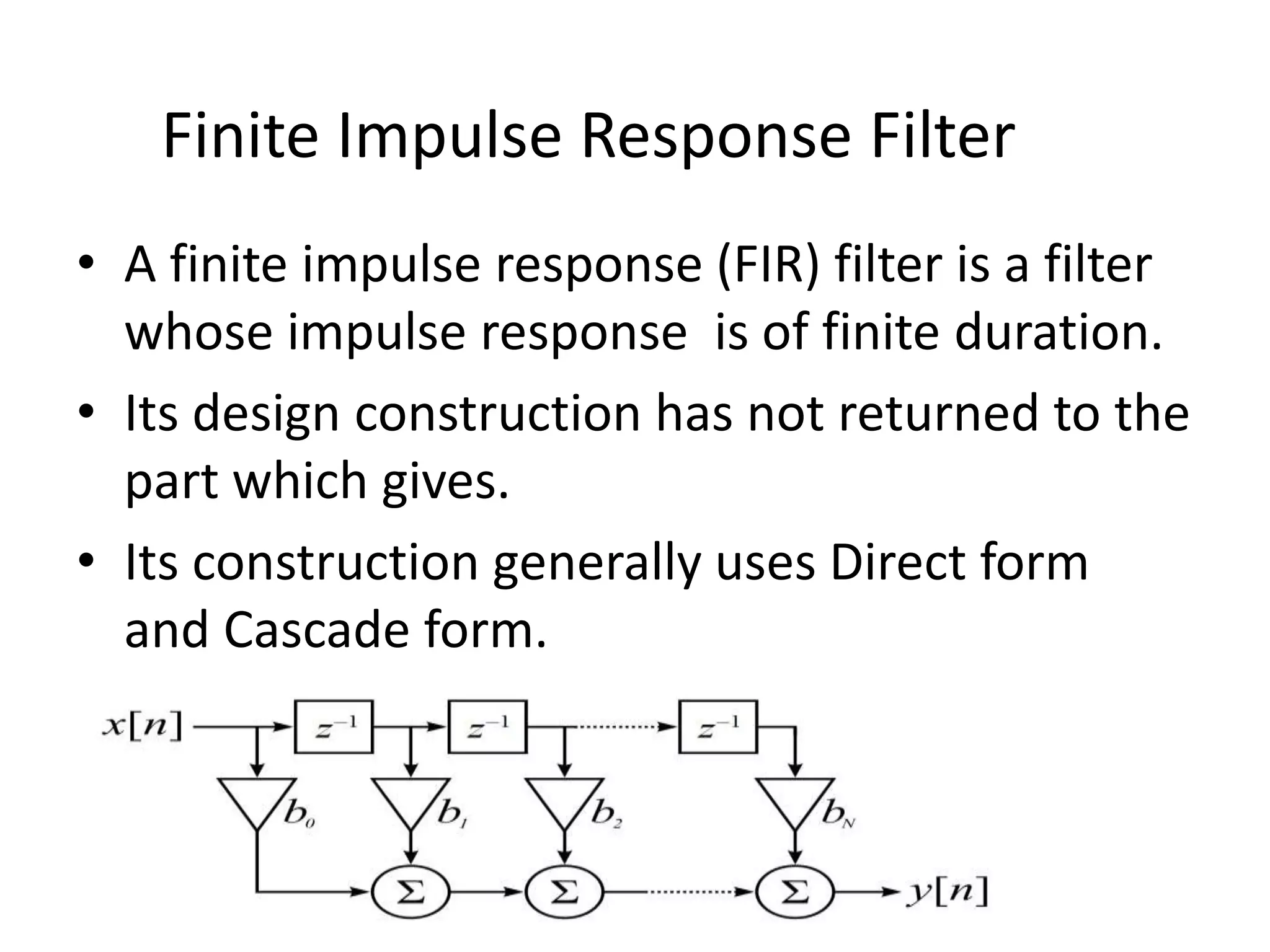
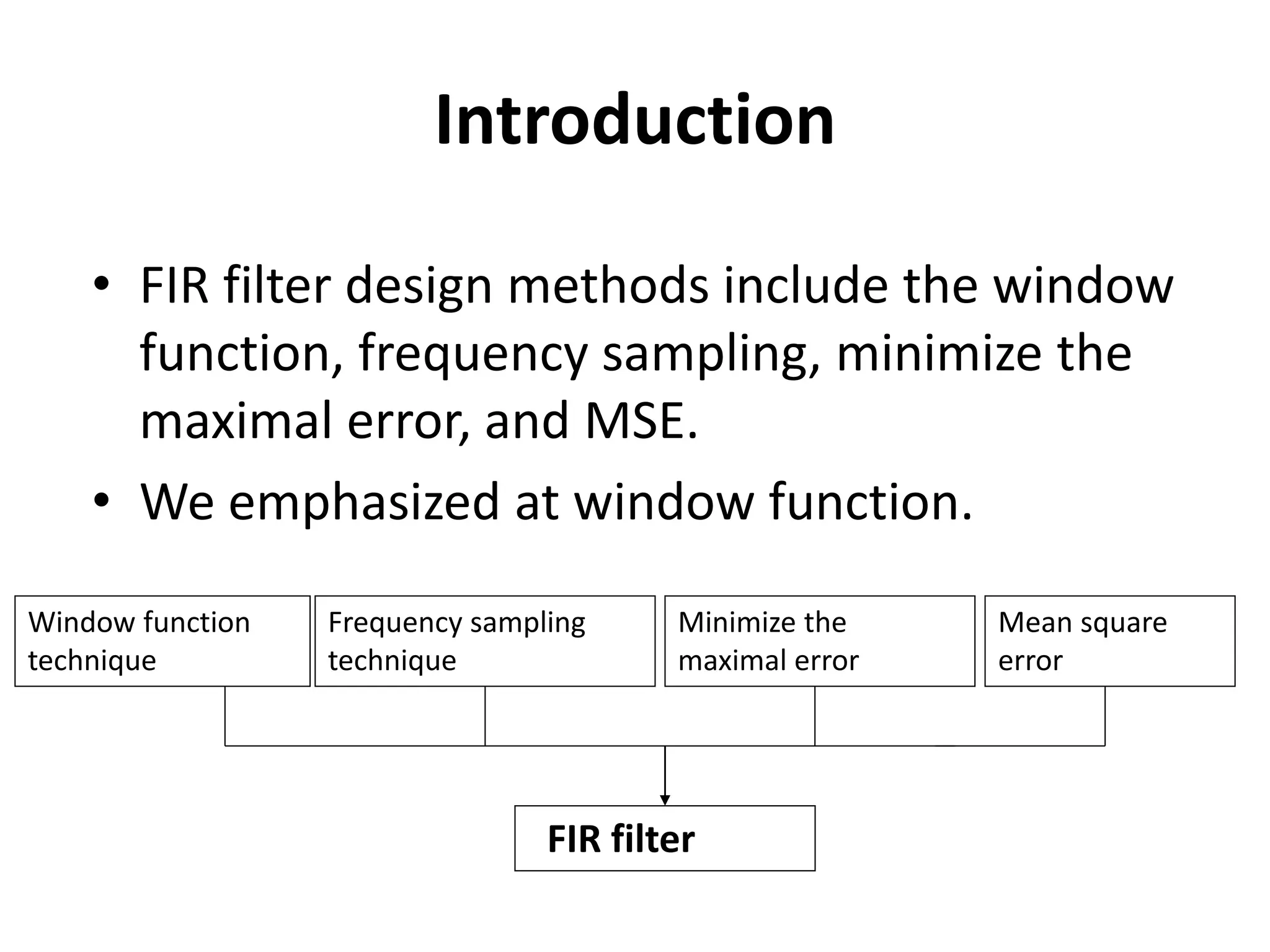
The document discusses electronic filters, emphasizing digital filters, particularly Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filters, which transform numerical sequences to enhance desired frequency components. It details FIR filter design methods, including the window function technique and frequency sampling, providing specific examples such as low and high pass filters designed using MATLAB. The implementation of these filters can be applied to DSP processors for noise reduction in electronic circuits.
![FIR Filter Design by Window function
technique
• Simplest FIR the filter design is window
function technique
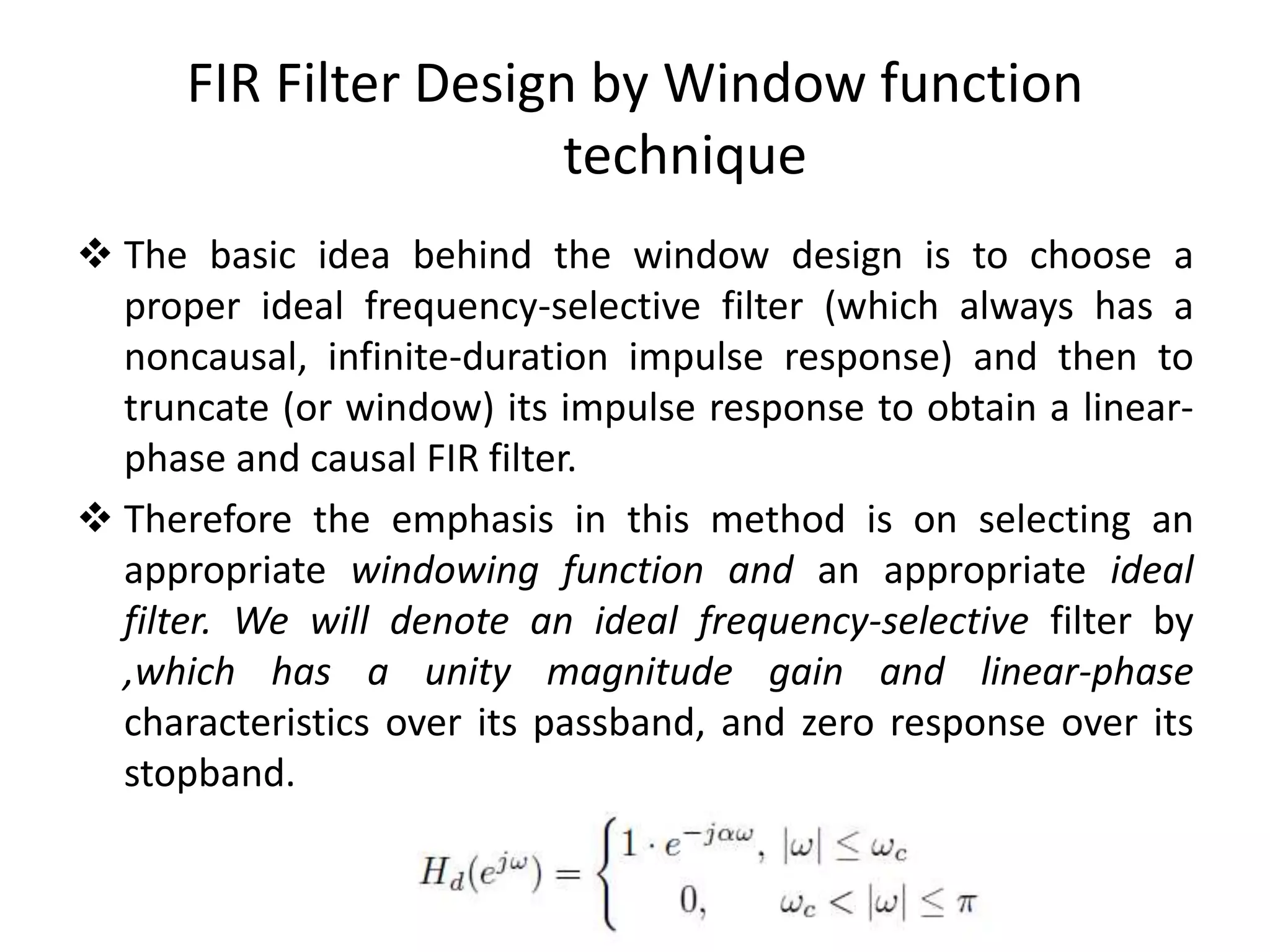
• A supposition ideal frequency response may
express
where
( ) [ ]j j n
d d
n
H e h n e
1
[ ] ( )
2
j j n
d dh n H e e d
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-151108073821-lva1-app6891/75/design-of-sampling-filter-9-2048.jpg)

![FIR Filter Design by Window function
technique
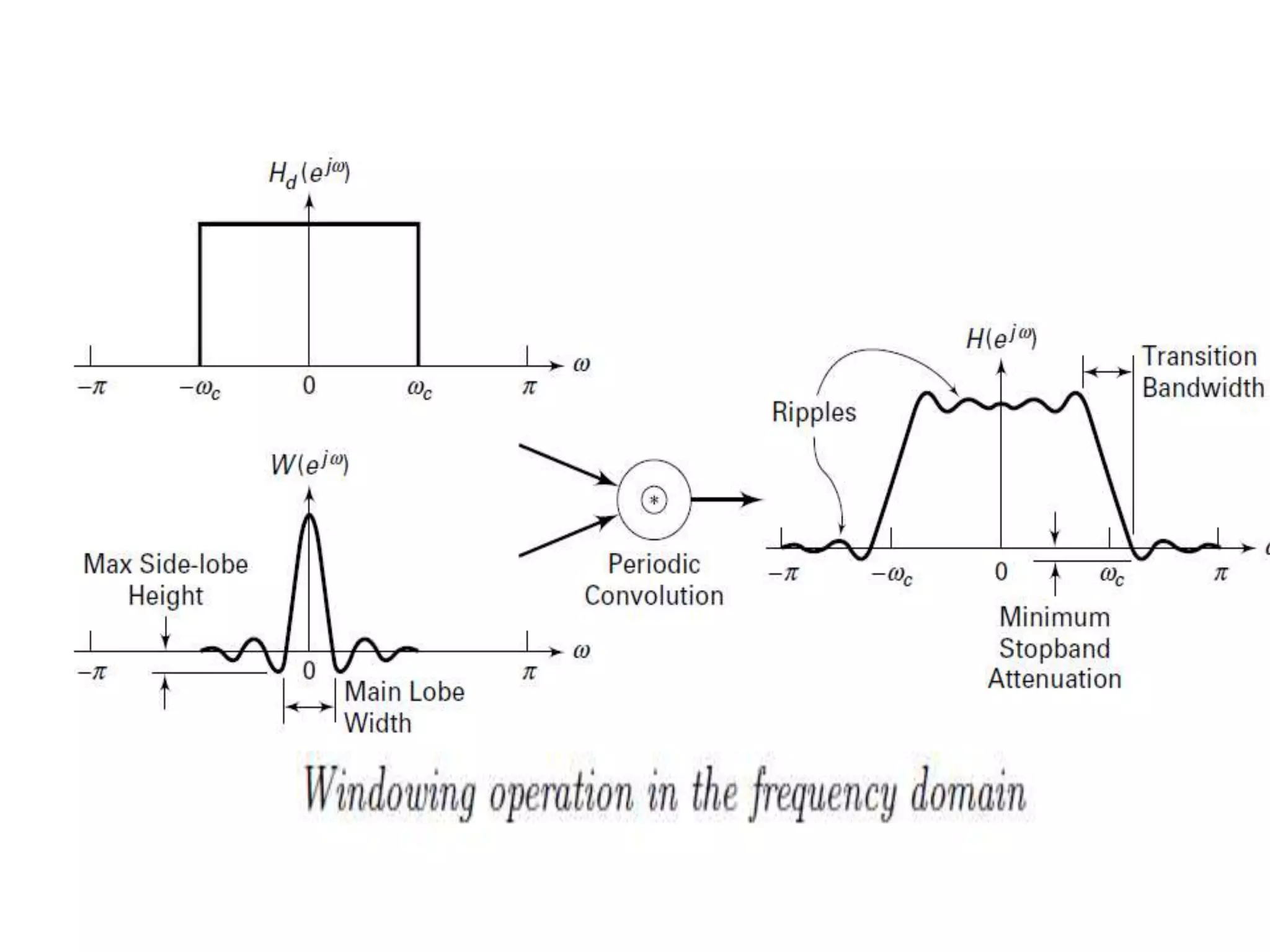
• To get this kind of systematic causal FIR to be
approximate, the most direct method
intercepts its ideal impulse response!
[ ] [ ] [ ]dh n w n h n
( ) ( ) ( )dH W H ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-151108073821-lva1-app6891/75/design-of-sampling-filter-11-2048.jpg)

![FIR Filter Design by Window function
technique
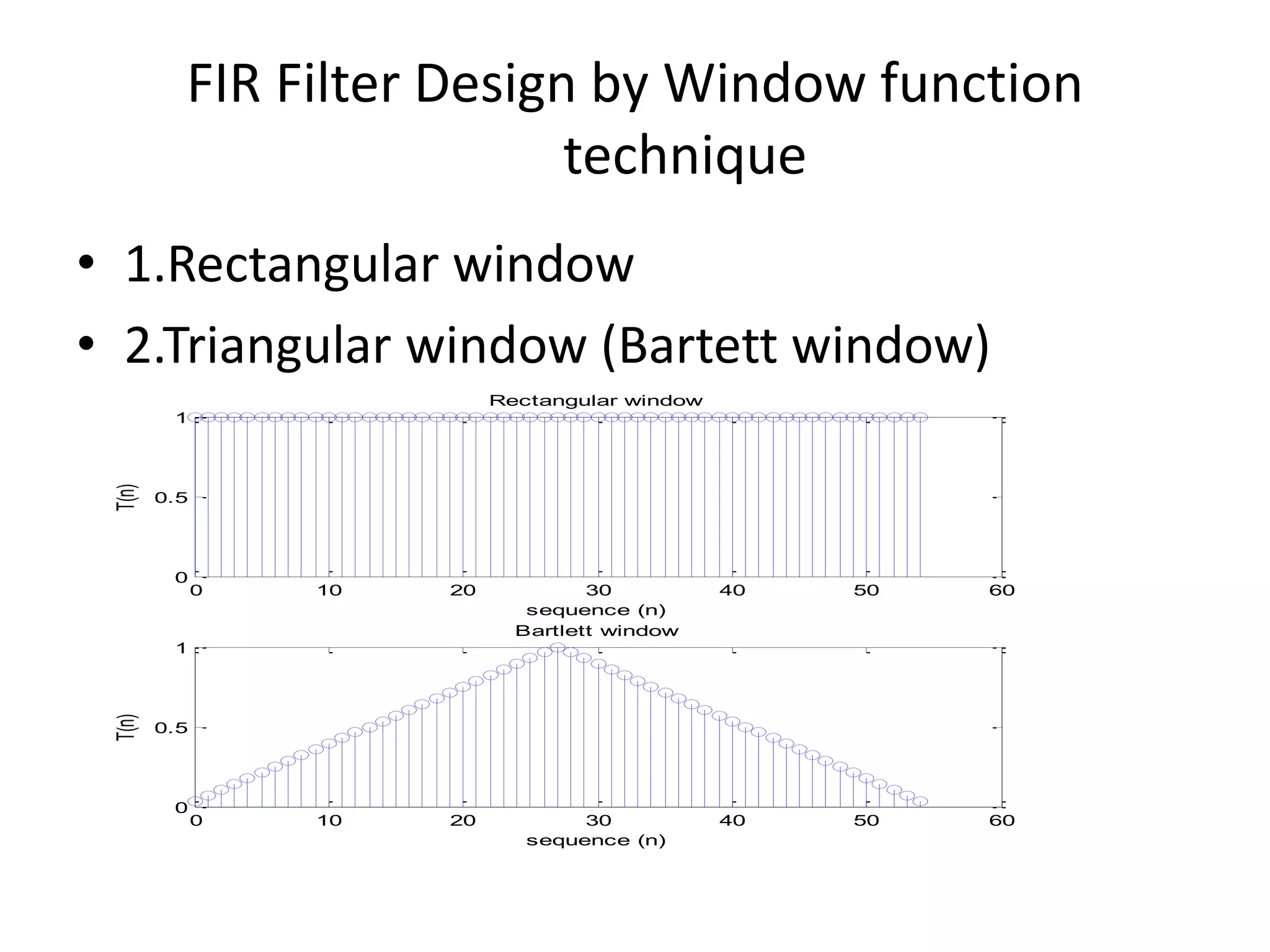
• 1.Rectangular window
• 2.Triangular window (Bartett window)
1, 0
[ ]
0,
n M
w n
otherwise
2 , 0
2
2[ ] 2 ,
2
0,
n Mn
M
n Mw n n M
M
otherwise
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-151108073821-lva1-app6891/75/design-of-sampling-filter-14-2048.jpg)
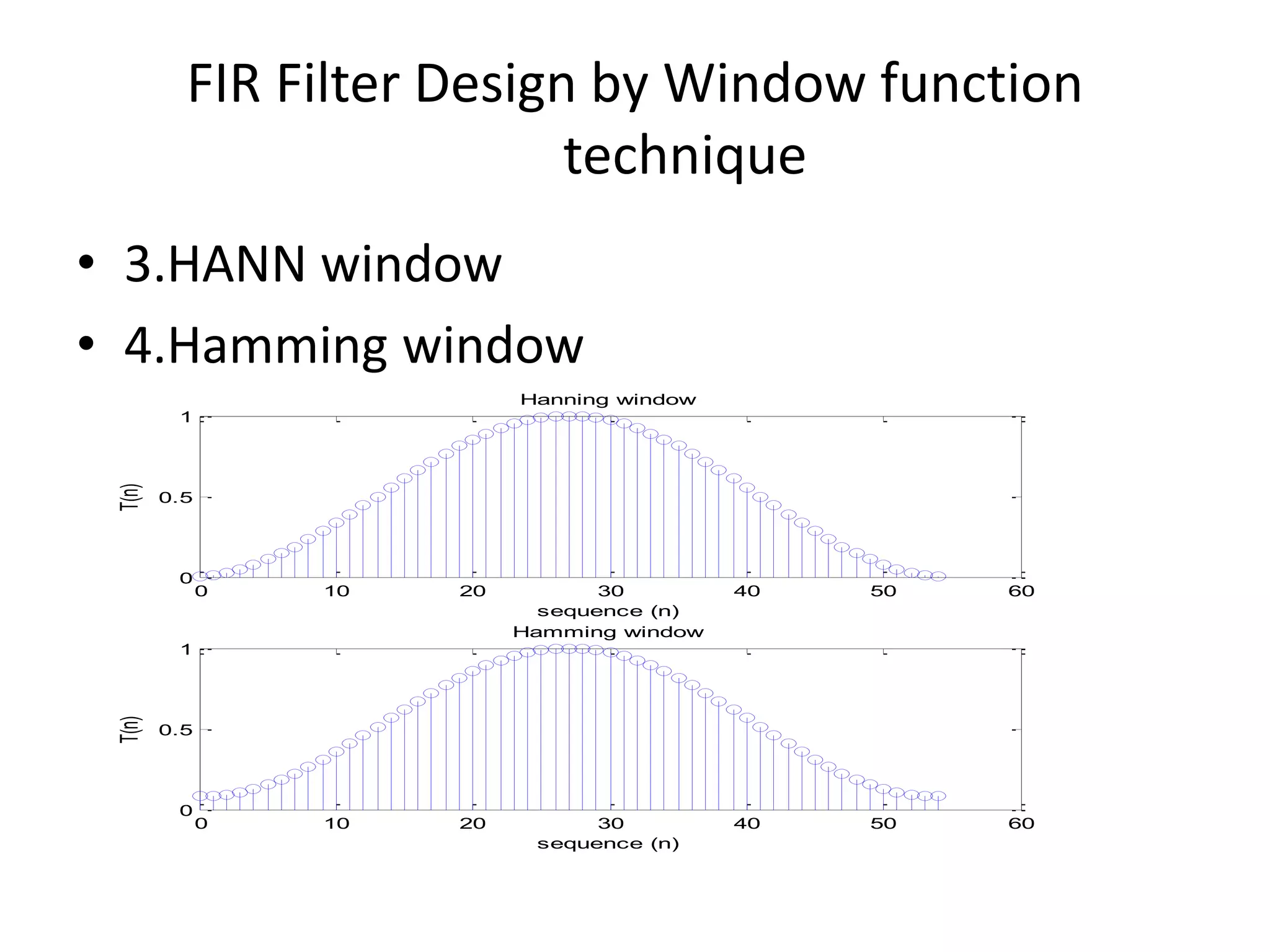
![FIR Filter Design by Window function
technique
• 3.HANN window
• 4.Hamming window
1 2
1 cos , 0
[ ] 2
0,
n
n M
w n M
otherwise
2
0.54 0.46cos , 0
[ ]
0,
n
n M
w n M
otherwise
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-151108073821-lva1-app6891/75/design-of-sampling-filter-16-2048.jpg)