Embed presentation
Downloaded 300 times


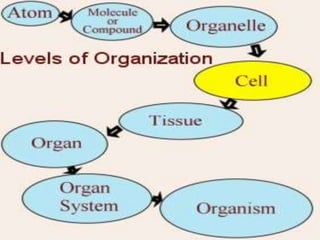




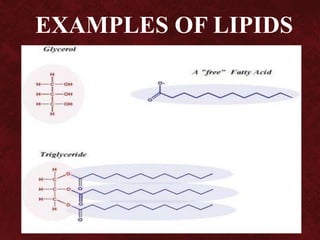

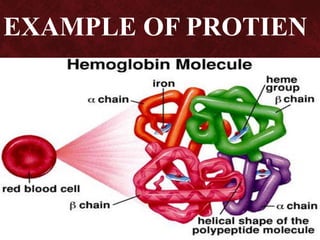

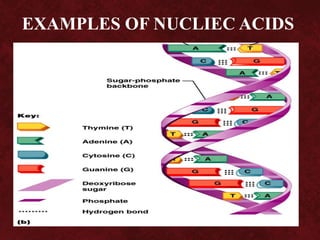


Biomolecules are groups of atoms containing more than one element that are involved in maintaining and metabolic processes of living organisms. There are four main types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and function as an energy source. Lipids also contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and function to store energy. Proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen and function in building and repairing cells as well as speeding up or slowing down chemical reactions. Nucleic acids contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus and function to store genetic information and determine physical appearance.












