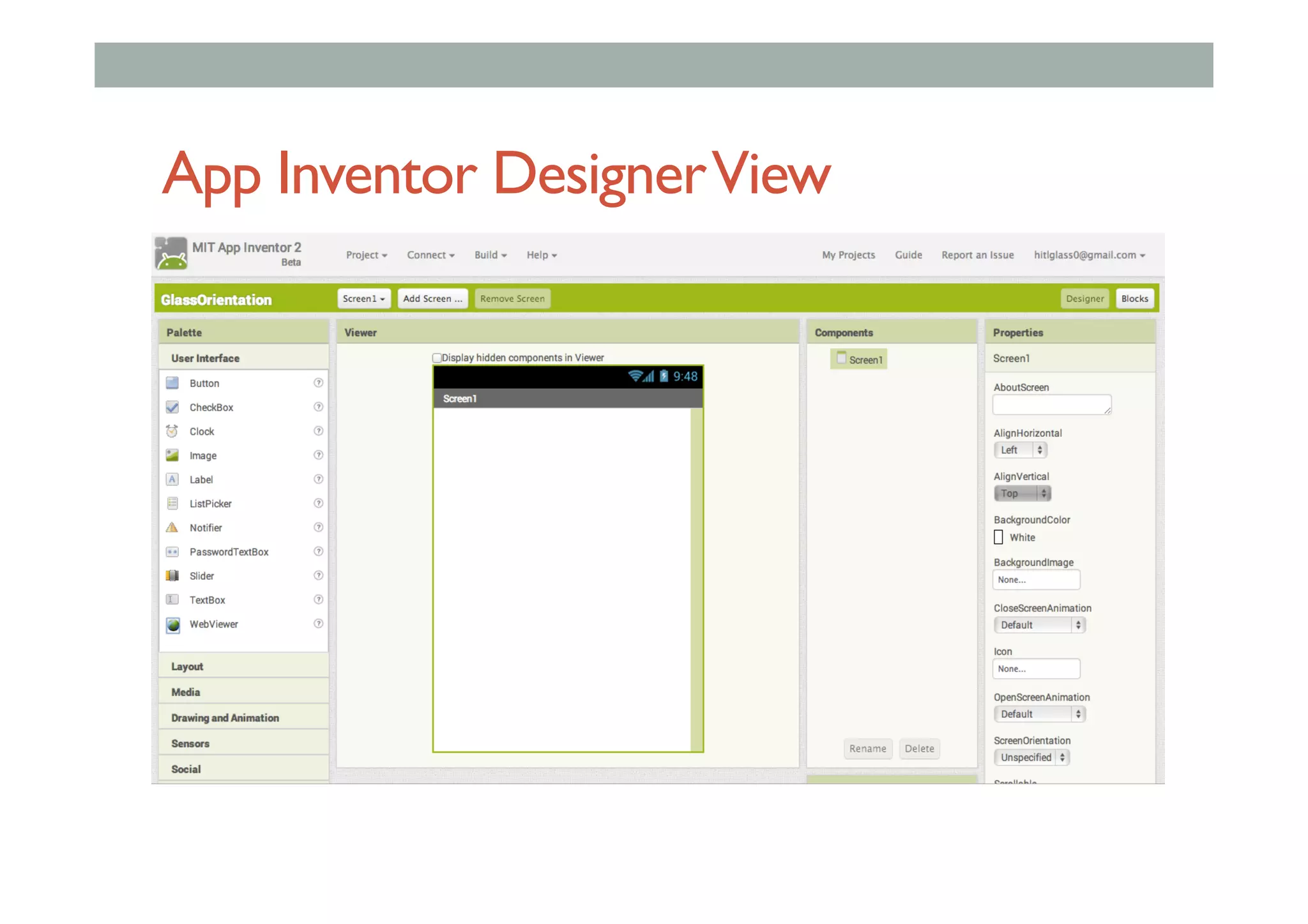
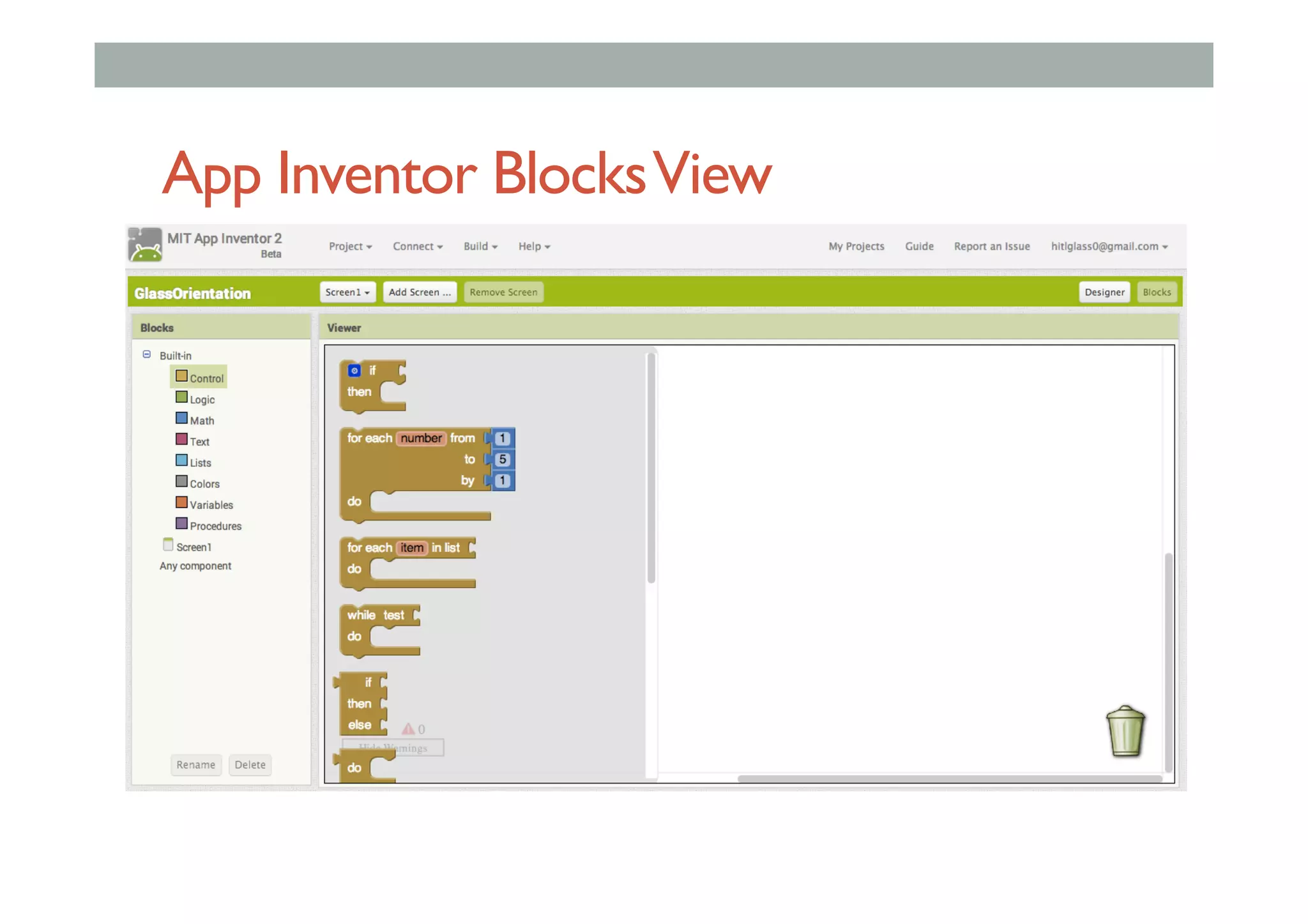
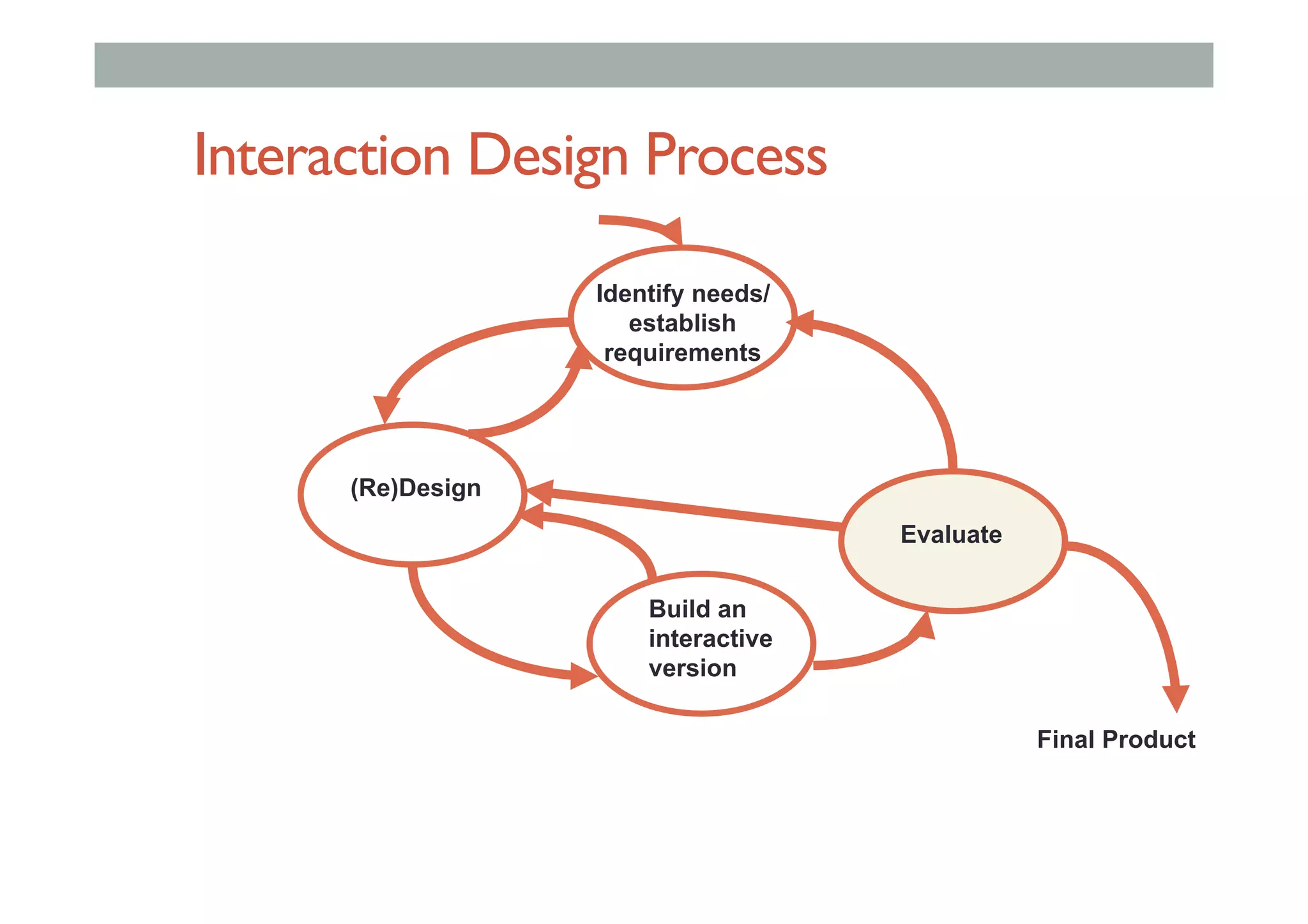
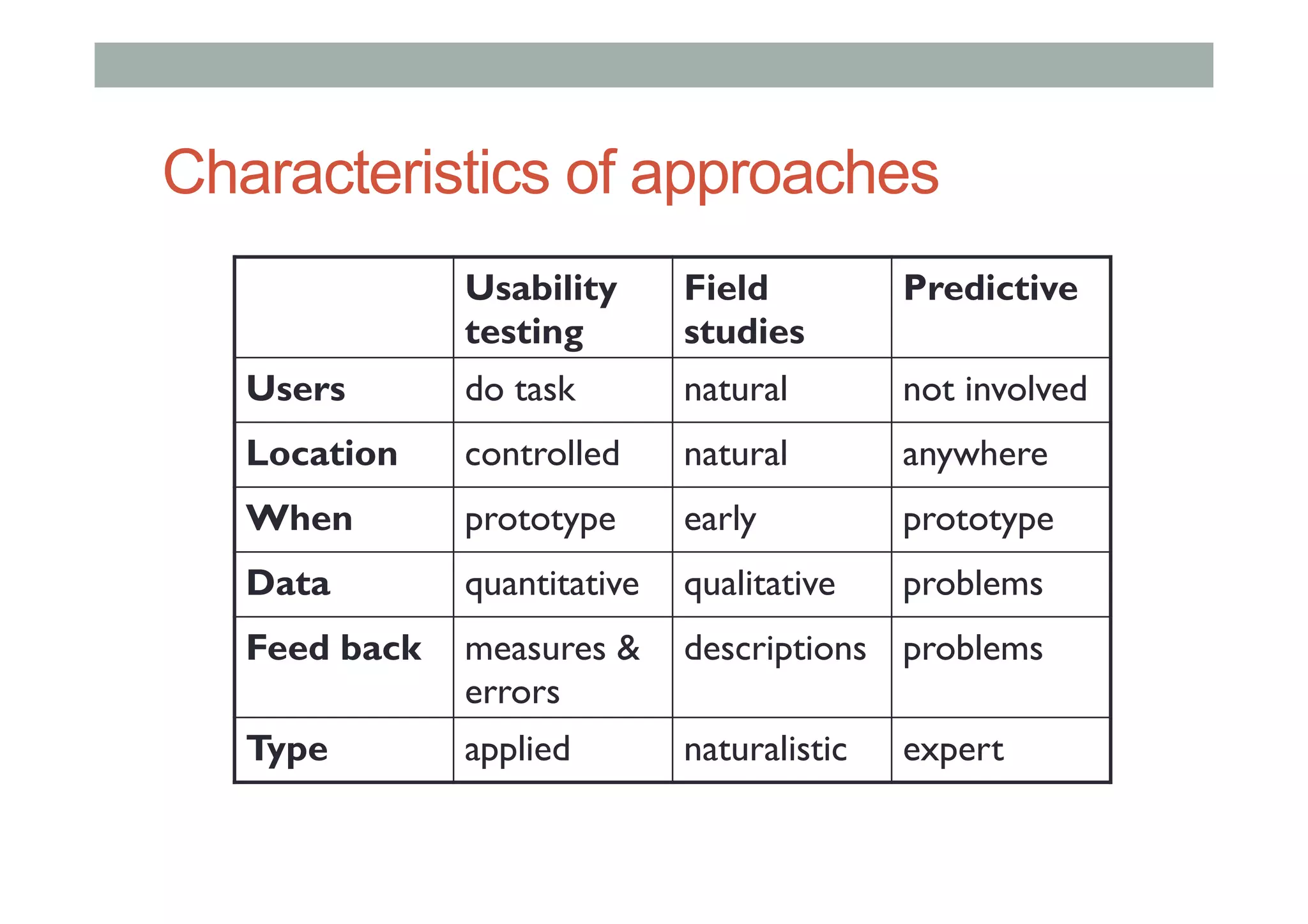
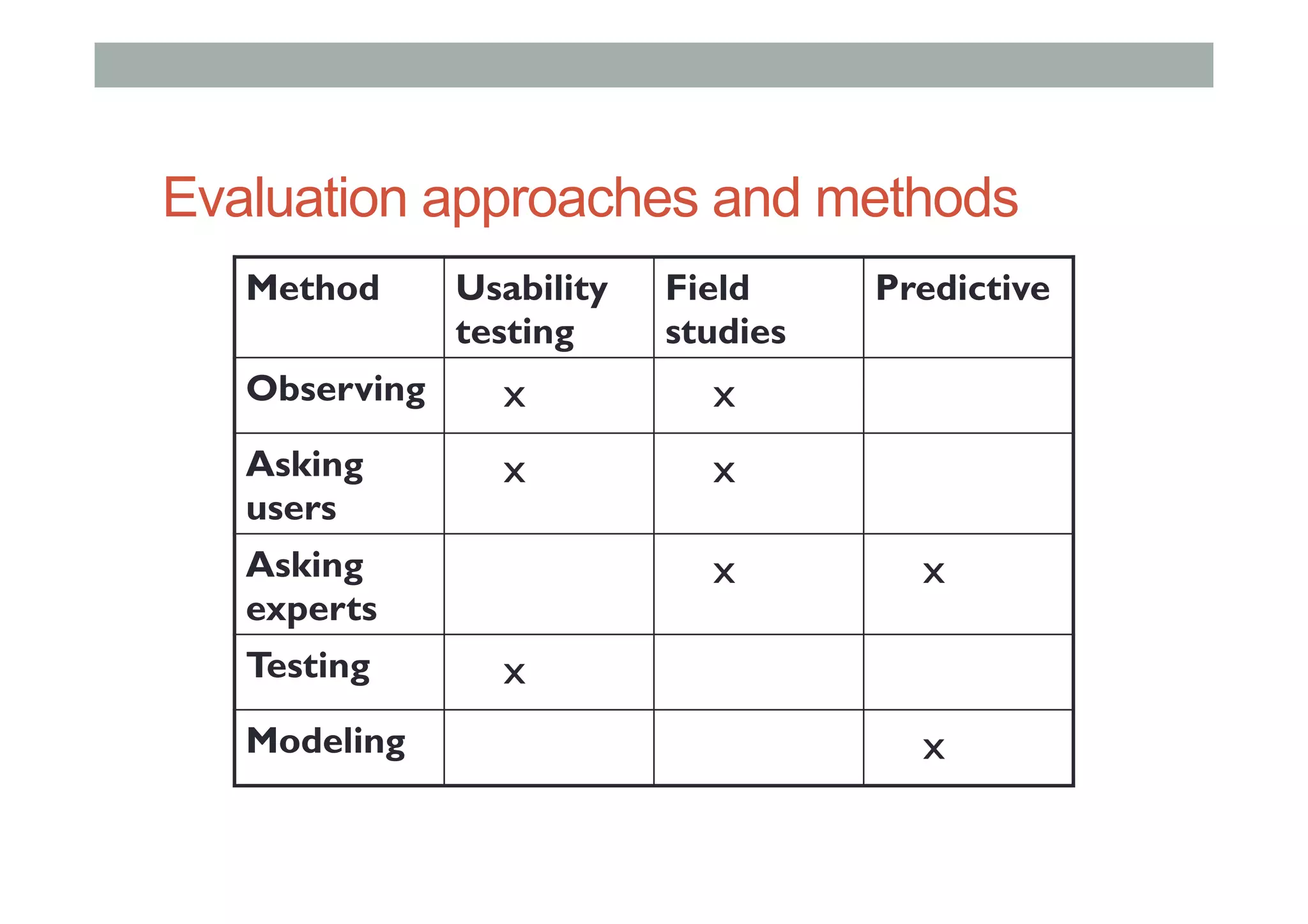
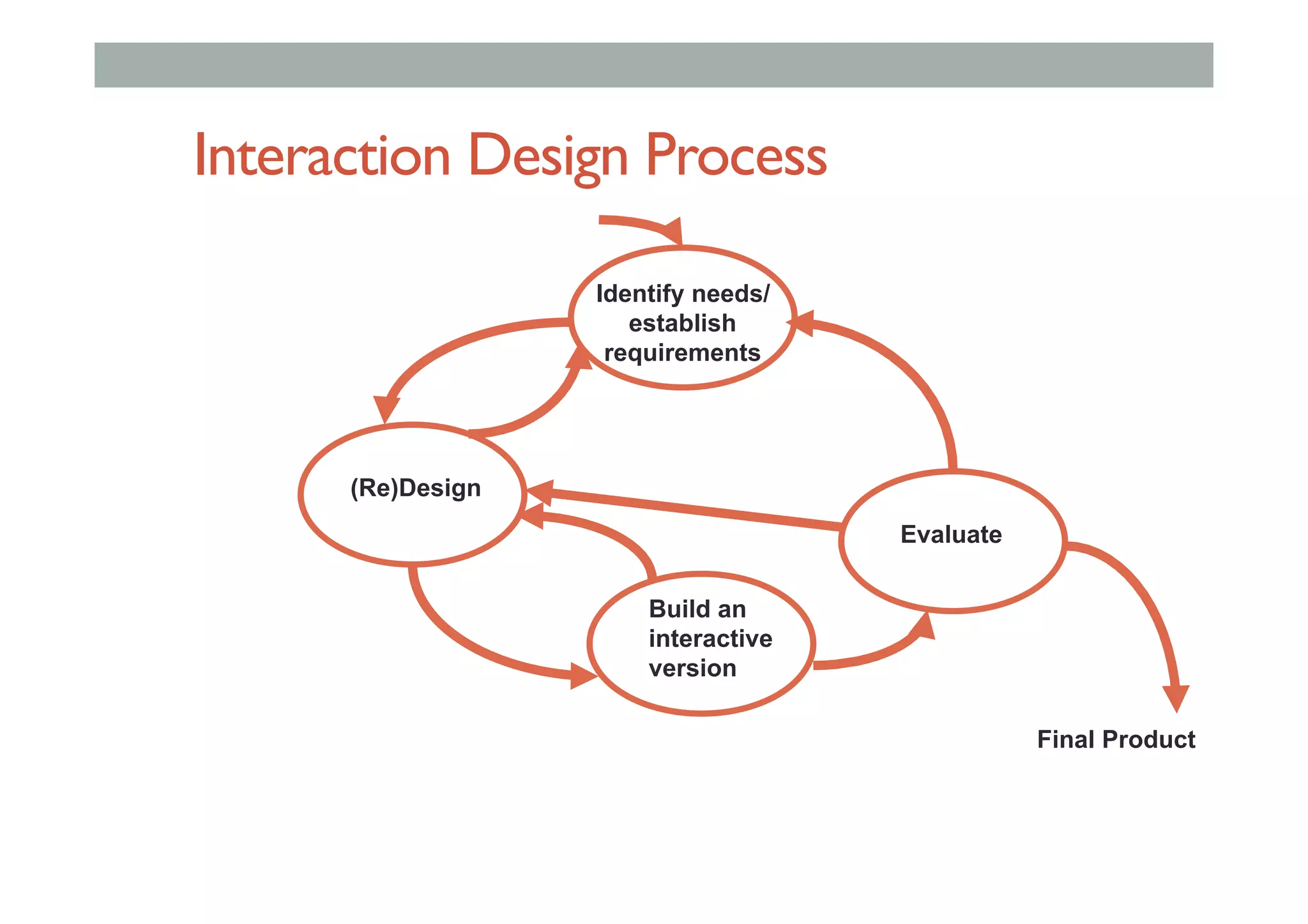
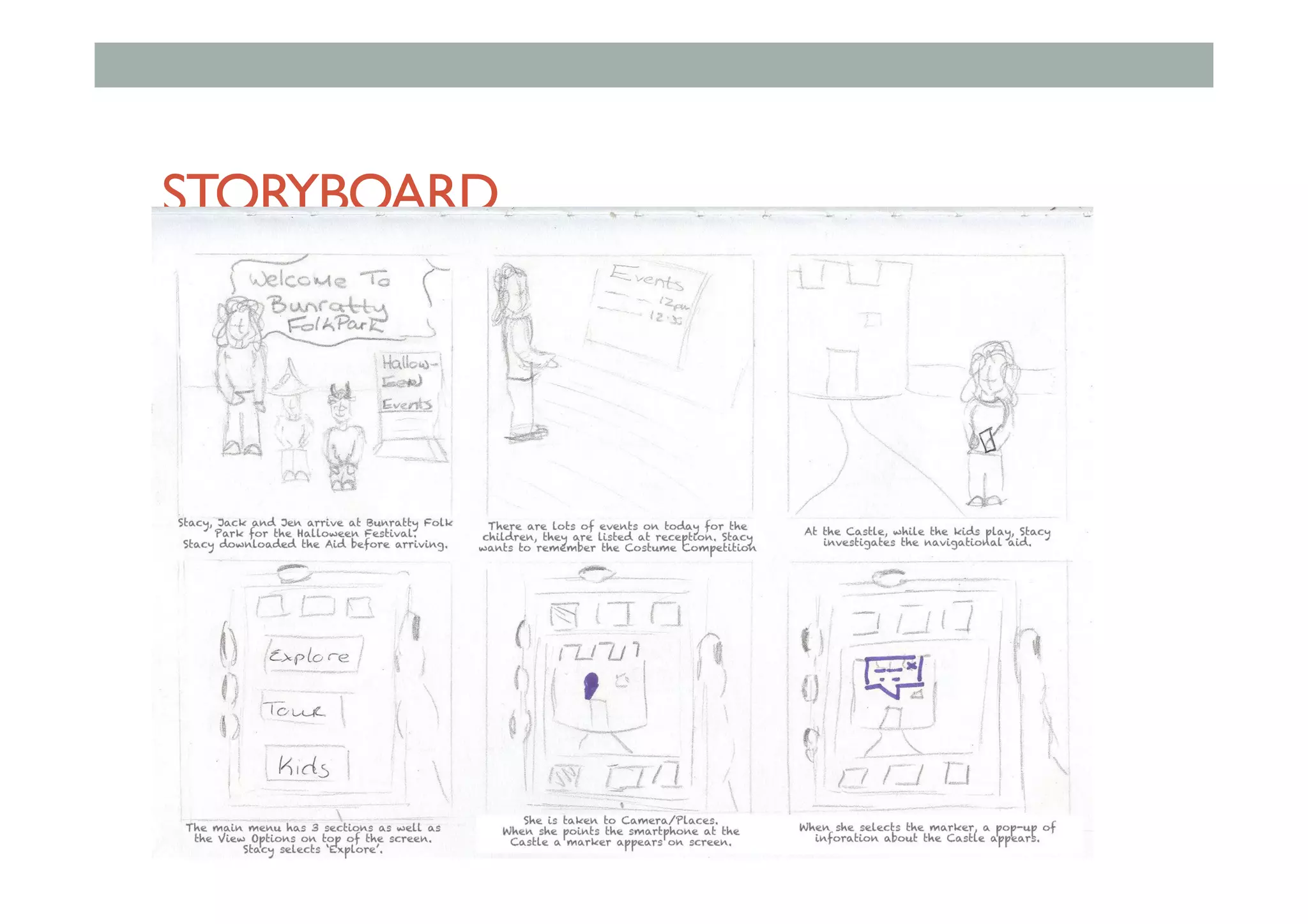
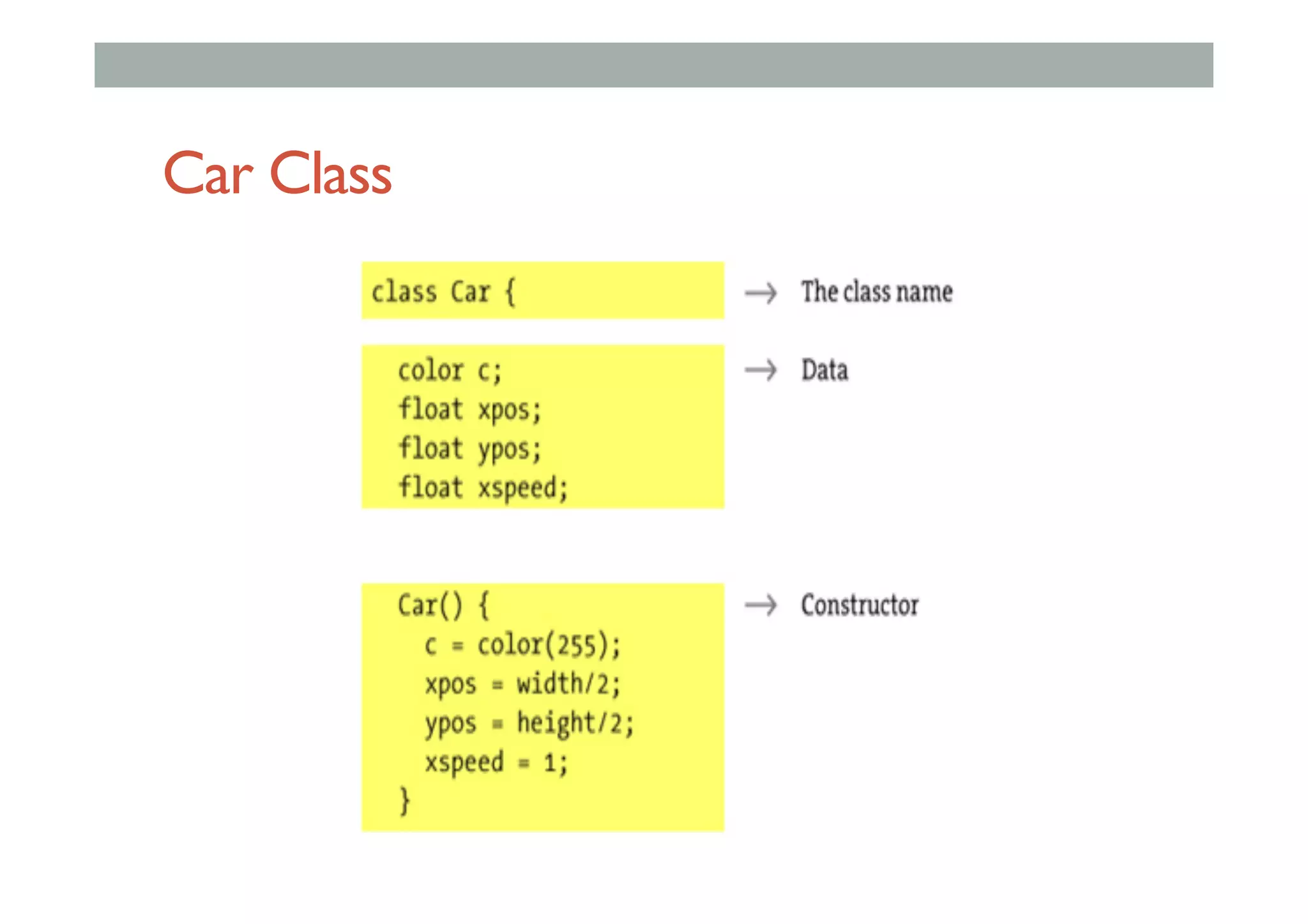
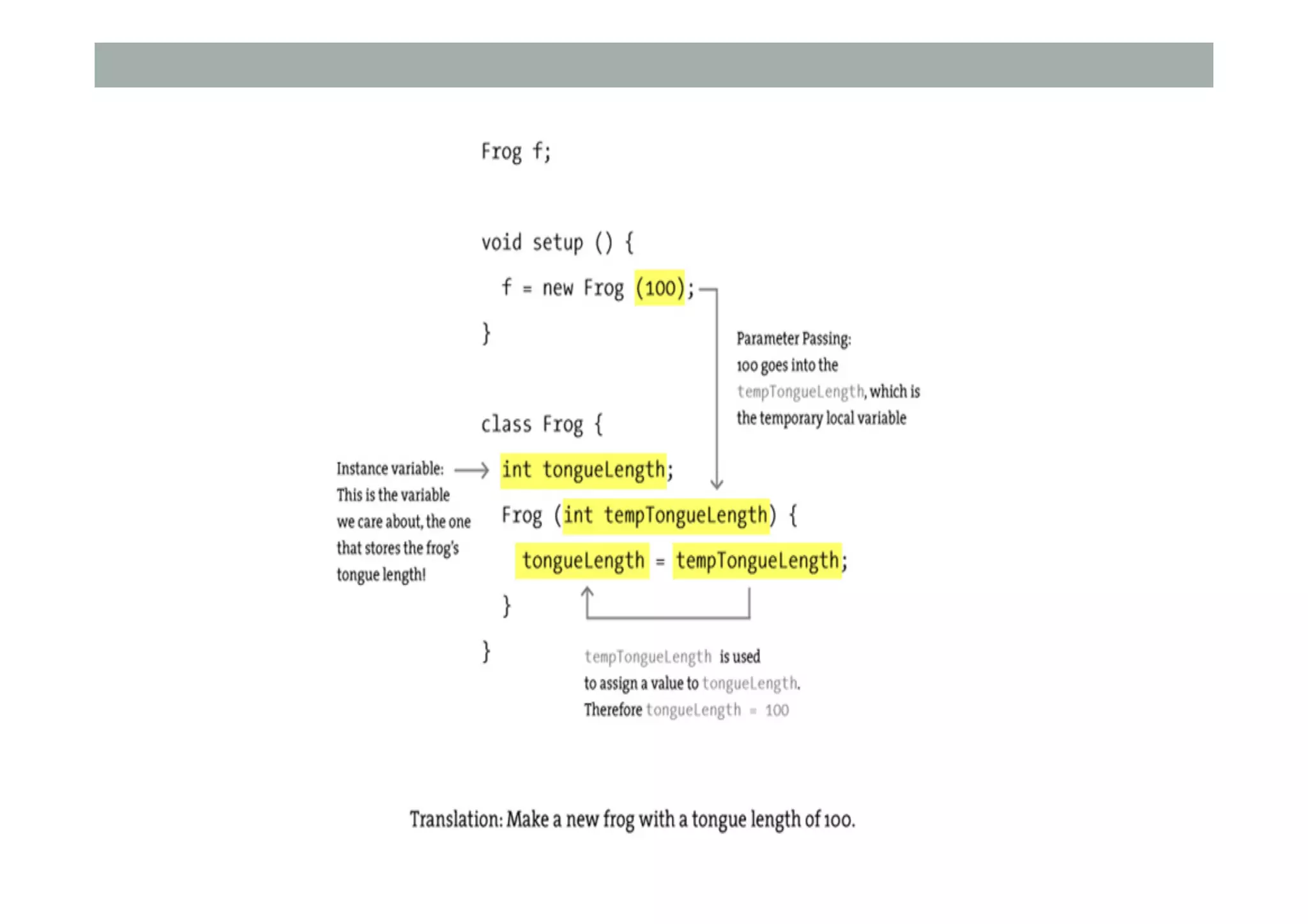
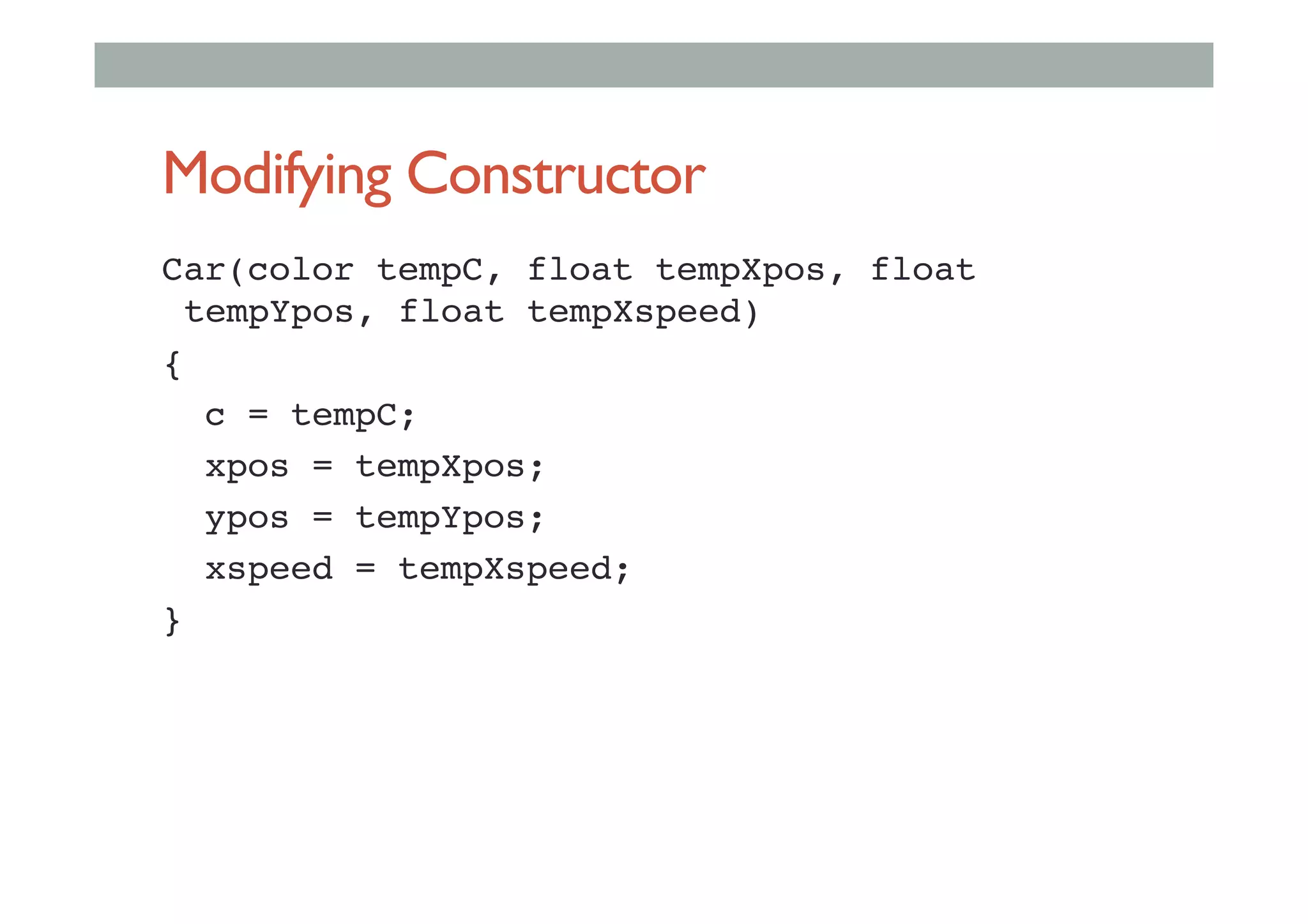
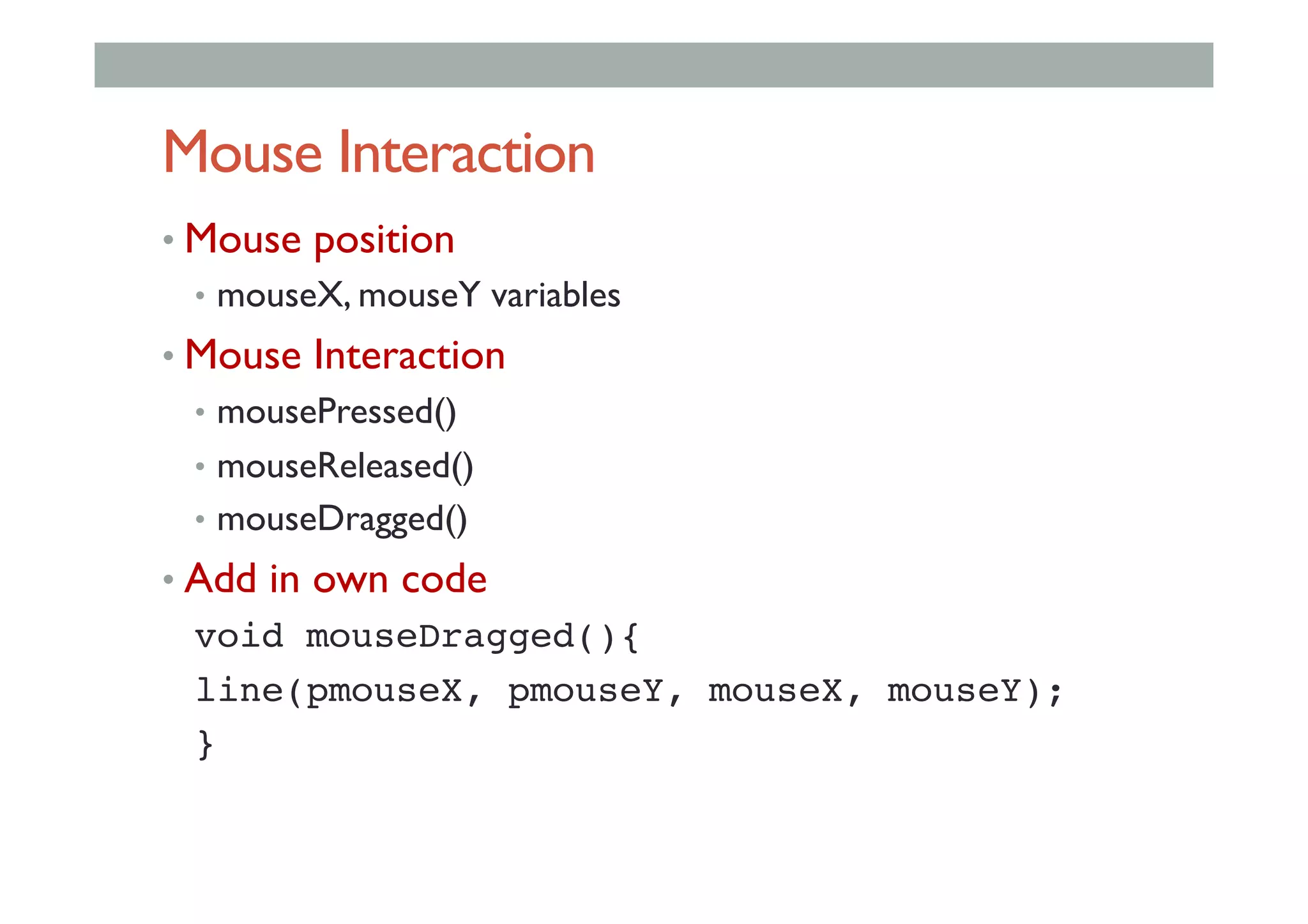
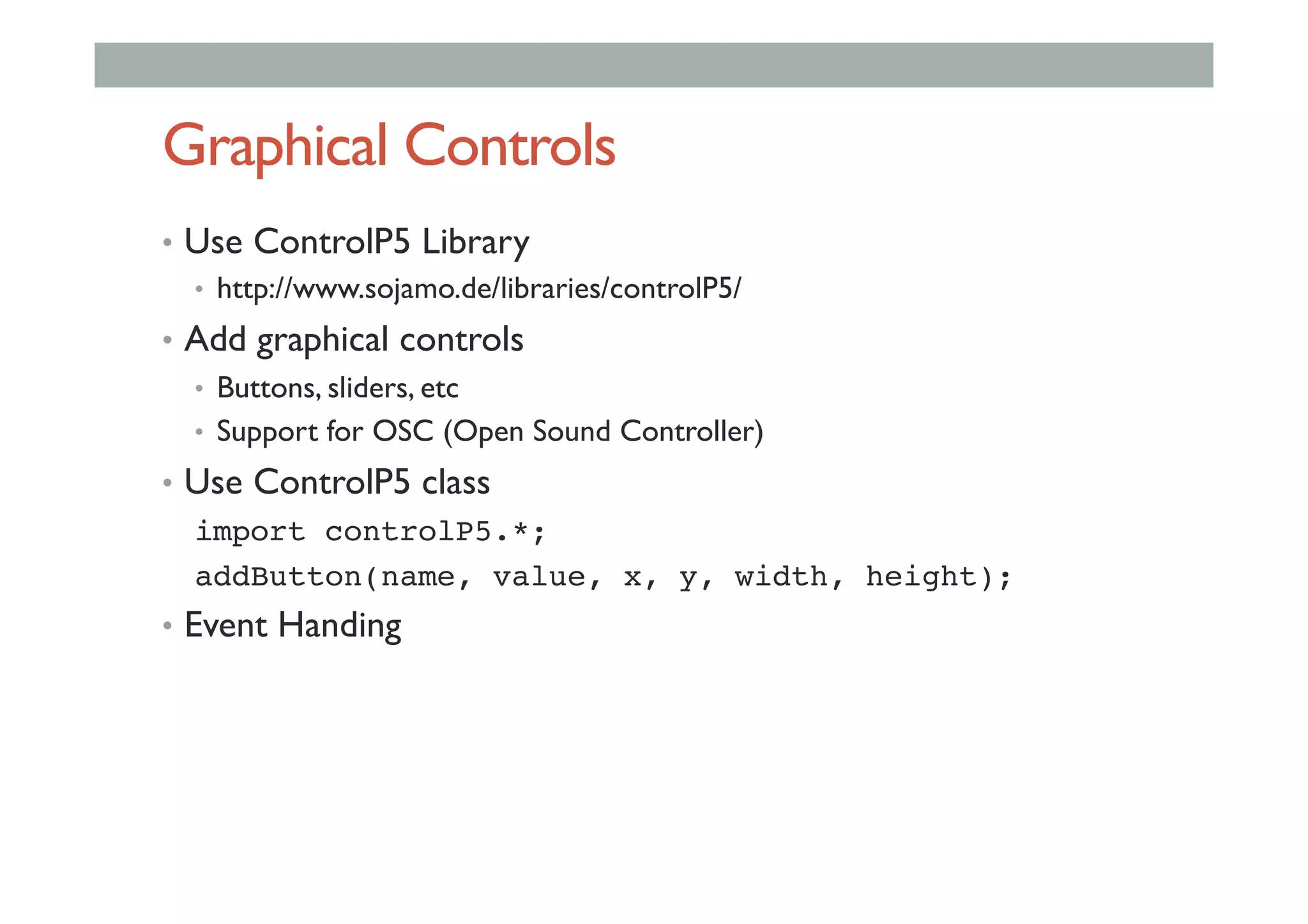
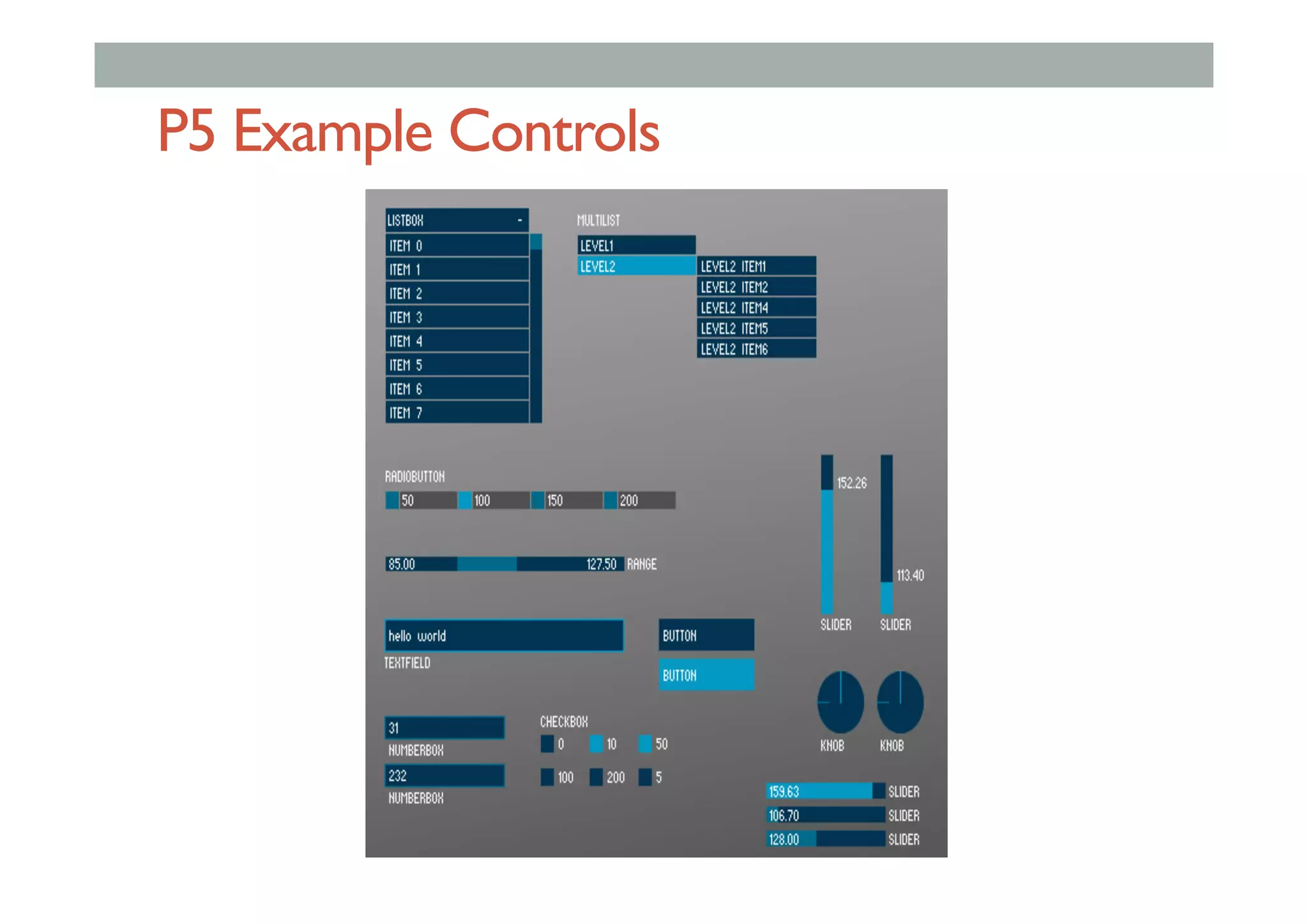
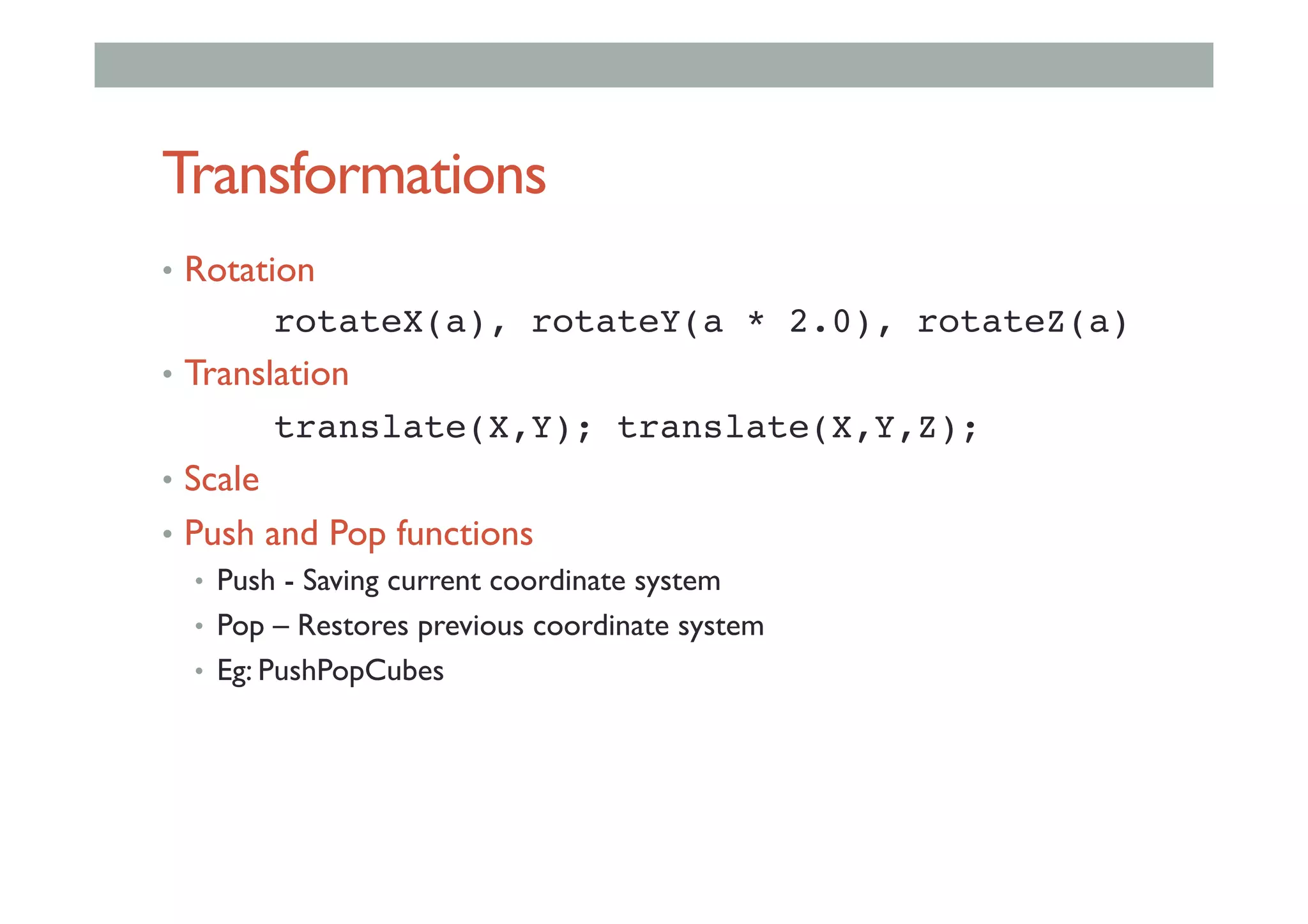
The document discusses advanced HCI concepts, focusing on tools like App Inventor and Processing for creating interactive applications, as well as various prototyping and evaluation methods. It covers interaction design processes, mobile augmented reality technologies, and interfaces for wearable and invisible computing, highlighting their challenges and research gaps. Finally, it addresses physiological sensing technologies and their applications in understanding user interactions and experiences.














































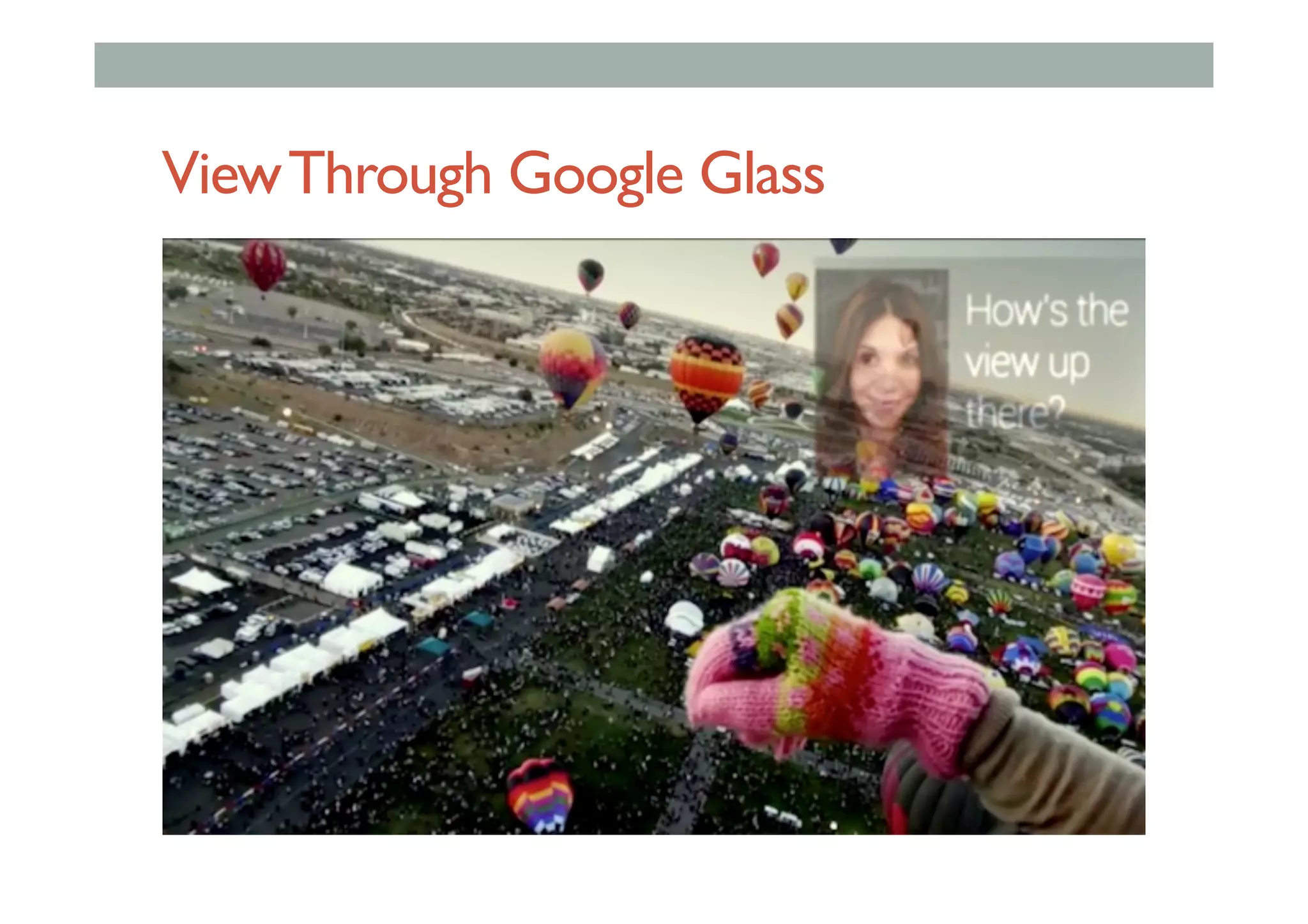



![Augmented Reality Definition
• Defining Characteristics [Azuma 97]
• Combines Real andVirtual Images
• Both can be seen at the same time
• Interactive in real-time
• The virtual content can be interacted with
• Registered in 3D
• Virtual objects appear fixed in space
Azuma, R. T. (1997). A survey of augmented reality. Presence, 6(4), 355-385.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-technologyfinalnovideo-160818053748/75/COMP-4026-Lecture4-Processing-and-Advanced-Interface-Technology-84-2048.jpg)
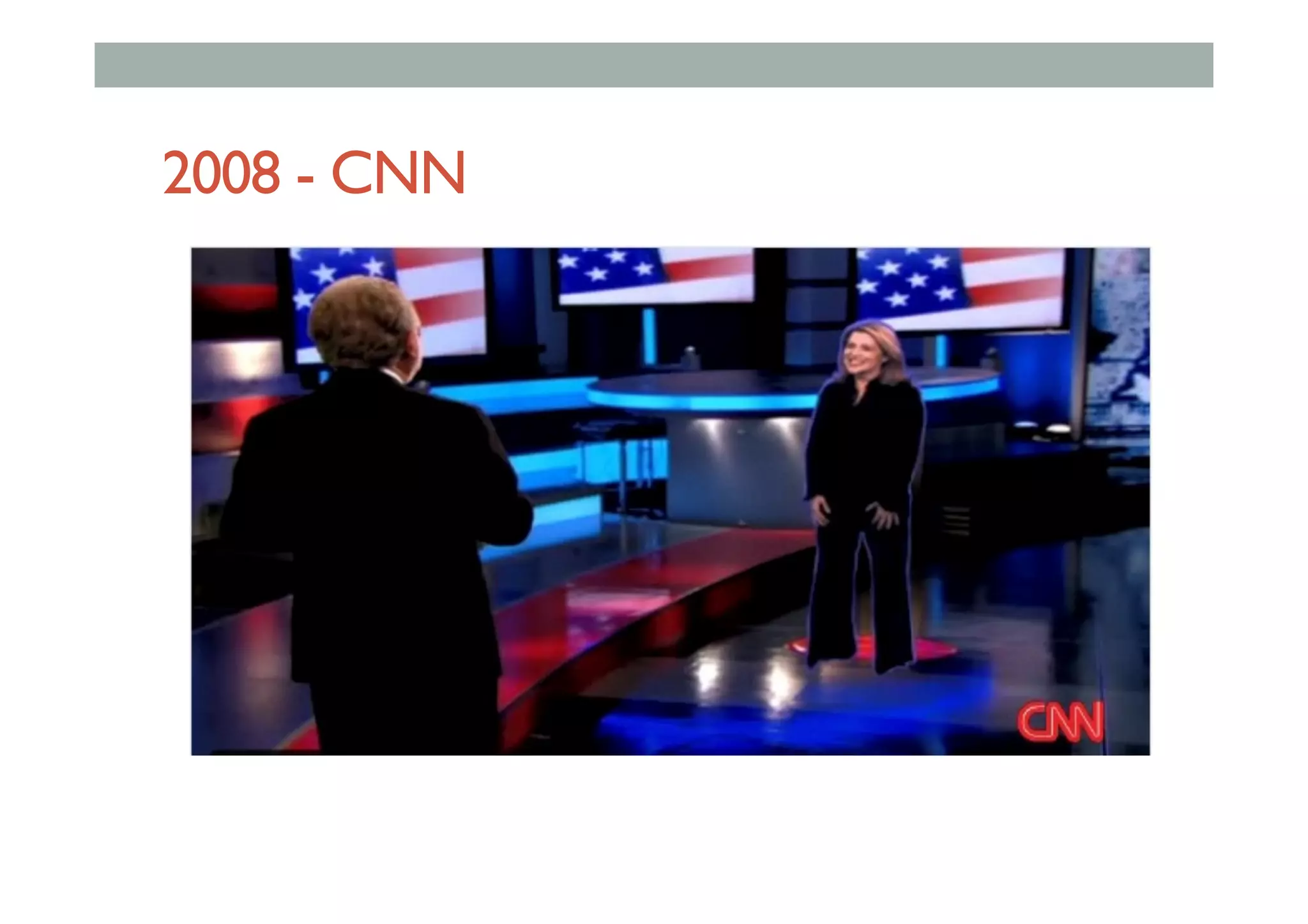










![Early Examples
• Interaction without devices:
• BodySpace [Strachan 2007]: Functions to body position
• Abracadabra [Harrison 2007]: Magnets on finger tips
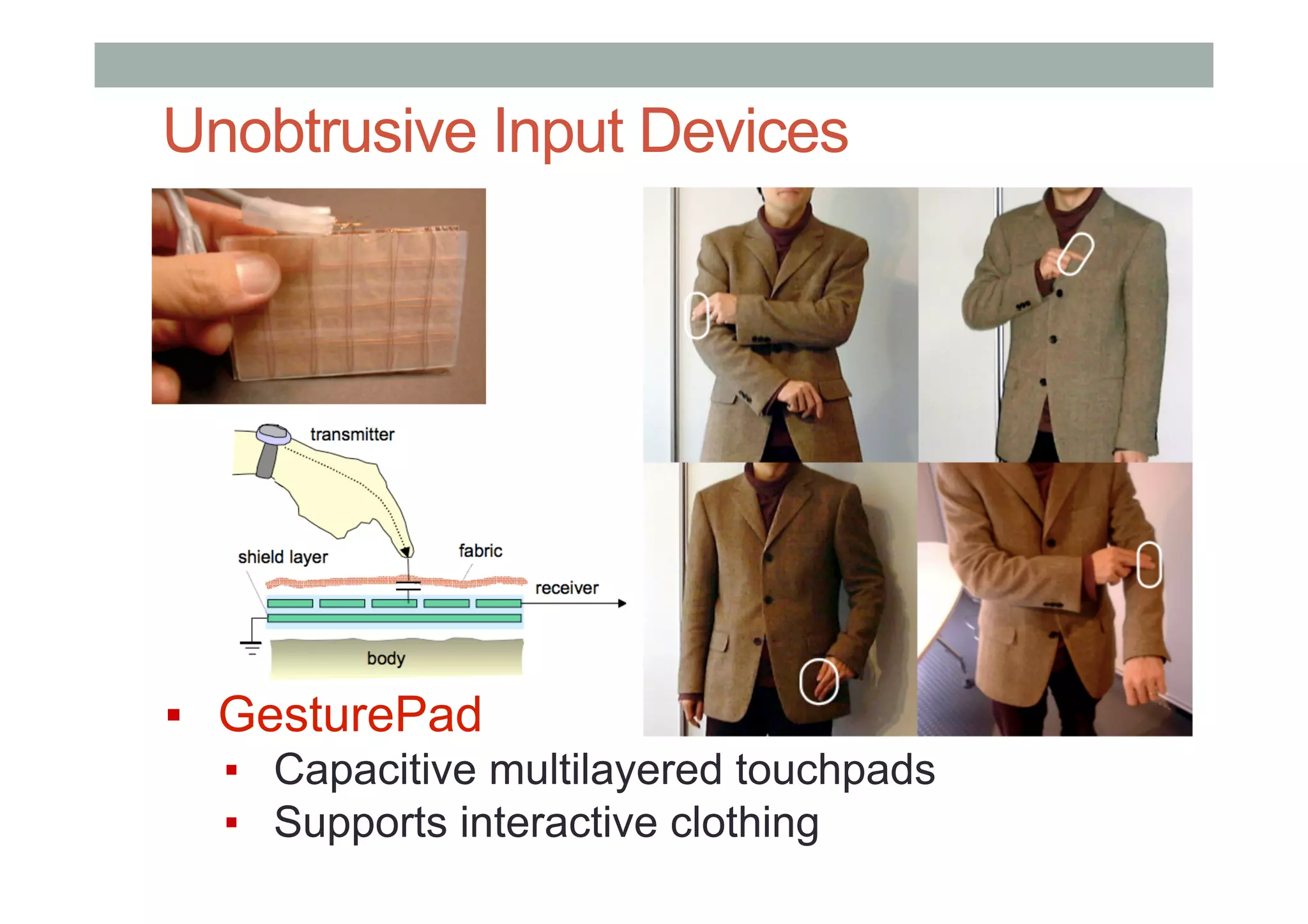
• GesturePad [Rekimoto 2001]: Capacitive sensing in clothing
• Palm-based Interaction
• Haptic Hand [Kohli 2005]: Using non-dominant hand in VR
• Sixth Sense [Mistry 2009]: Projection on hand
• Brainy Hand [Tamaki 2009]: Head worn projector/camera](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-technologyfinalnovideo-160818053748/75/COMP-4026-Lecture4-Processing-and-Advanced-Interface-Technology-98-2048.jpg)
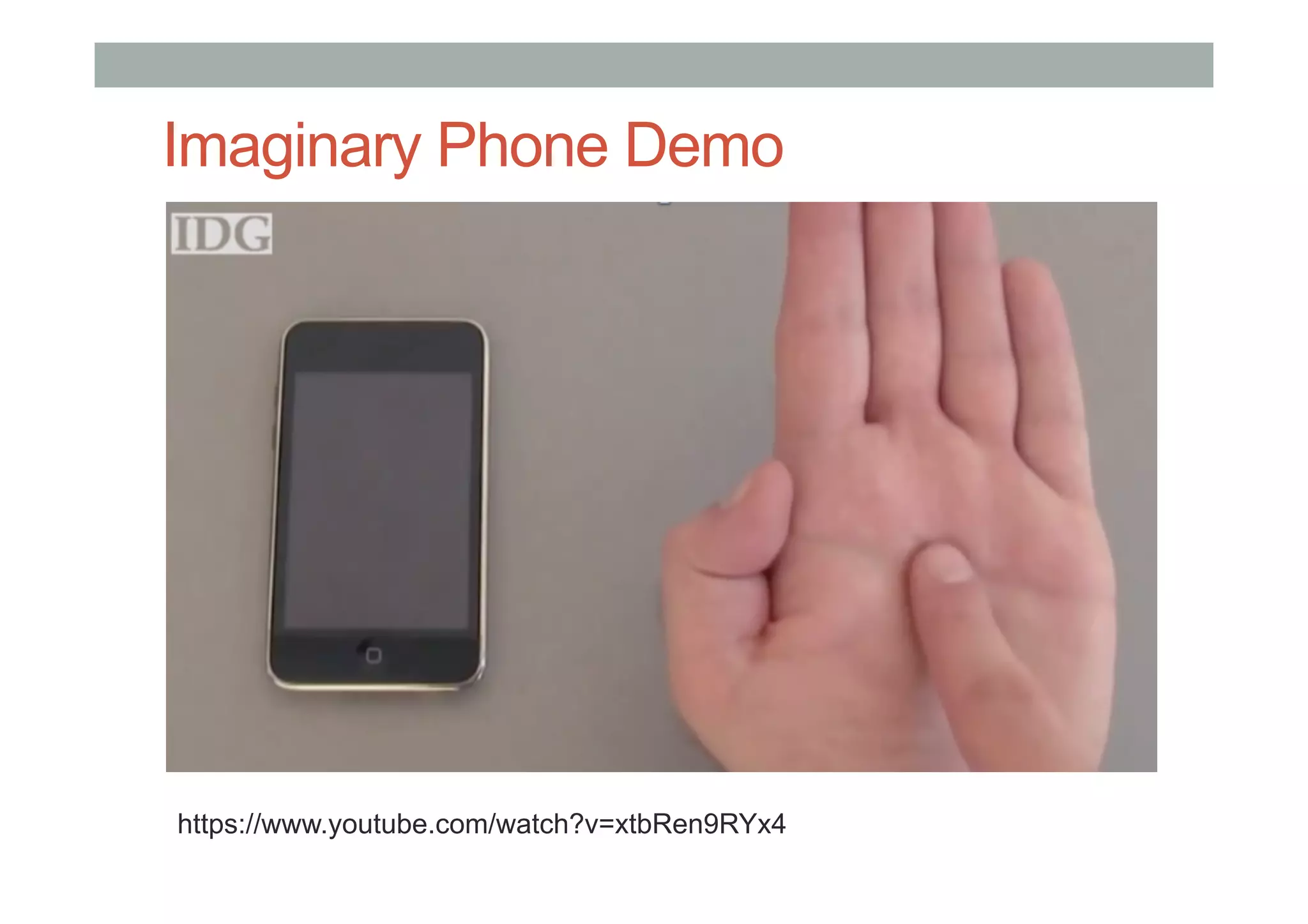
![ImaginaryPhone
• Gustafson, S., Holz, C., & Baudisch, P. [2011]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-technologyfinalnovideo-160818053748/75/COMP-4026-Lecture4-Processing-and-Advanced-Interface-Technology-100-2048.jpg)
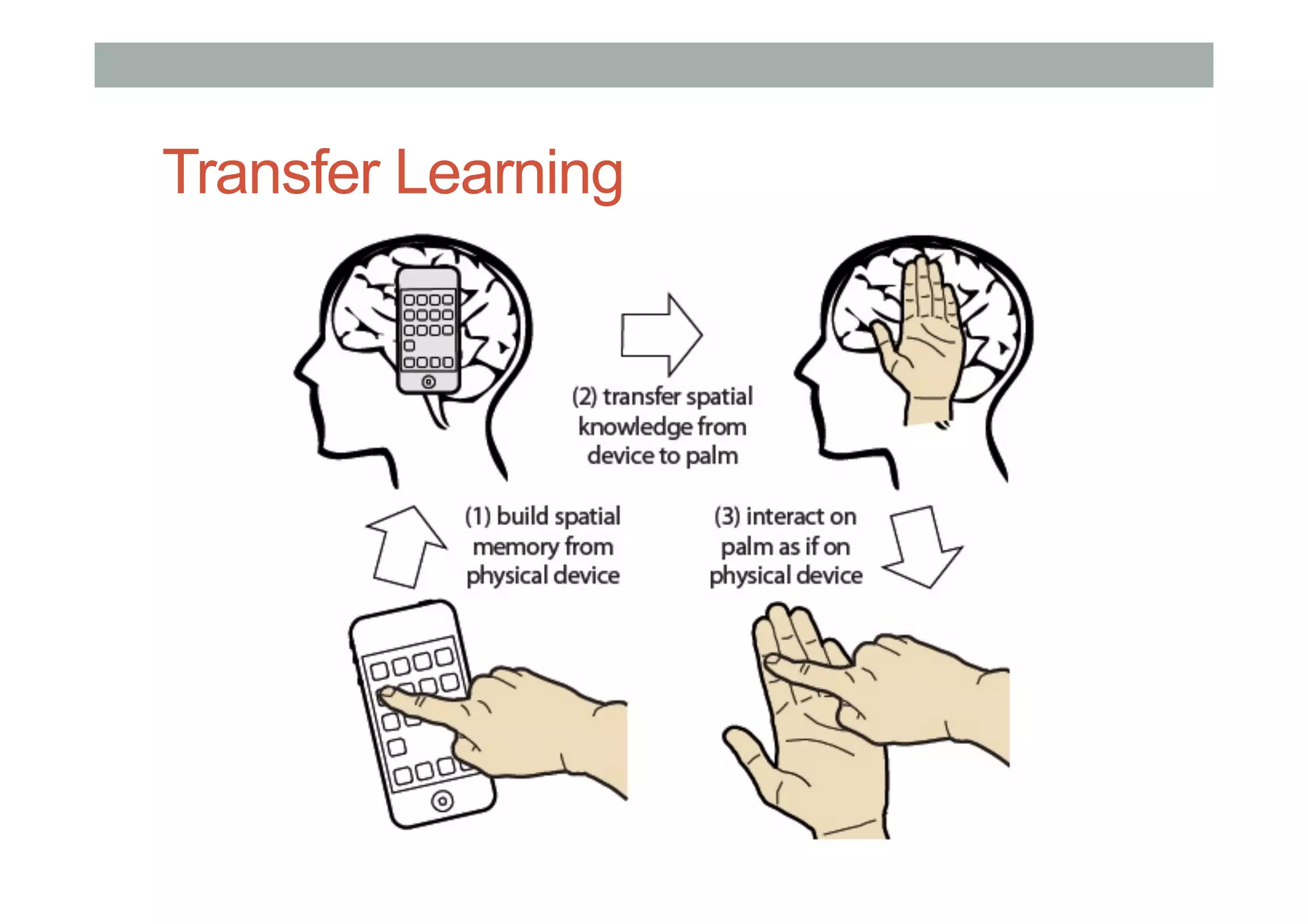
![Invisible Interfaces – Gestures in Space
• Gustafson, S., Bierwirth, D., & Baudisch, P. [2010]
• Using a non-dominant hand stabilized interface.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-technologyfinalnovideo-160818053748/75/COMP-4026-Lecture4-Processing-and-Advanced-Interface-Technology-103-2048.jpg)