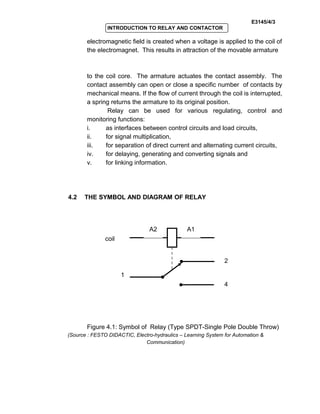
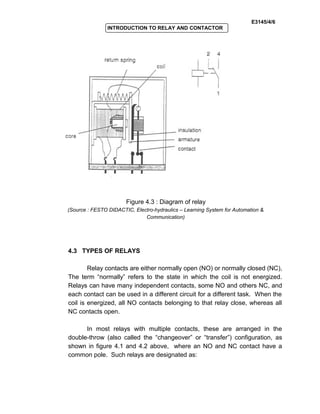
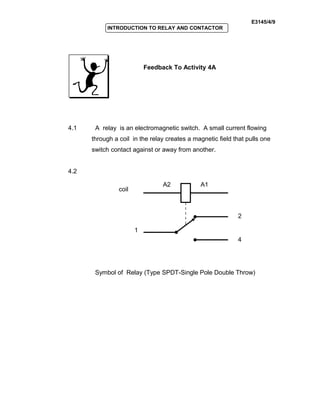
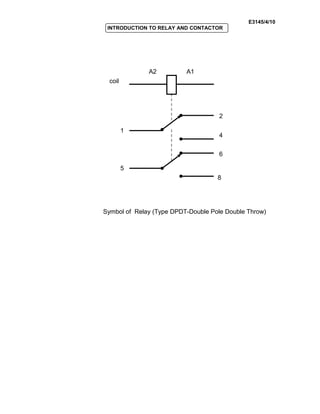
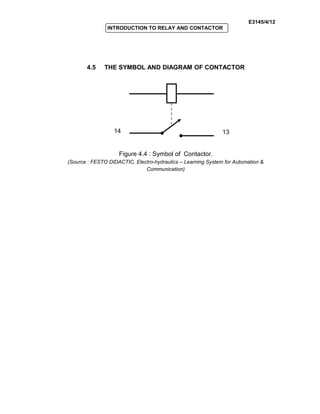
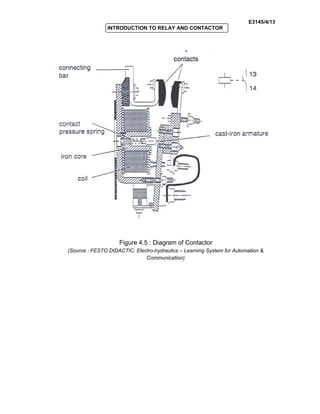
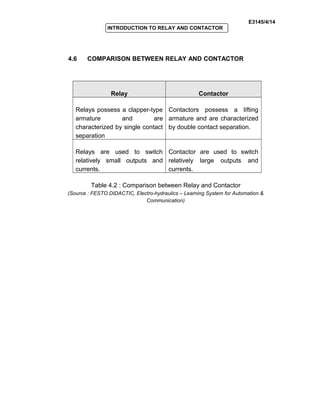
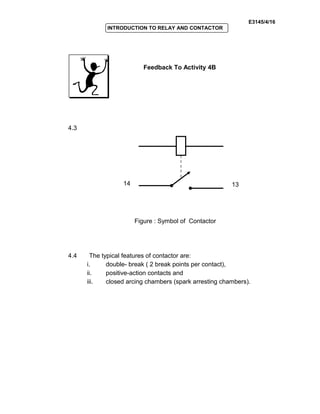
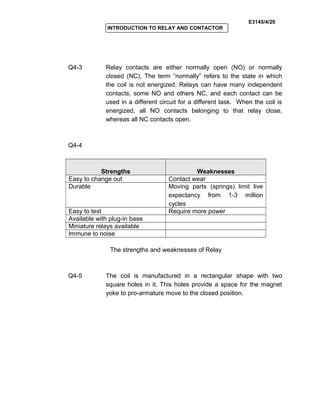
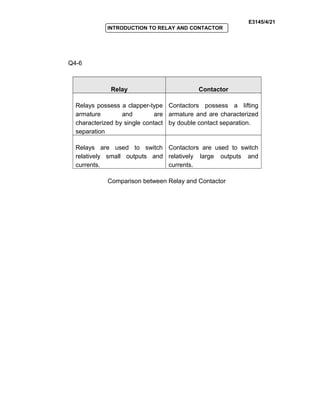
The document provides an introduction to relays and contactors. It defines relays as electromagnetically actuated switches that use a magnetic field created by a coil to switch contacts. Relays are used to switch small outputs and currents, while contactors are used to switch larger outputs and currents. The document discusses relay and contactor symbols, diagrams, types, and provides a comparison of their key differences. Specifically, it notes that relays have a clapper-type armature and single contact separation, while contactors have a lifting armature and double contact separation.