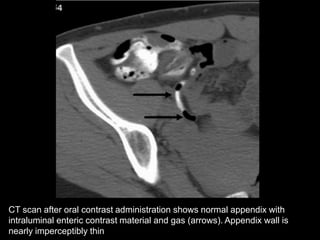
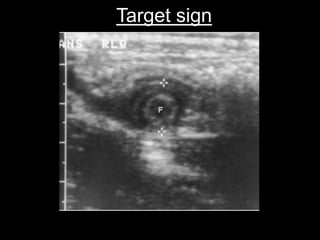
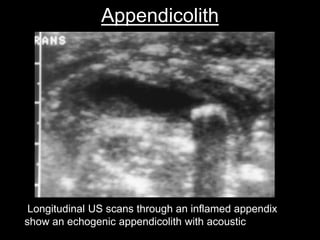
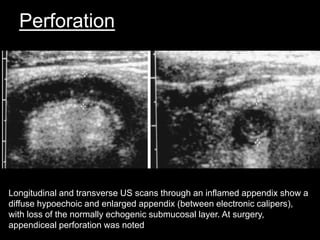
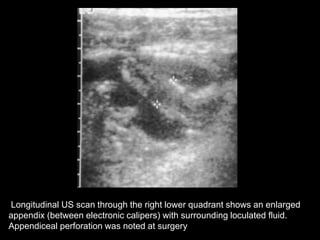
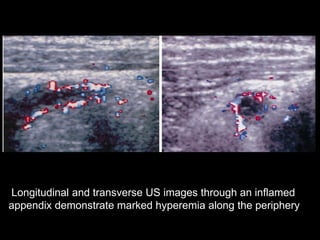
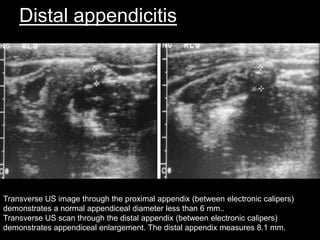
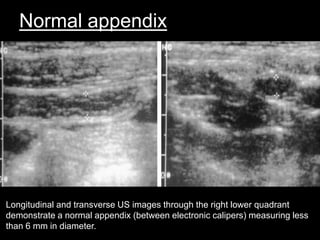
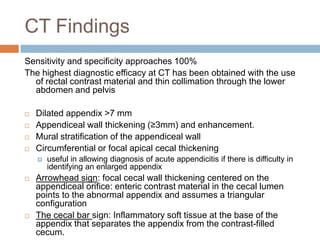
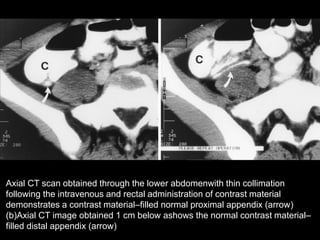
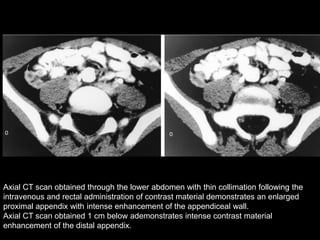
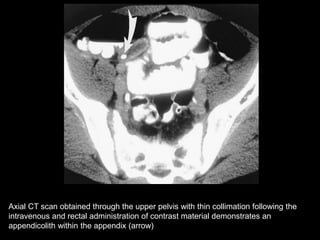
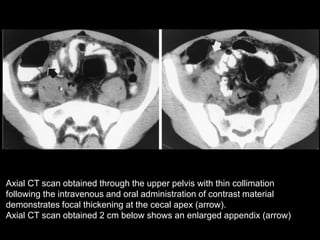
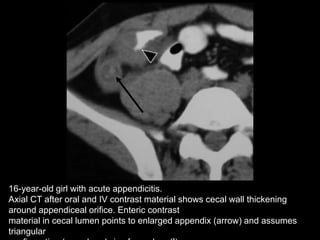
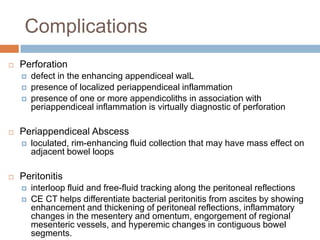
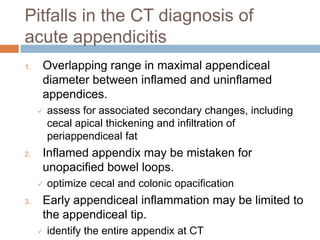
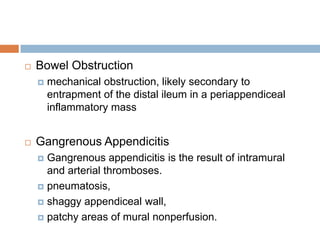
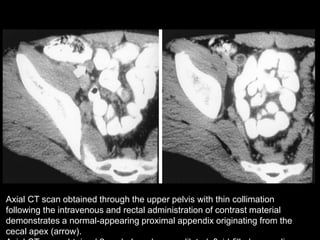
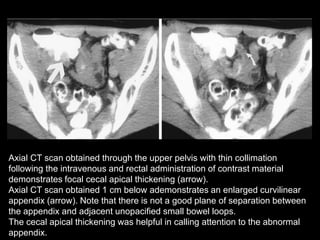
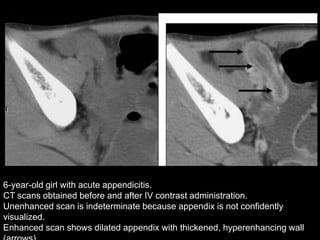
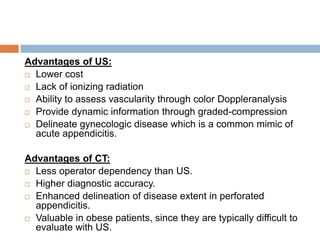
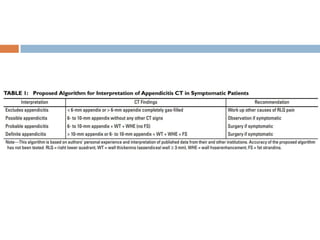
Acute appendicitis occurs when the appendiceal lumen is obstructed, leading to inflammation. CT and ultrasound are effective imaging modalities for diagnosis. On CT, findings suggestive of appendicitis include an appendix over 7mm in diameter, wall thickening, enhancement, and periappendiceal fat stranding. Ultrasound findings include an enlarged, non-compressible appendix with increased wall flow on Doppler. Both modalities can detect complications like perforation seen as fluid collections or abscesses. Accurate imaging allows avoiding negative appendectomies.