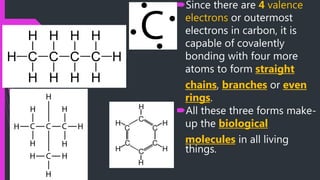
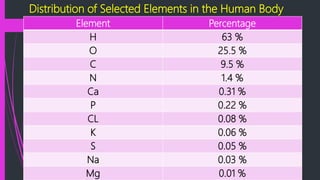
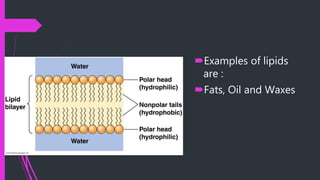
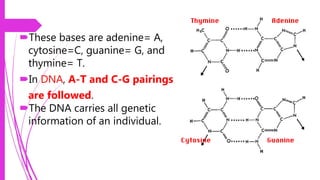
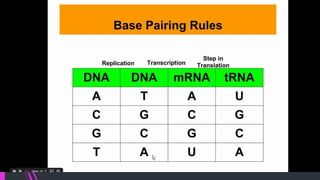
This document discusses the key biomolecules found in living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It explains that carbohydrates like sugars, starches, and cellulose are used for energy storage and as structural components. Lipids such as fats and oils store energy and make up cell membranes. Proteins have many functions like structure, movement, defense, and catalysis as enzymes. Nucleic acids DNA and RNA carry genetic information and enable inheritance and protein synthesis. The four main biomolecules all contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen arranged into larger structures that allow life.