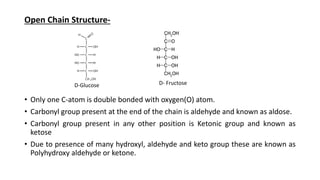
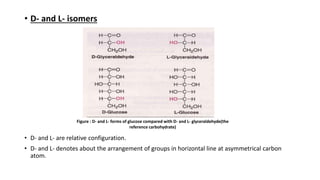
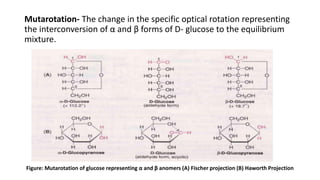
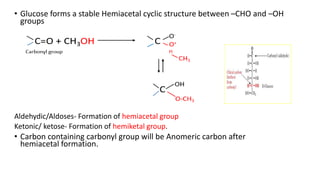
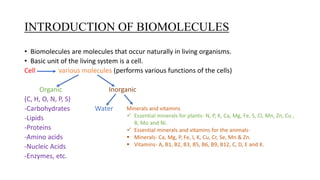
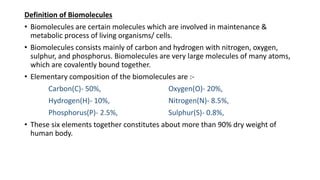
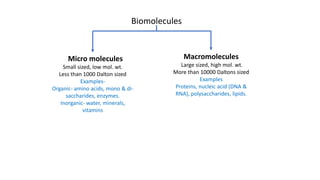
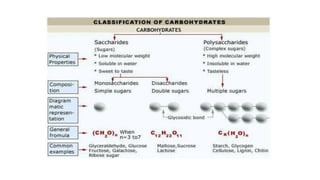
1) Carbohydrates are an essential class of biomolecules that serve as the primary energy source for many organisms. They are classified into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides depending on their size.
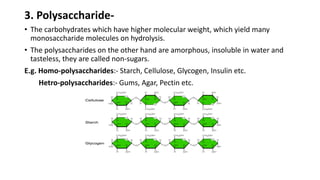
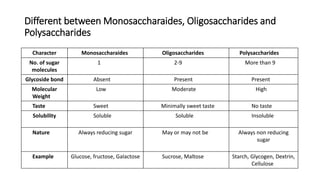
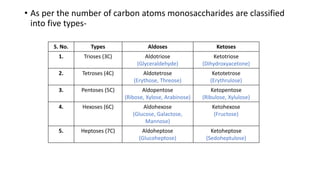
2) Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Oligosaccharides consist of 2-9 monosaccharide units and include disaccharides like sucrose and maltose. Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharide units and include starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
3) Carbohydrates play important biological roles like energy storage, structure, transport, and prevention of diseases. Glucose is a key energy source, while




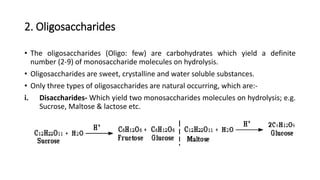
![ii. Trisaccharides - Which yield three monosaccharides molecules on hydrolysis and
have molecular formula is C18H32O16. e.g.: Raffinose.
iii. Tetrasaccharides - Which yield four monosaccharides molecules on hydrolysis
and have molecular formula is C22H42O21.
e.g.: Stachyose[gal(α1→6)gal(α1→6)glu(α1↔2β)fru]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biomoleculesandcarbohydrates-210705050512/85/Biomolecules-and-carbohydrates-13-320.jpg)