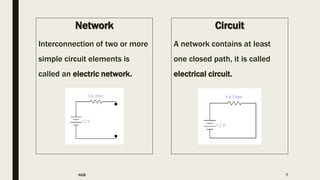
The document outlines the basic concepts of electrical charge, current, voltage, power, and circuit elements. It defines crucial terms such as coulomb for charge, ampere for current, volt for voltage, and watts for power, alongside characteristics of active and passive elements in circuits. Key components like resistance, inductance, and capacitance are also discussed, detailing their properties and units of measurement.