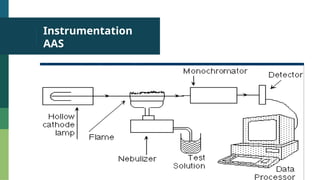
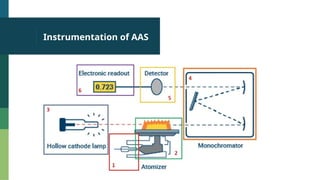
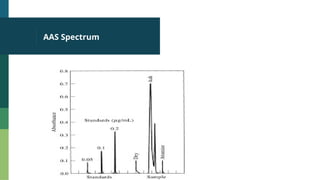
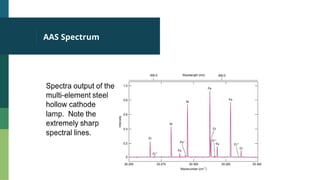
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is an analytical technique introduced in 1955 that measures the concentration of specific elements in a sample based on their ability to absorb light at unique wavelengths. The process involves converting samples into free atoms in a flame, followed by the use of a light source and a monochromator to isolate specific wavelengths for analysis. AAS has applications in agriculture, environmental studies, food testing, and forensics.