Embed presentation
Downloaded 21 times
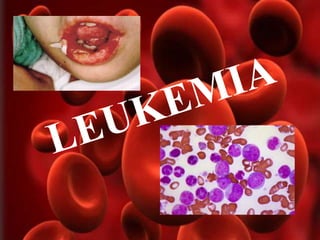
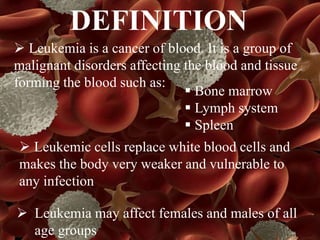
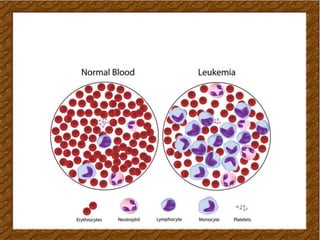
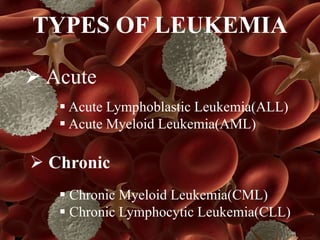

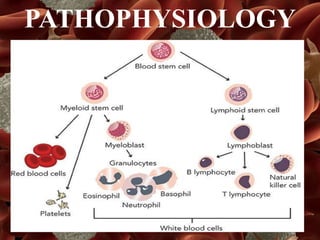

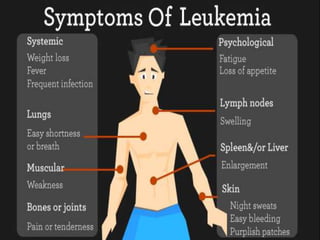
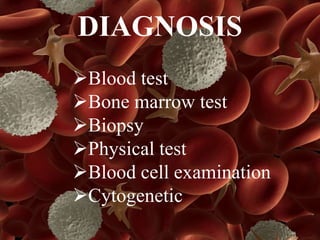
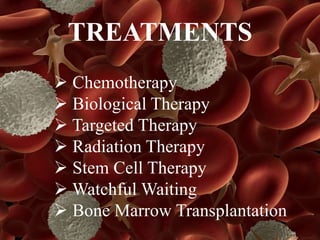
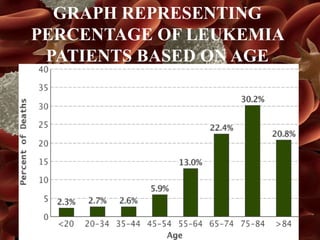


Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that affects various blood-forming tissues, including bone marrow and the lymphatic system, and can occur in individuals of any age. There are two main types, acute and chronic, with acute forms progressing rapidly and requiring immediate treatment, while chronic types progress slowly and can sometimes be asymptomatic. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests and biopsies, with treatment options ranging from chemotherapy to stem cell therapy.












