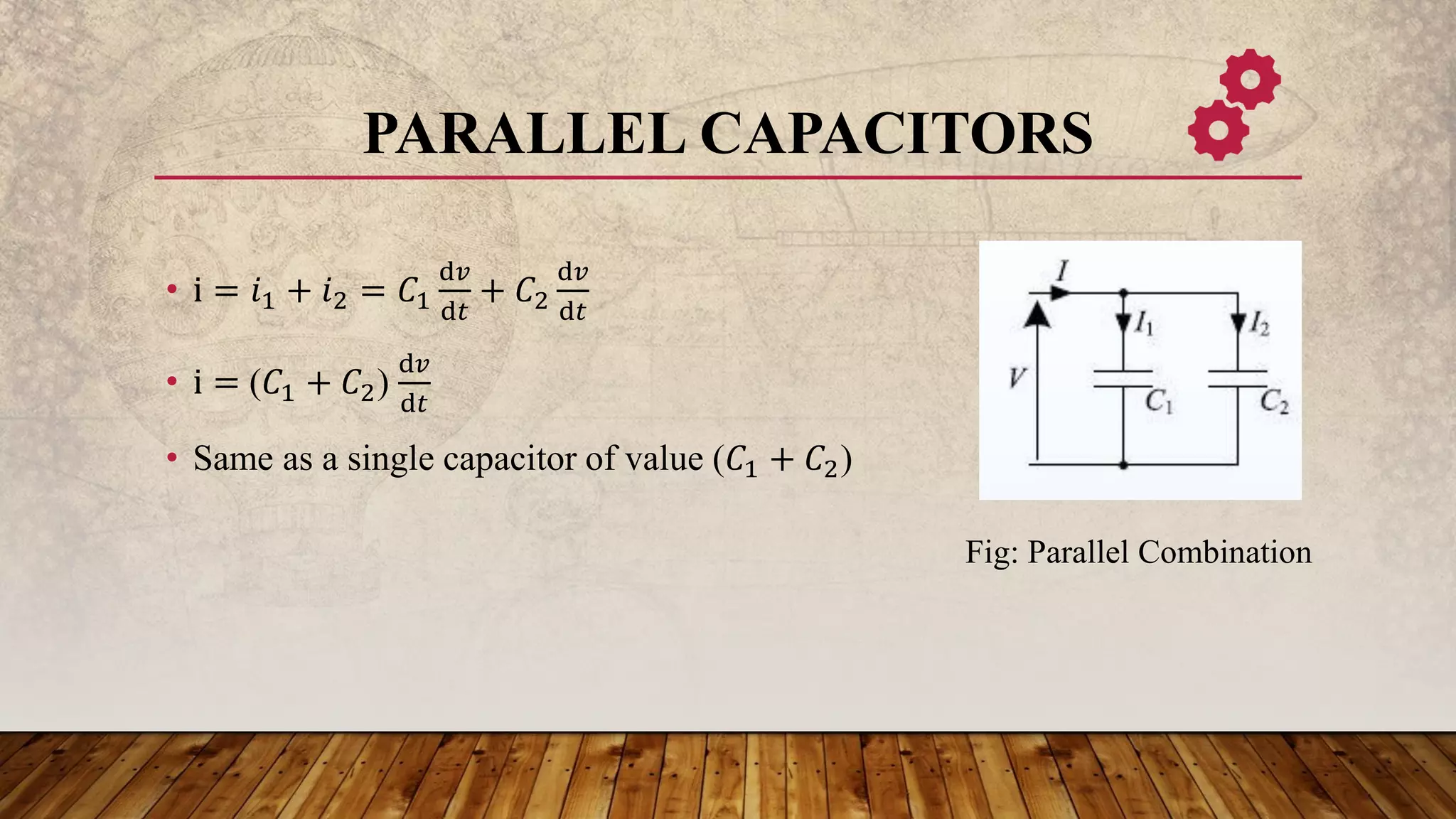
The document provides a comprehensive overview of capacitors and inductors, detailing their energy storage mechanisms, equations governing their behavior, and how they operate in series and parallel combinations. It outlines the formulas for current-voltage relationships, energy storage, and the differences in behavior for AC and DC circuits. Additionally, it includes examples and typical values for capacitors and inductors, as well as calculations for combined inductances.