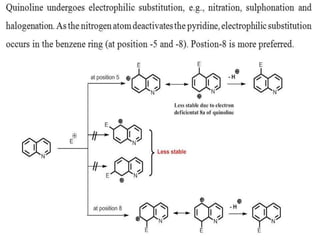
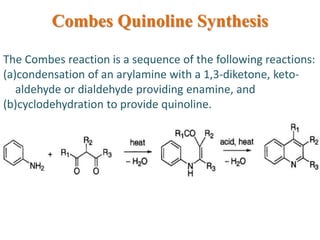
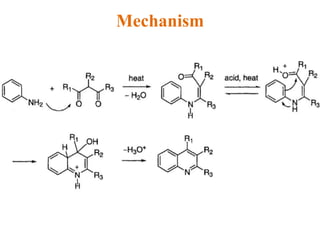
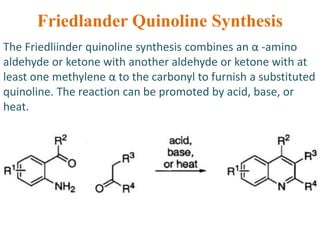
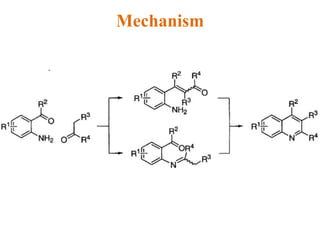
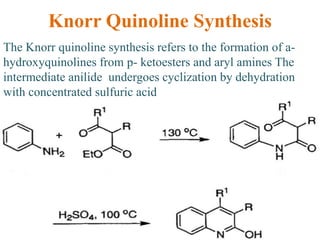
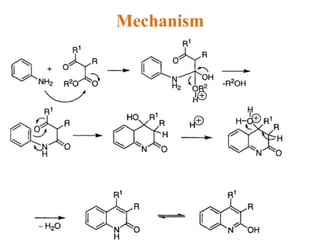
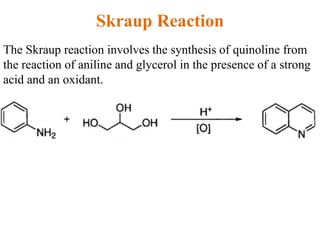
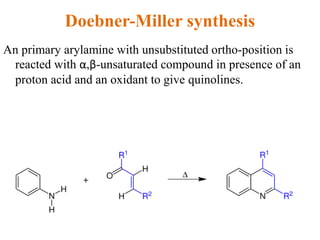
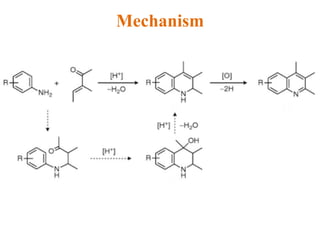
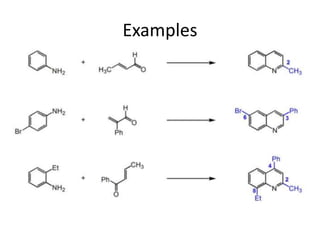
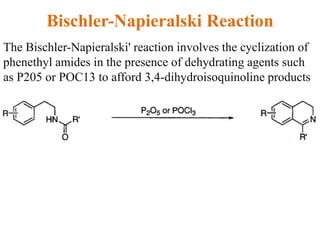
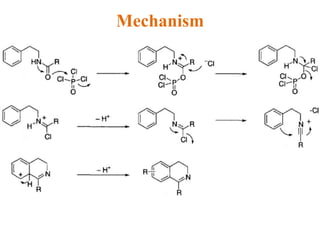
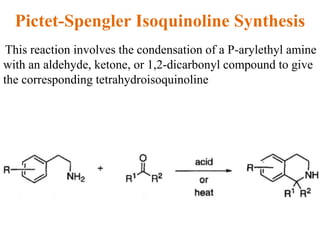
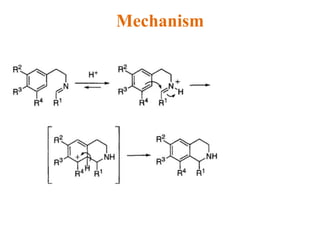
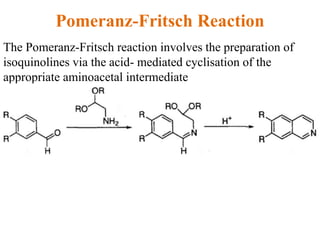
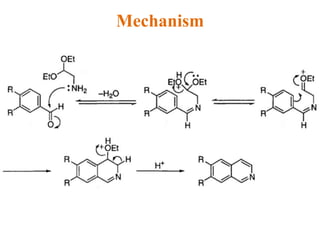
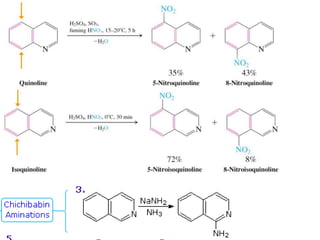
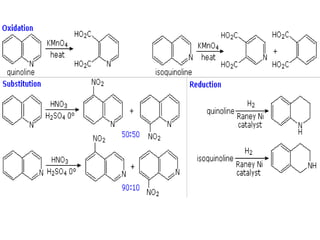
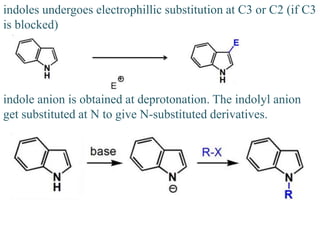
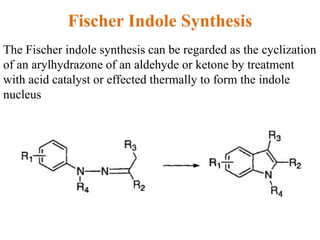
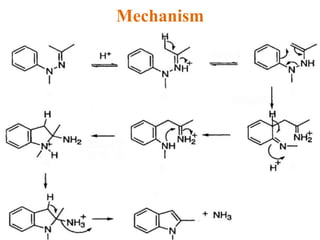
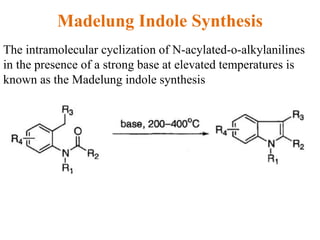
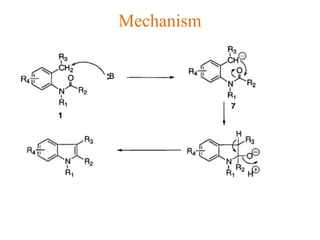
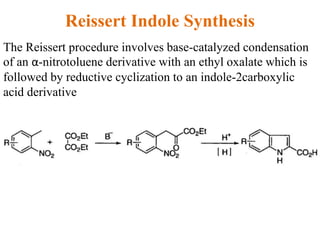
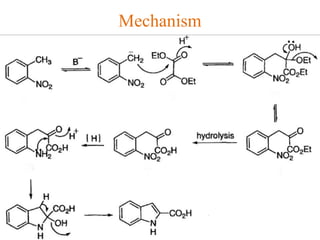
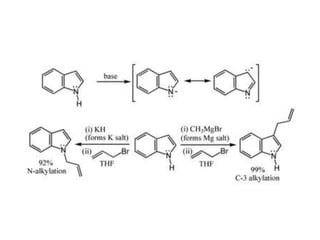
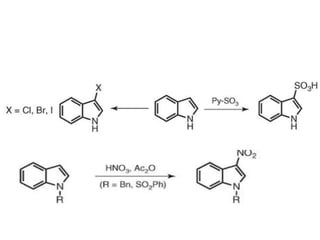
The document discusses several heterocyclic compounds including quinolines, isoquinolines, and indoles. It summarizes key reactions used to synthesize these compounds, including the Combes, Friedlander, Knorr, and Skraup reactions for quinoline synthesis. It also discusses the Bischler-Napieralski, Pictet-Spengler, and Pomeranz-Fritsch reactions for isoquinoline synthesis and the Fischer, Madelung, and Reissert reactions for indole synthesis, along with mechanisms and examples of each reaction. Reactivity and substitution patterns are also covered for quinolines, isoquinolines and indoles.