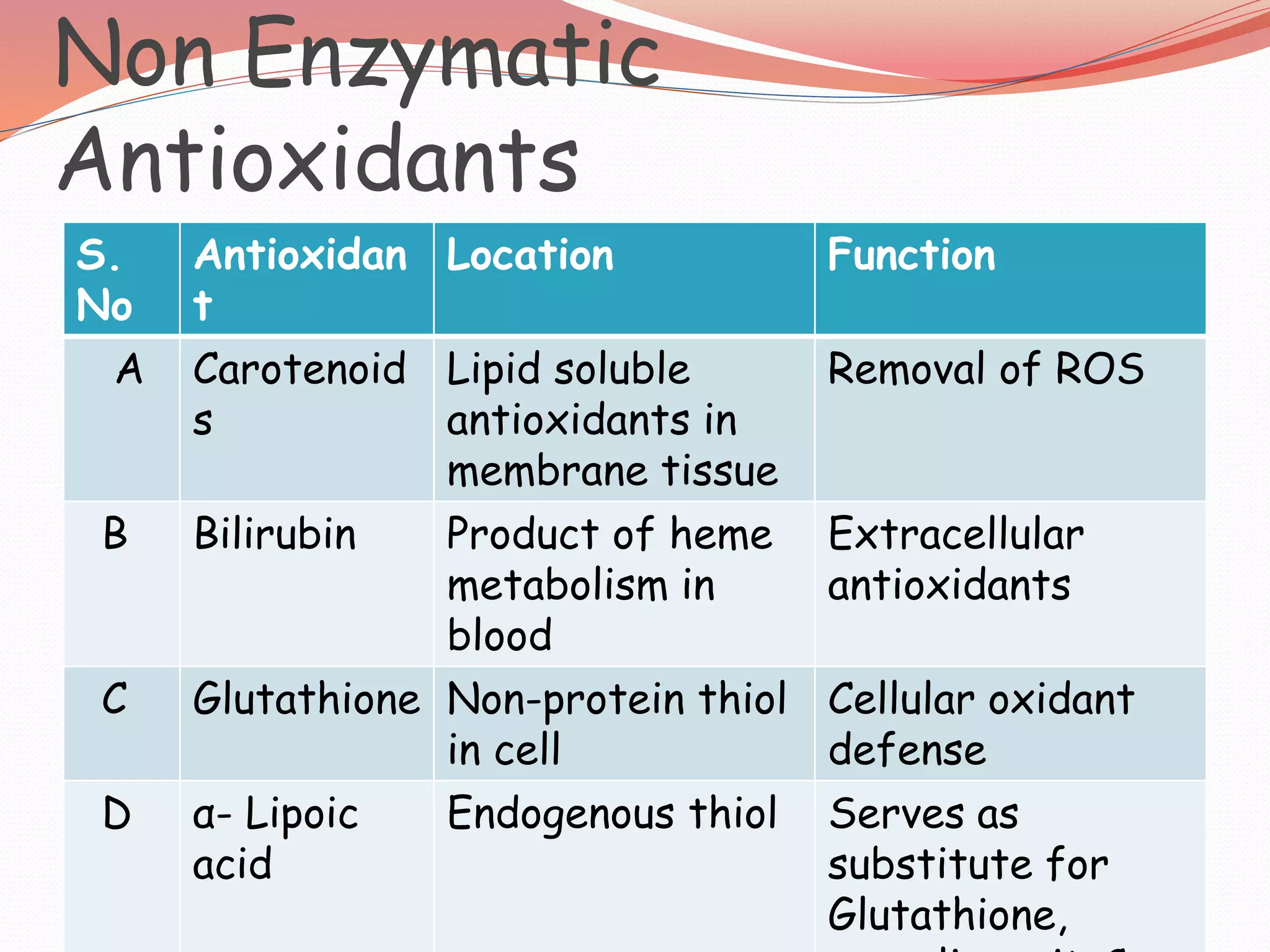
The document discusses antioxidants, which are molecules that inhibit oxidation and prevent cell damage caused by free radicals. It categorizes antioxidants into enzymatic, non-enzymatic, natural, dietary, and based on their defense mechanisms, while emphasizing their various functions in enhancing immune response, preventing diseases, and protecting genetic material. Additionally, it outlines sources of key antioxidants like vitamins C and E, alpha-lipoic acid, and minerals such as selenium, alongside their roles in health and technological applications.