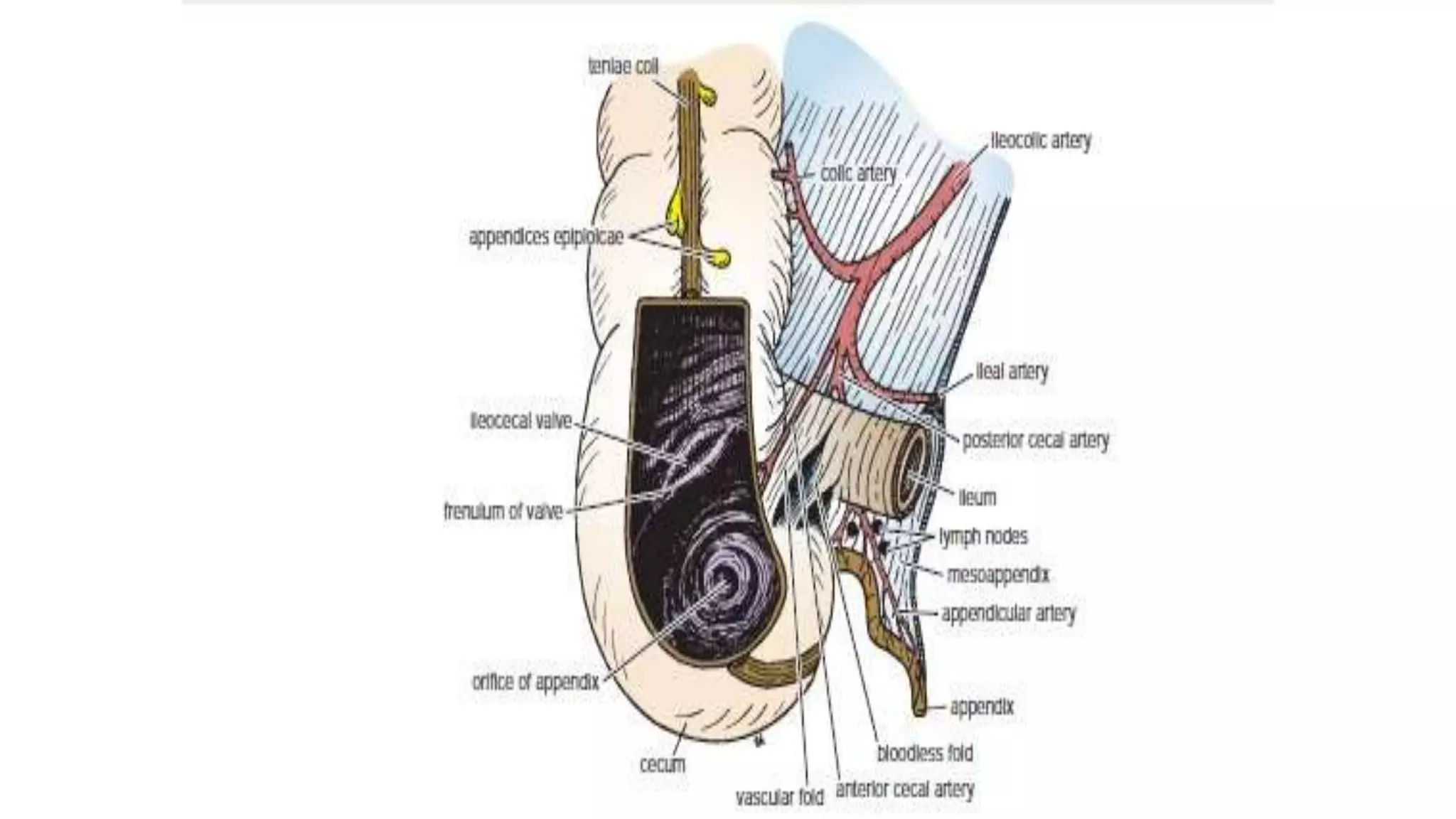
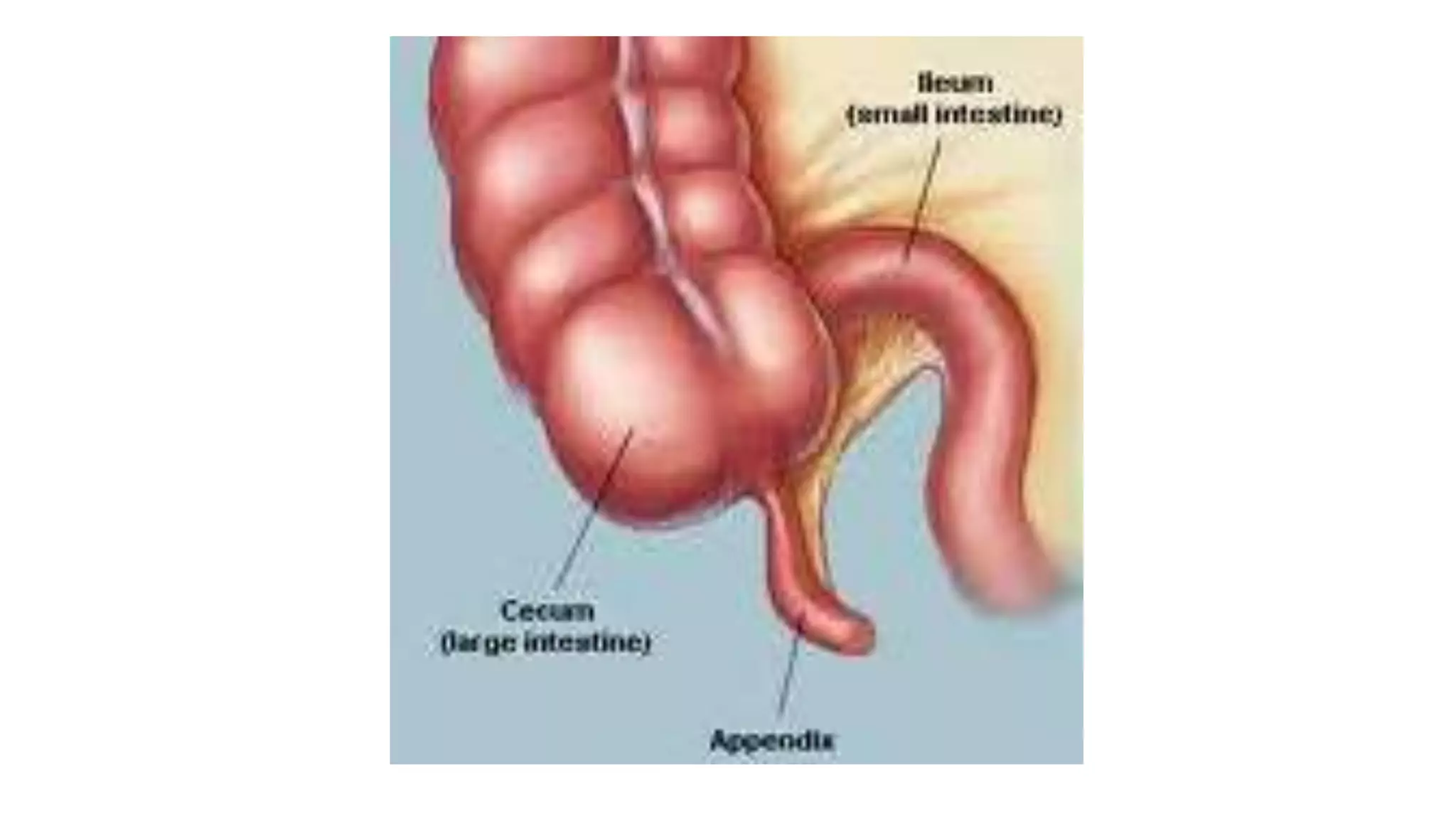
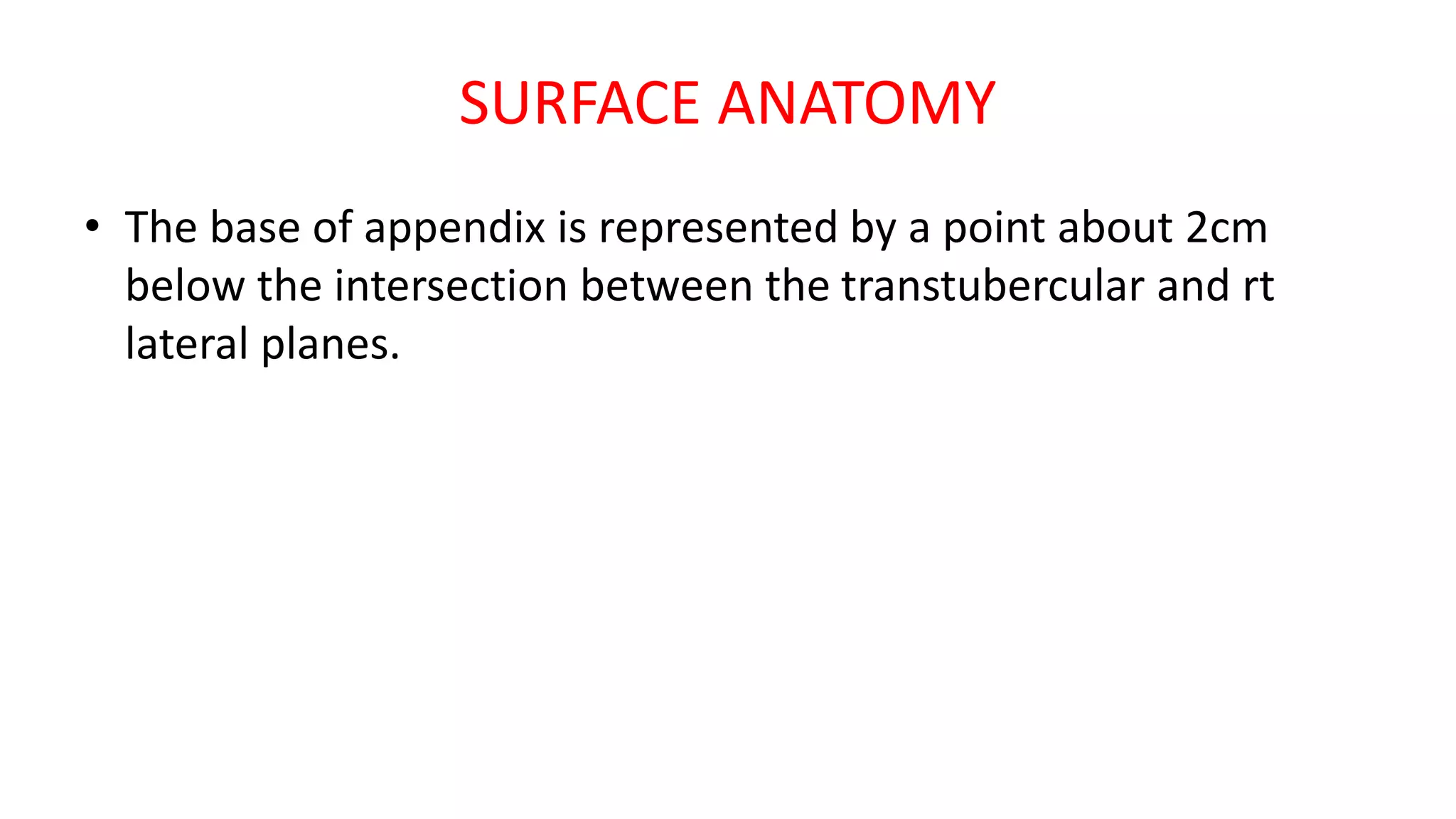
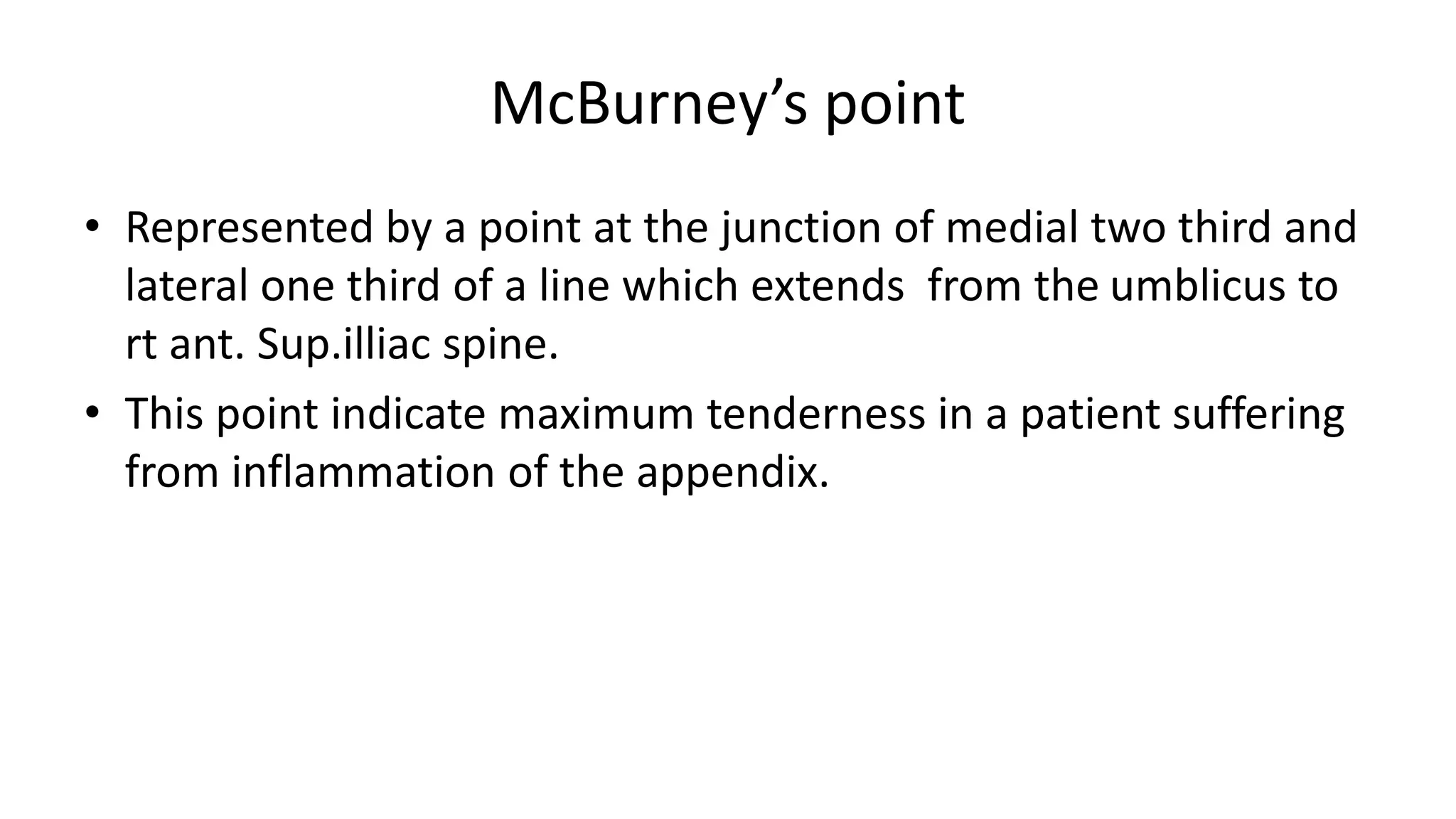
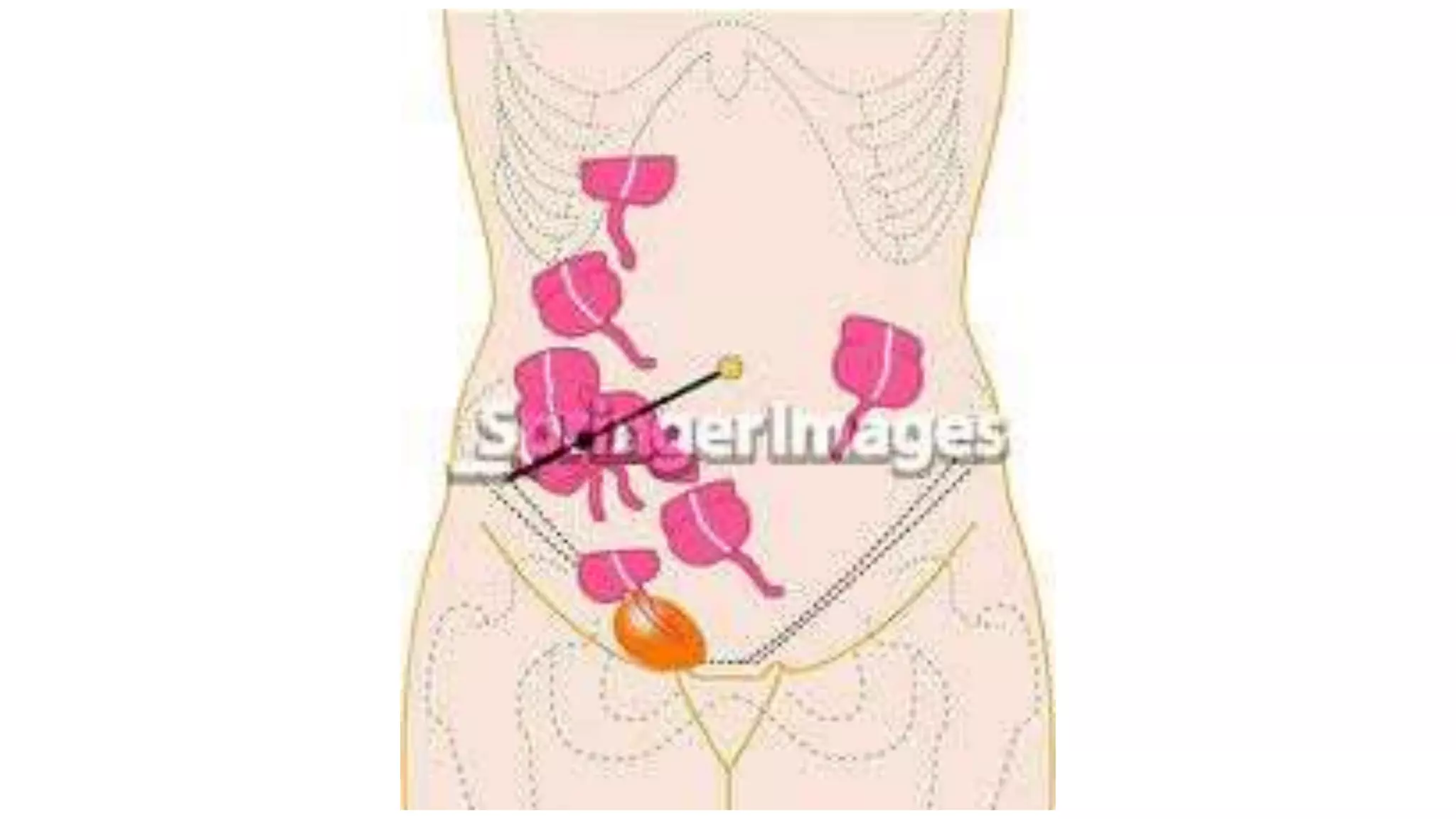
The vermiform appendix is a narrow, tubular structure approximately 9 cm long that protrudes from the posteromedial wall of the cecum. It is attached to the cecum by a mesoappendix and its tip can point in various directions. The appendix has three parts - a base where it attaches to the cecum, a narrow tubular body, and a tip. It is supplied by the appendicular artery and drains lymphatically into superior mesenteric lymph nodes. Inflammation of the appendix is called appendicitis and removal of the inflamed appendix is known as an appendectomy.