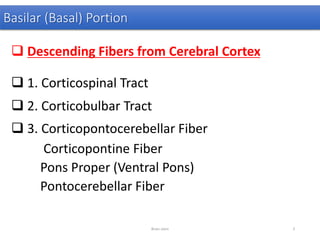
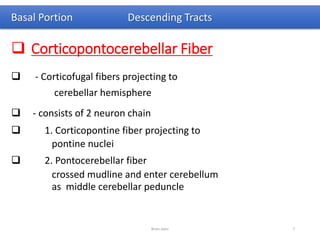
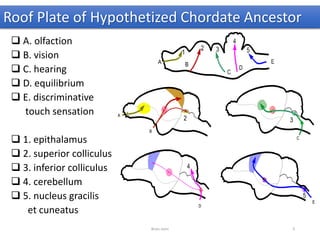
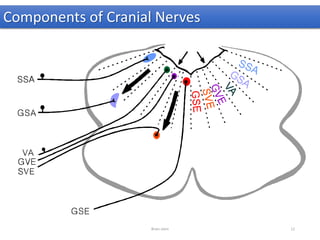
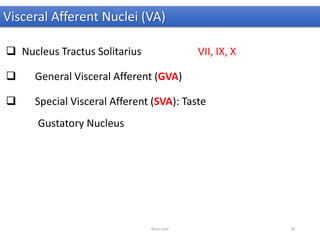
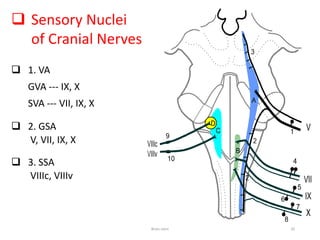
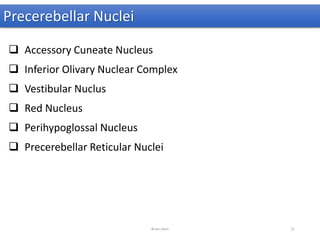
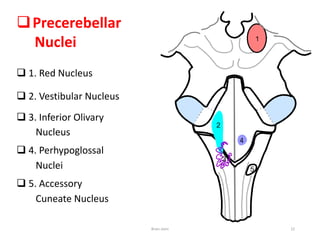
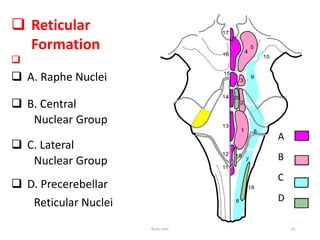
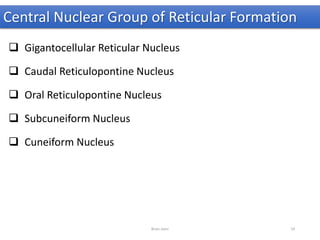
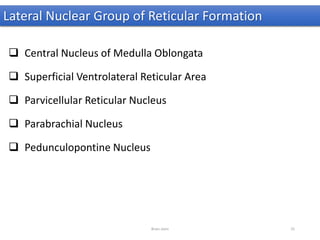
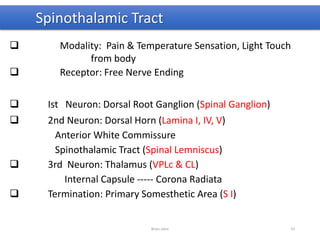
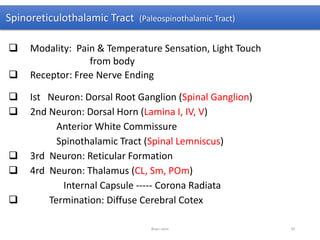
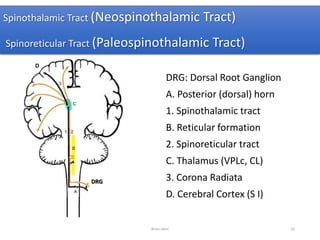
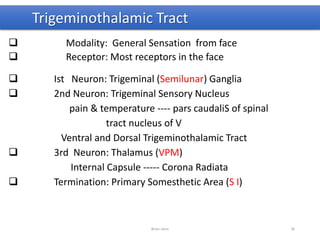
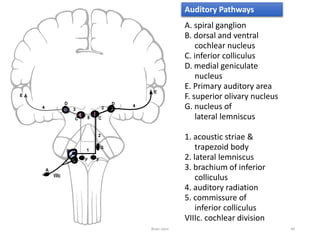
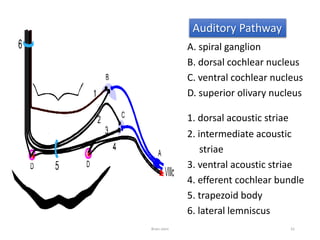
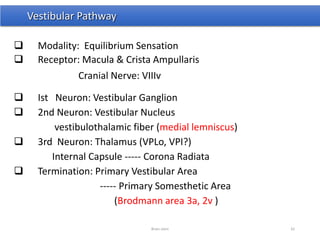
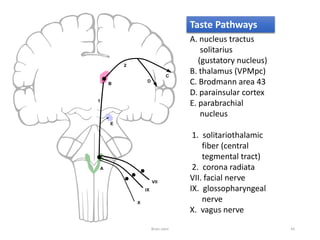
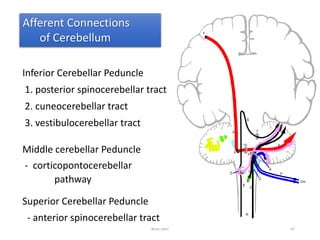
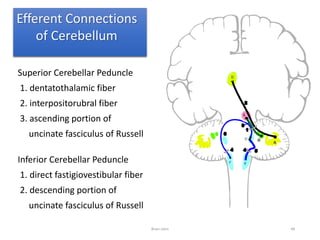
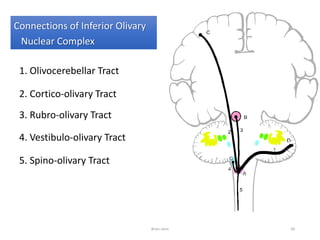
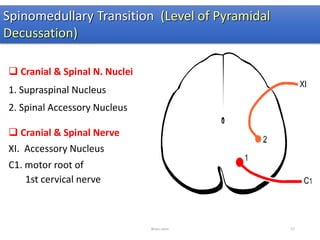
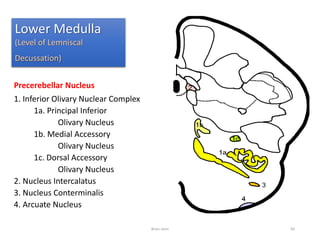
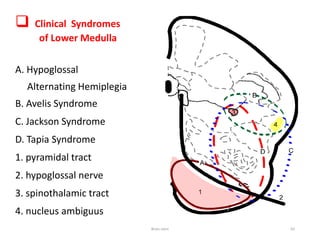
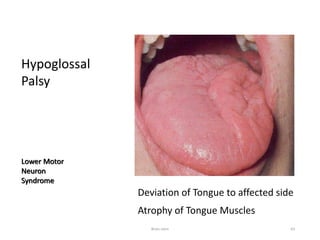
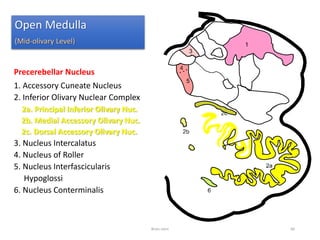
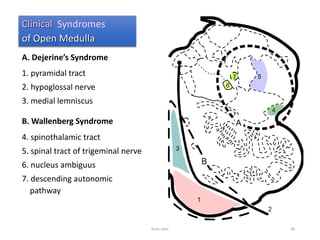
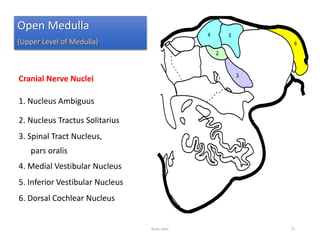
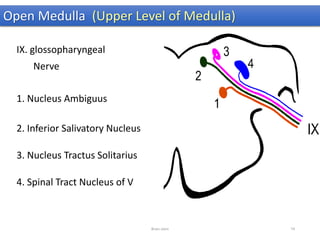
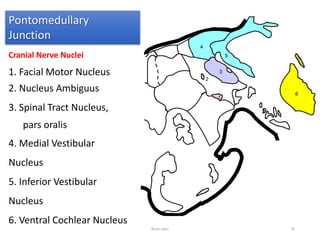
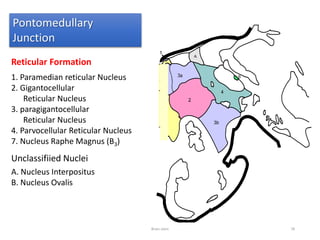
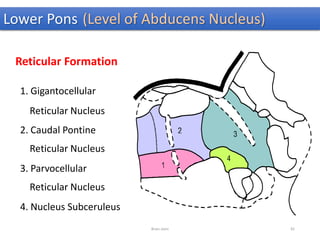
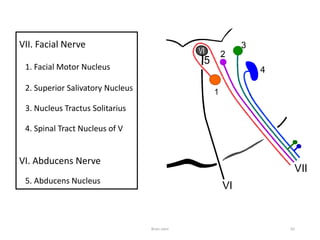
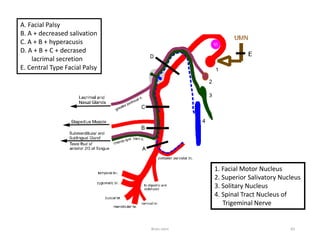
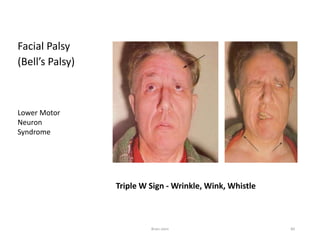
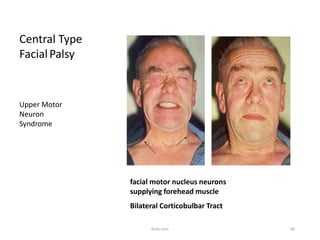
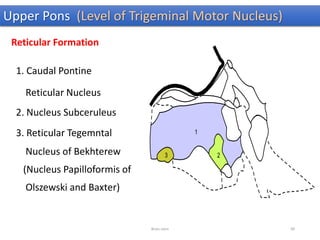
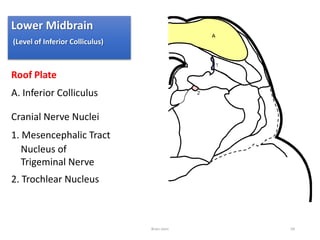
The document discusses the basic structure and components of the brain stem. It describes the three main portions as the roof plate, tegmentum, and basal portion. It then provides detailed information on the descending tracts in the basal portion, including the corticospinal, corticobulbar, and corticopontocerebellar fibers. It also discusses the various cranial nerve nuclei, precerebellar nuclei, and ascending sensory pathways located within the brain stem that are involved in motor and sensory functions.