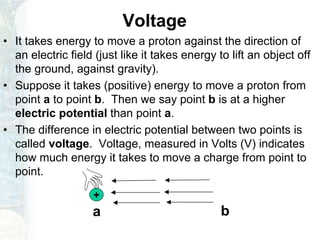
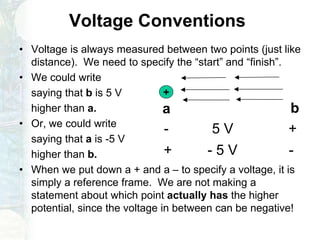
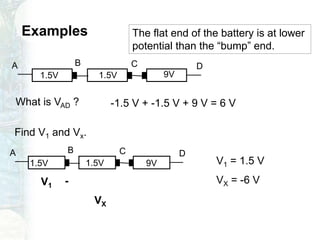
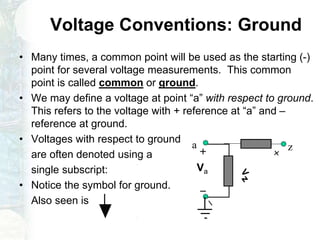
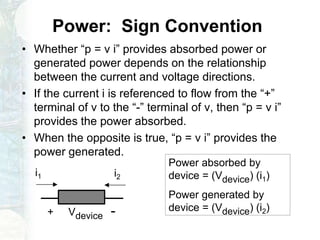
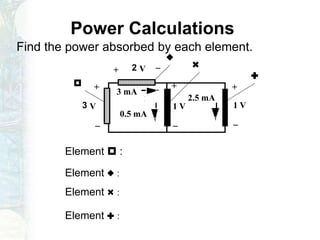
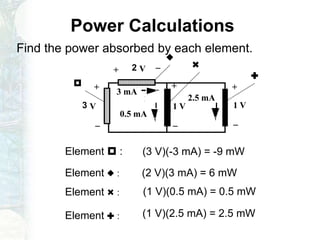
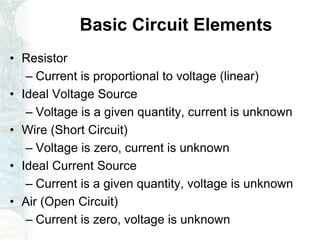
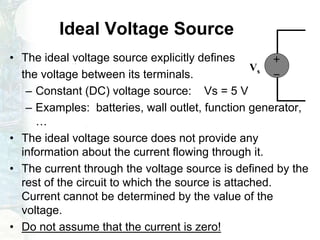
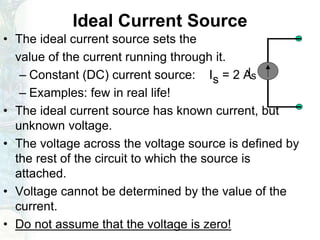
The document outlines the course on linear circuit analysis taught by Dr. Muhammad Talha Gul, covering essential topics such as circuit variables, simplification techniques, and key electrical concepts. It includes information on grading criteria, course structure, and required readings for class discussions. The course emphasizes the practical applications of circuit theories in electrical engineering.