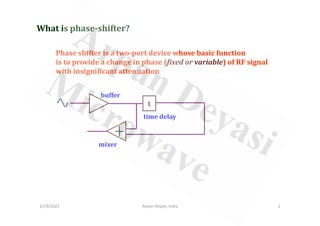
The document discusses different types of microwave phase shifters. It describes that a phase shifter is a two-port device that provides a fixed or variable phase shift of an RF signal with minimal attenuation. It then focuses on ferrite phase shifters, which use ferrite materials to provide a variable phase shift by changing the bias field of the ferrite. The document also discusses distributed phase shifters, active vs. passive phase shifters, analog vs. digital phase shifters, and fixed vs. variable phase shifters.