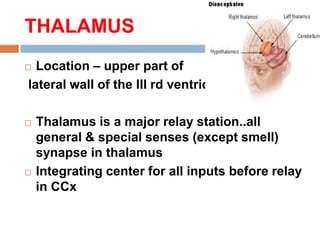
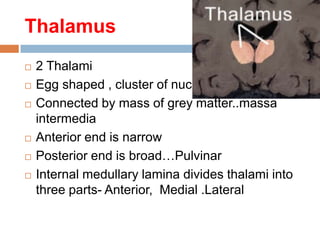
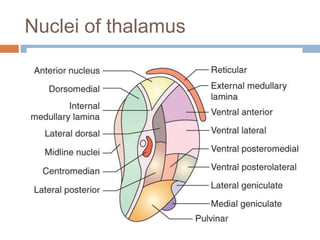
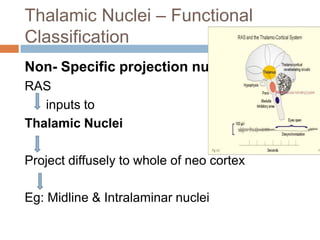
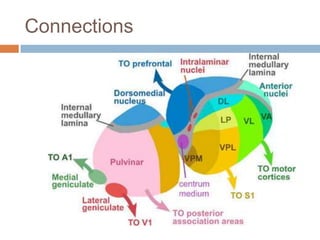
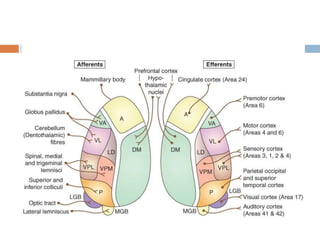
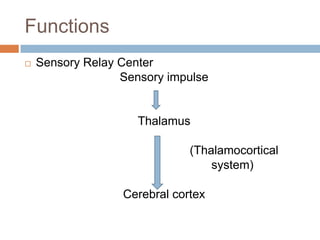
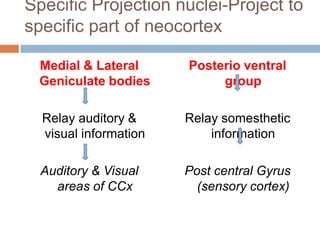
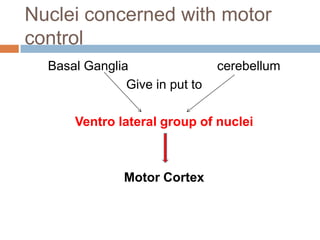
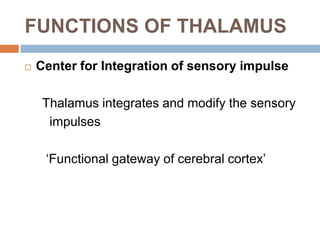
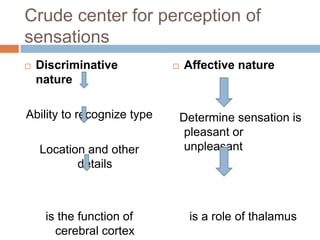
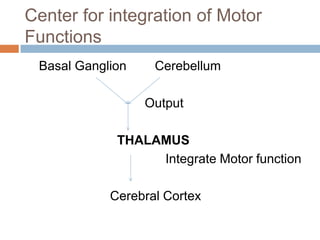
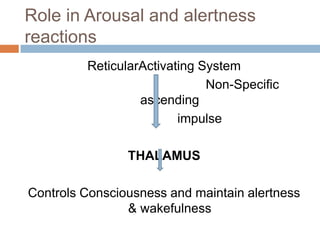
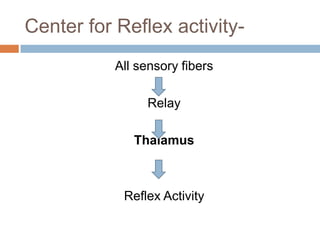
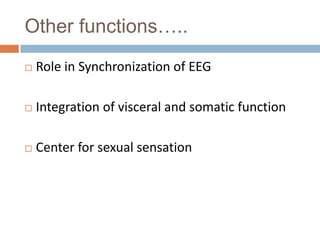
The thalamus, located in the upper part of the lateral wall of the third ventricle, serves as a major relay station for sensory information (except smell) and integrates motor functions, playing a crucial role in consciousness and emotional responses. It consists of two thalami connected by massa intermedia and is involved in specific projections to parts of the neocortex for sensory and motor processing. Damage to thalamic nuclei can lead to sensory and motor symptoms, including astereognosis, thalamic phantom limb, and Korsakoff's syndrome, which affects memory.