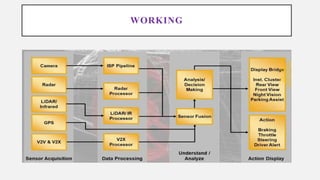
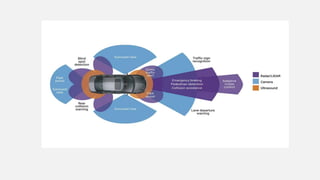
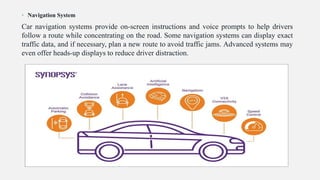
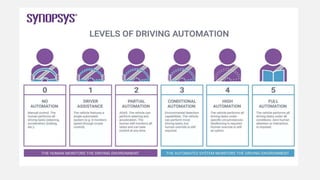
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) use sensors and computer vision algorithms to detect objects, warn drivers of potential accidents, and take actions to avoid collisions. ADAS applications have evolved from simple cruise control in the 1950s to now include lane keeping, automatic emergency braking, and other systems. As ADAS becomes more advanced with 64-bit processors and neural networks, vehicles are progressing toward full autonomy. The goal of ADAS is to reduce the over 90% of accidents caused by human error by assisting drivers or taking control in dangerous situations.