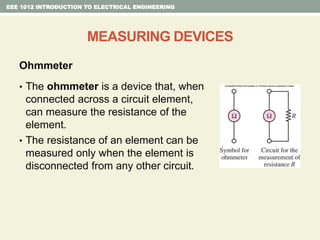
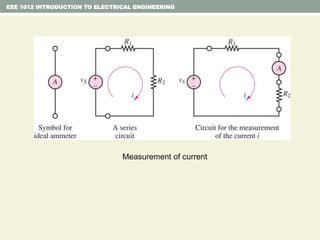
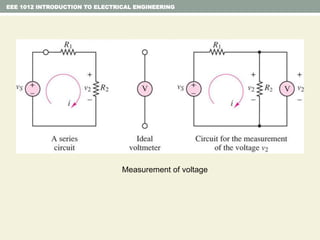
This document provides an overview of fundamental electrical engineering concepts including:
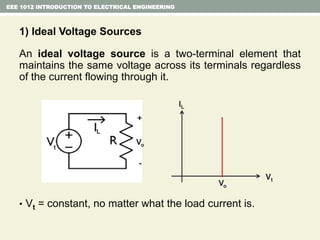
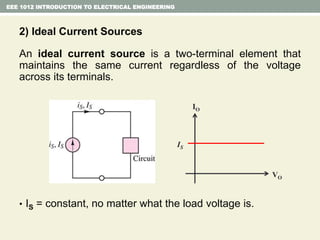
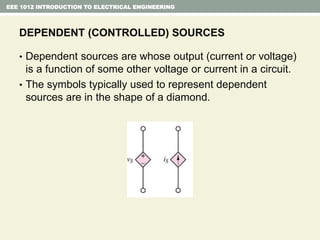
- Independent and dependent voltage/current sources and ideal sources that maintain constant voltage/current.
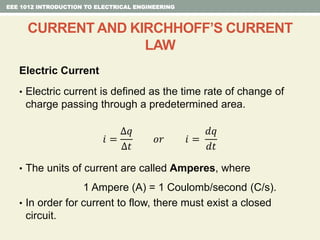
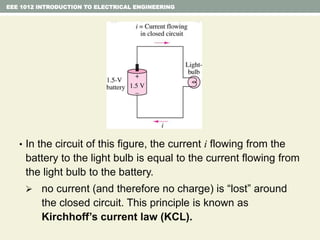
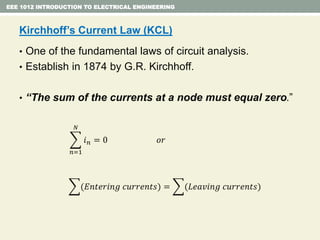
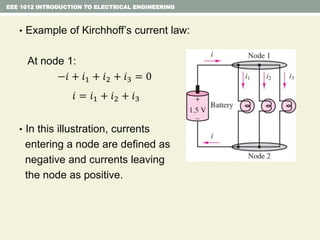
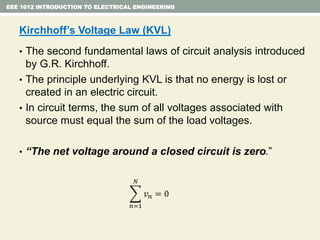
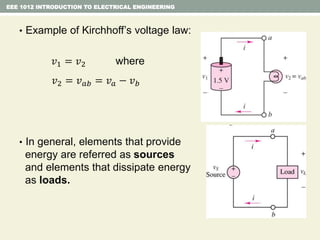
- Kirchhoff's laws for circuits - KVL states the net voltage around any closed loop is zero and KCL states the algebraic sum of currents at any node is zero.
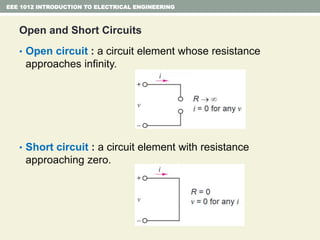
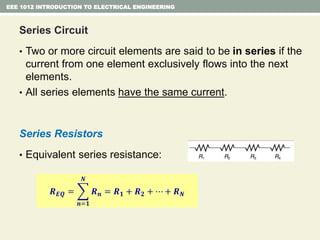
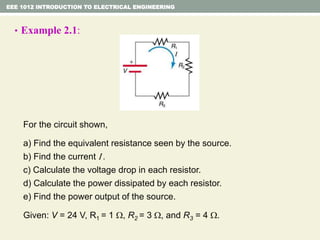
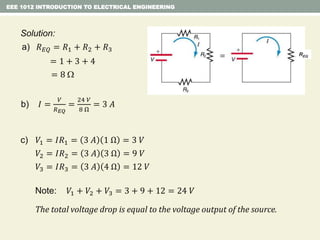
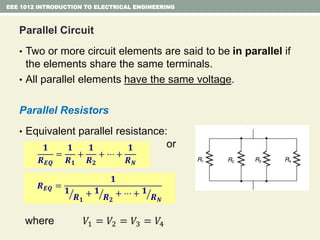
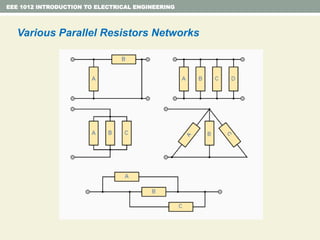
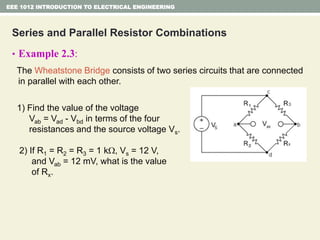
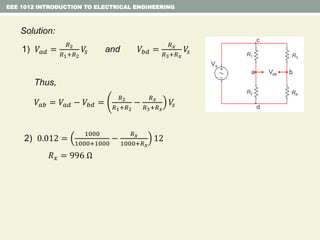
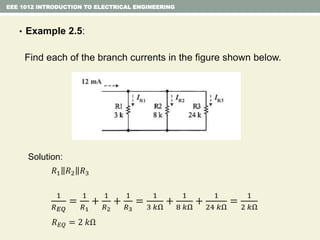
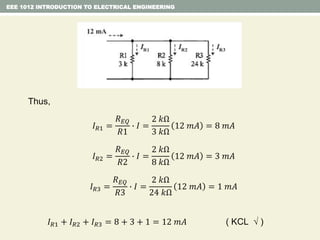
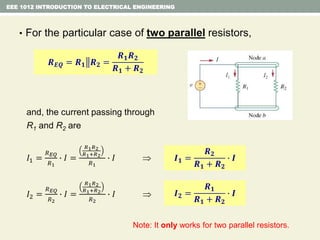
- Series and parallel resistor circuits and how to calculate equivalent resistance and current/voltage in each component.
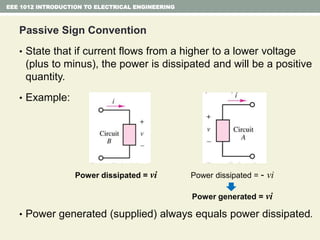
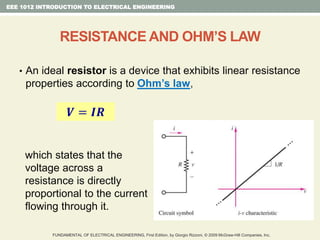
- Ohm's law relating voltage, current, and resistance and the power formula.
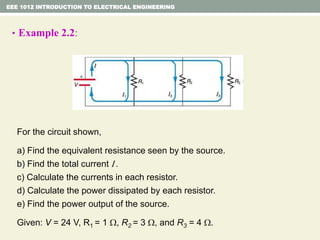
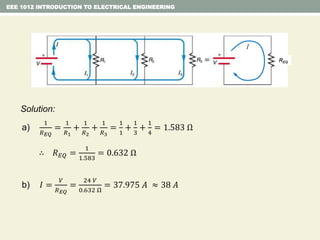
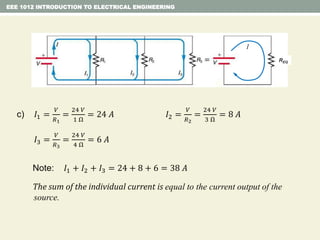
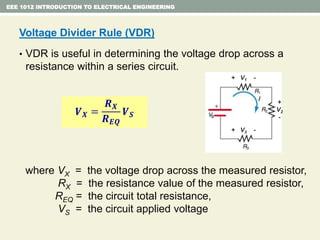
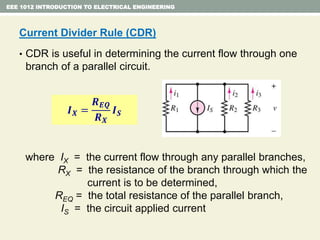
- Examples are provided to demonstrate applying concepts like nodal analysis, mesh analysis, and voltage divider rule to solve for values in circuits.