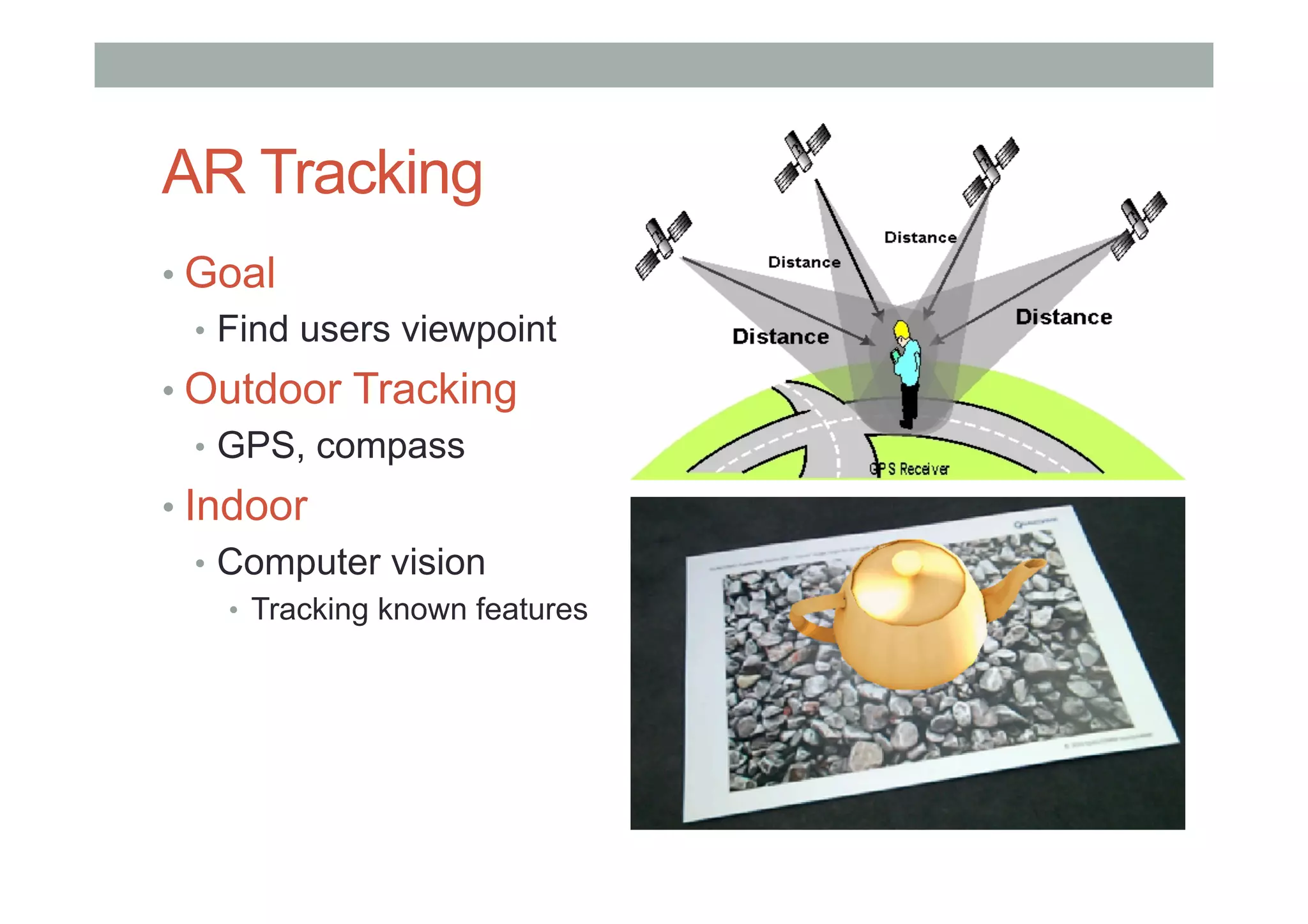
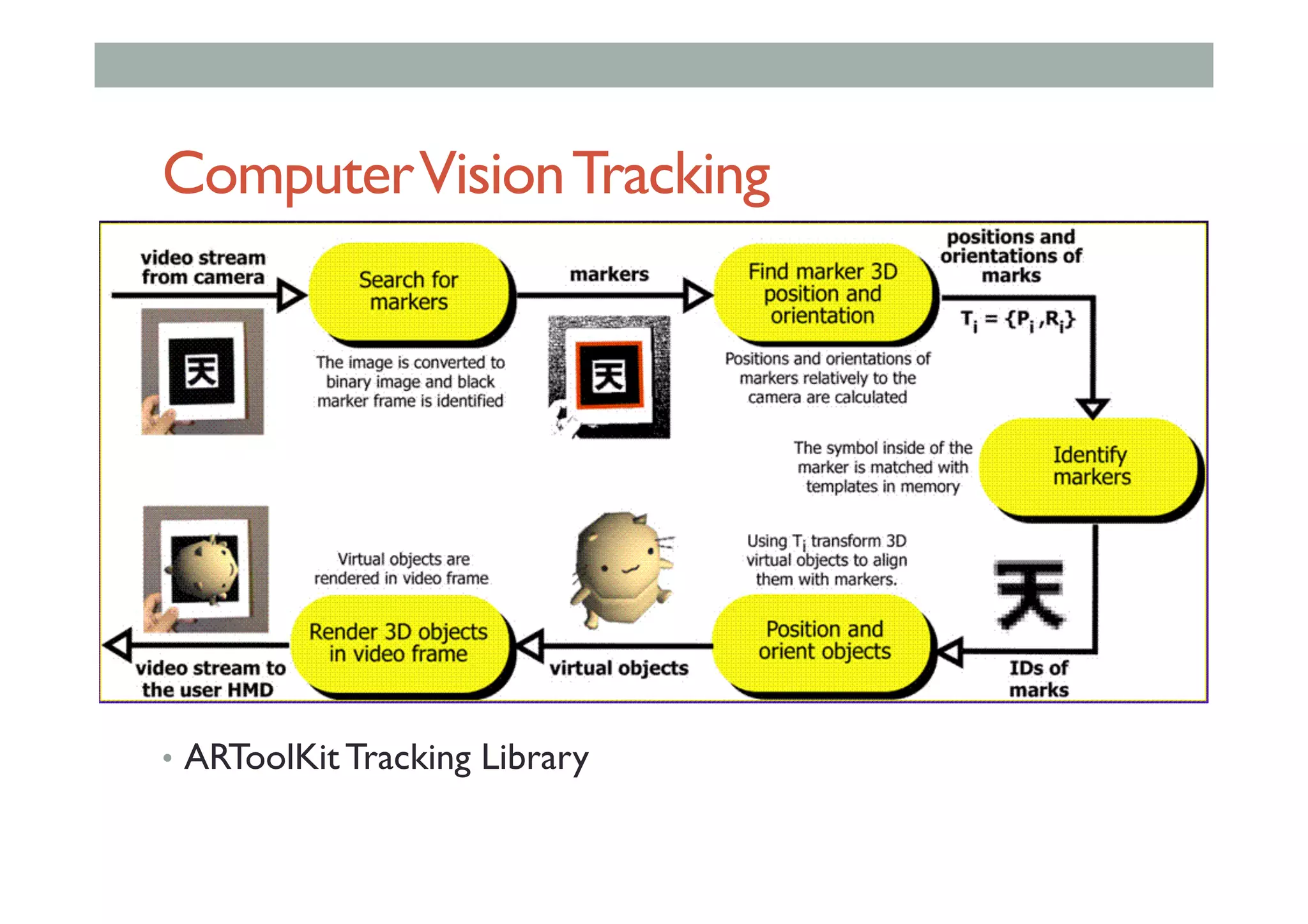
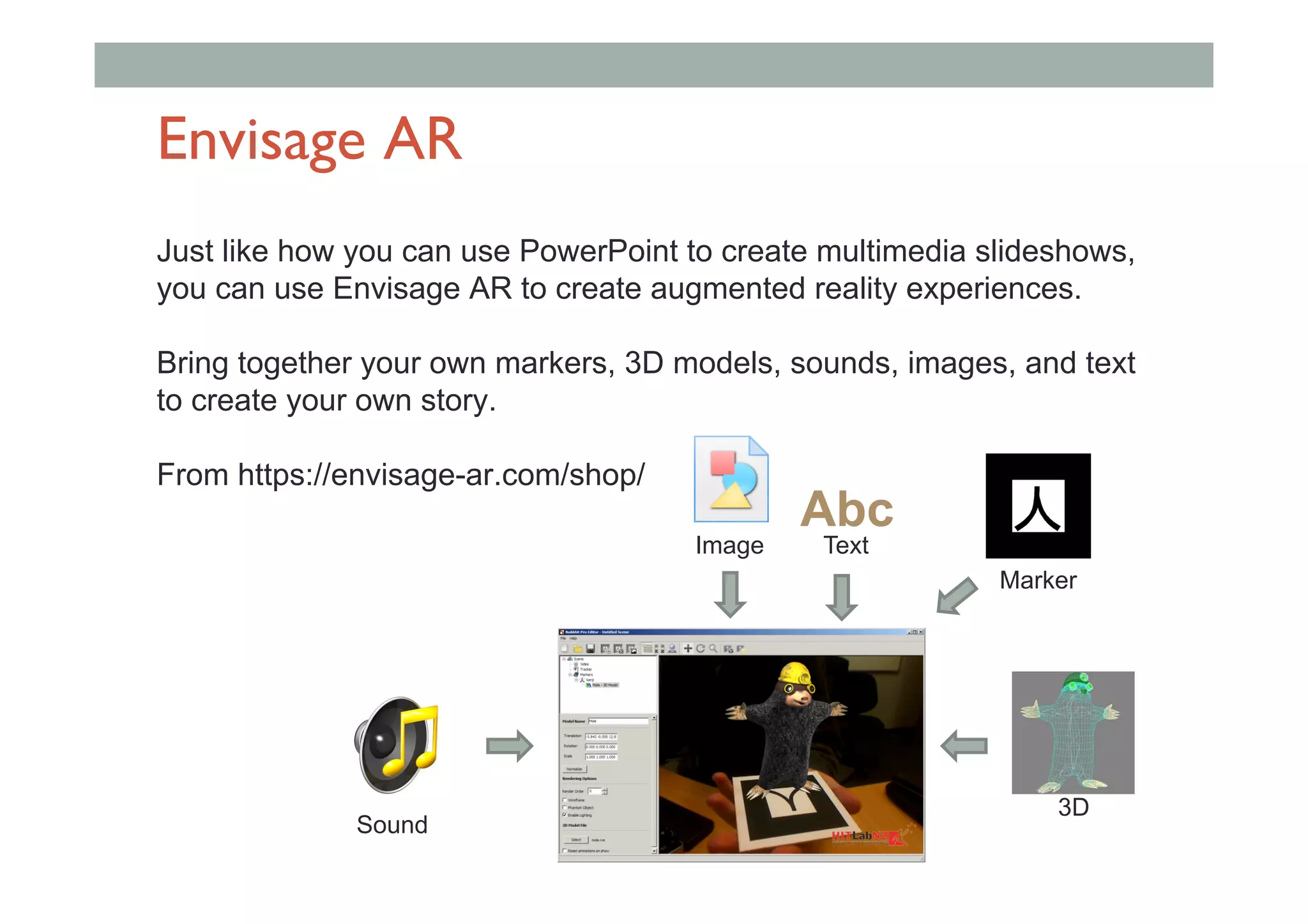
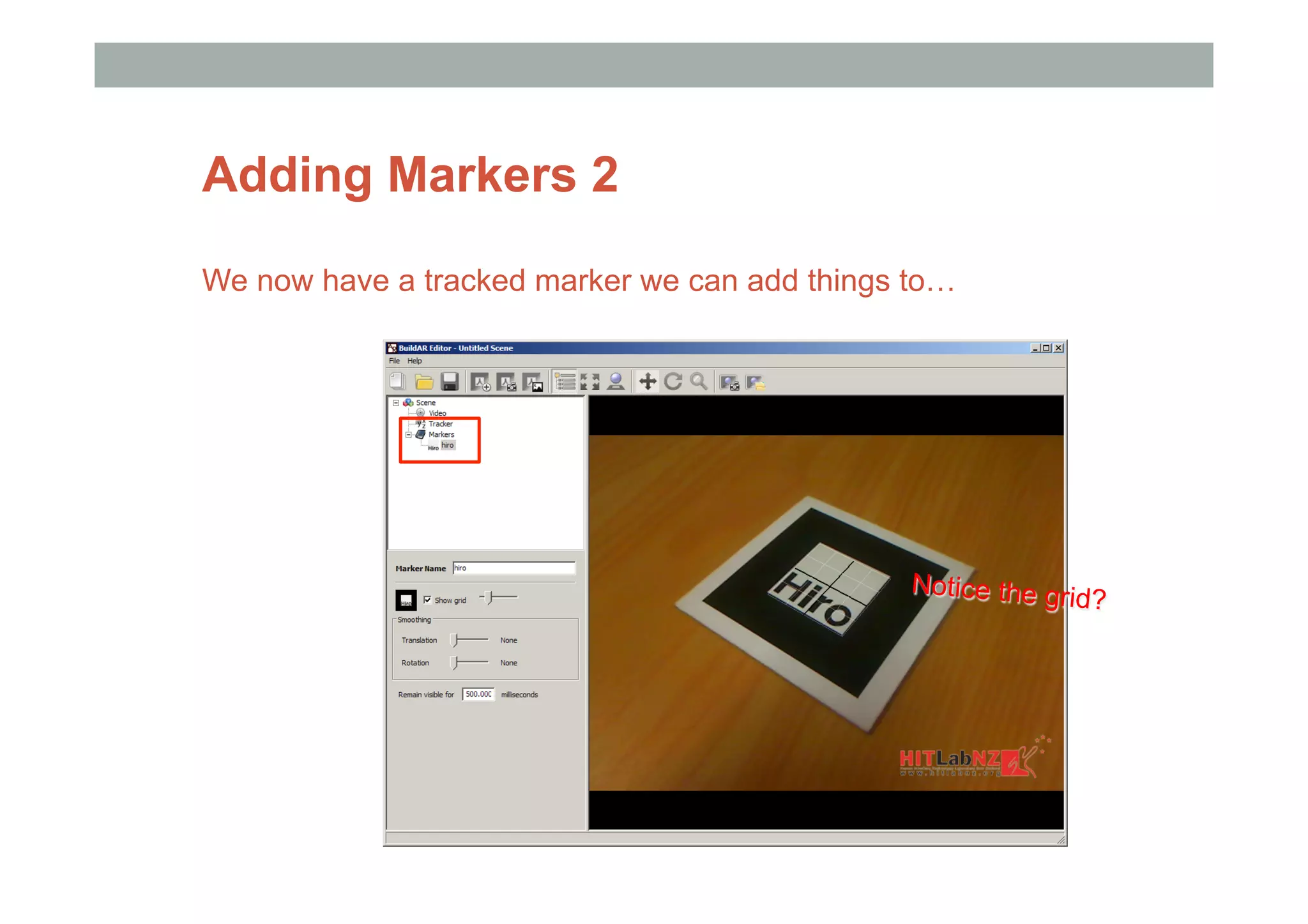
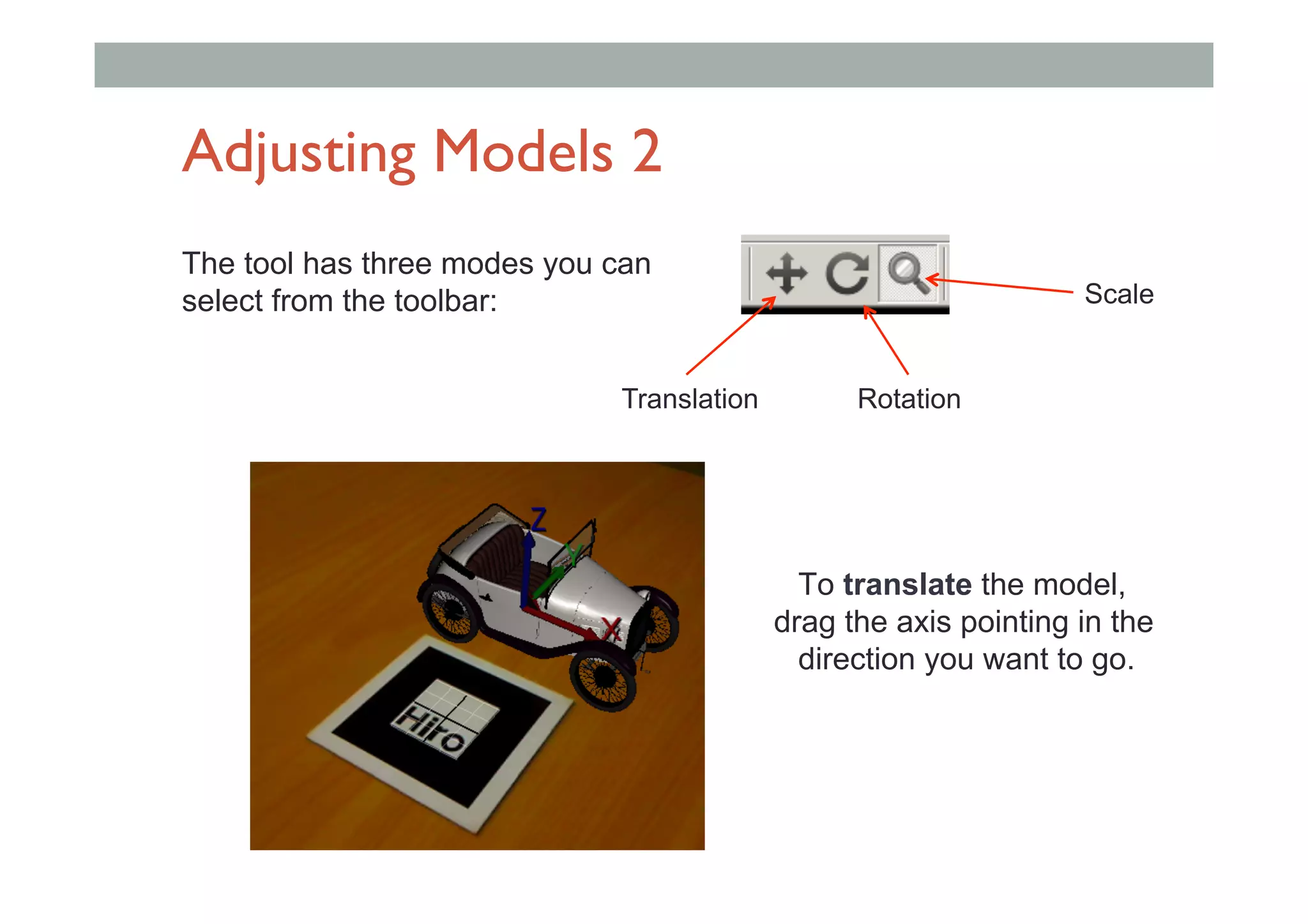
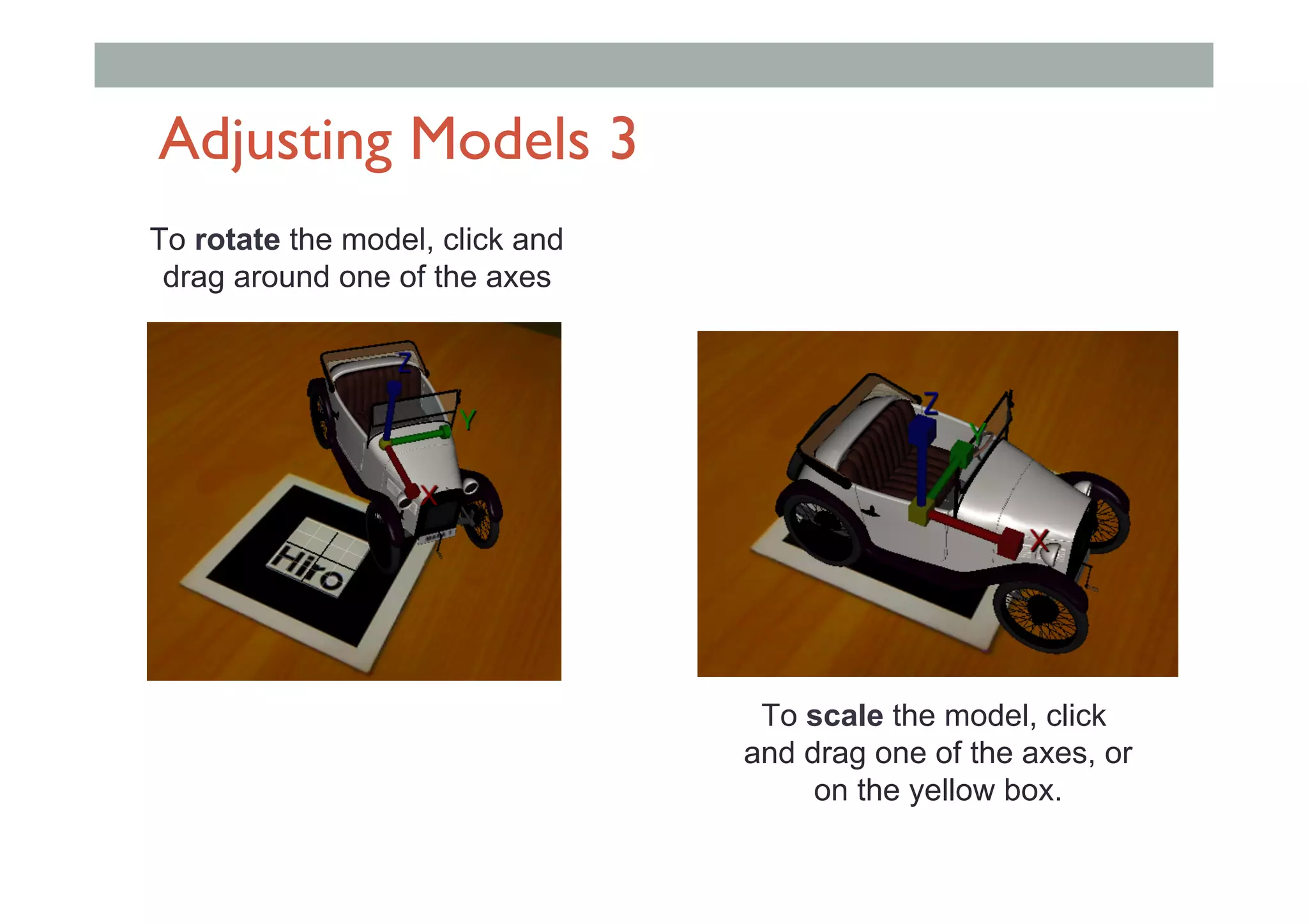
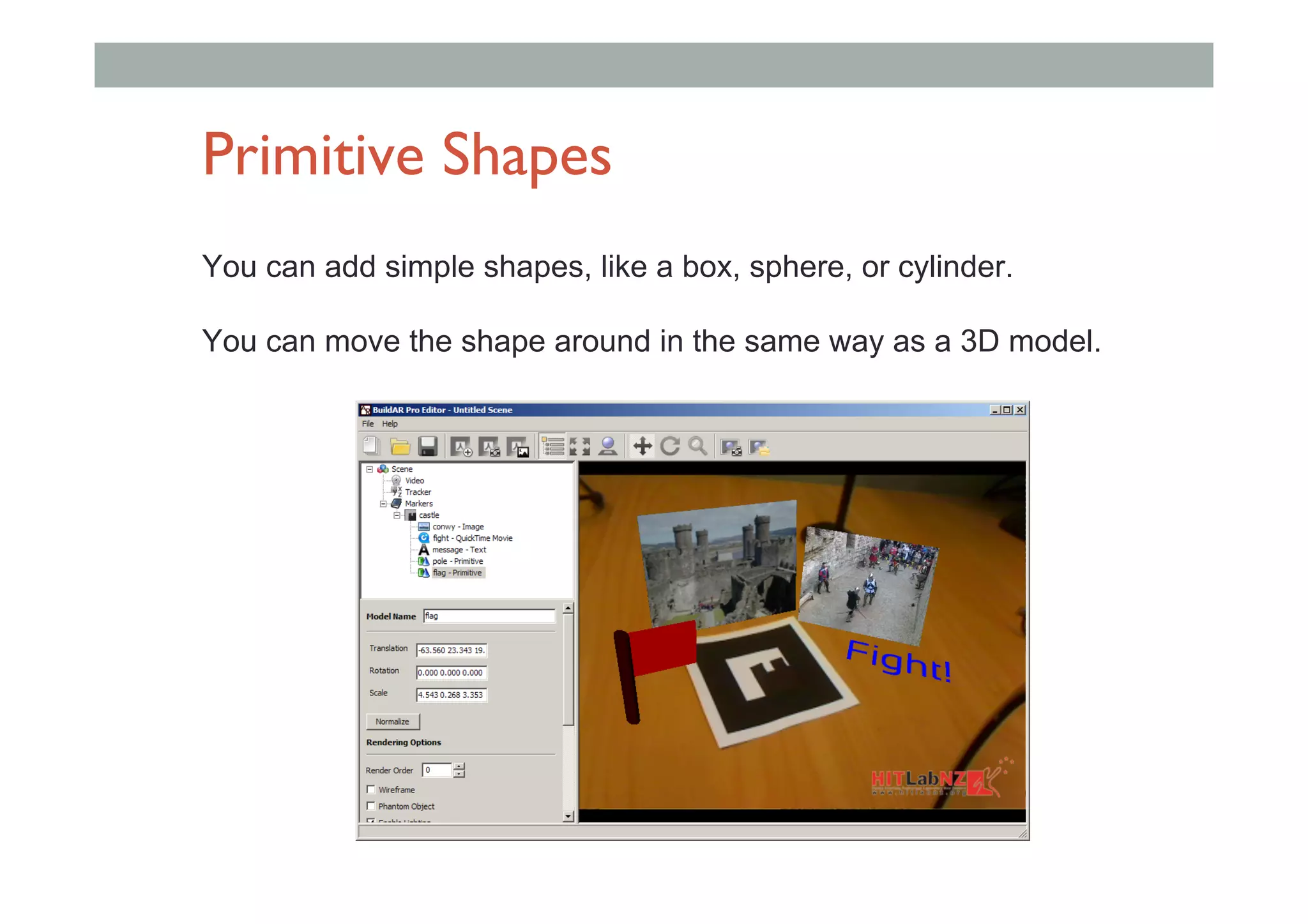
The document discusses augmented reality (AR) and its potential applications in education. It provides an overview of AR, including definitions and examples. The history of AR is explored, from early prototypes in the 1960s-70s to recent consumer adoption on mobile devices. Educational uses of AR are examined, such as visualizing concepts spatially and improving understanding of real environments. The document demonstrates an AR authoring tool called Envisage that allows users to create AR scenes. Future research directions are also outlined, such as improved displays, interaction methods, and educational experiences using AR.