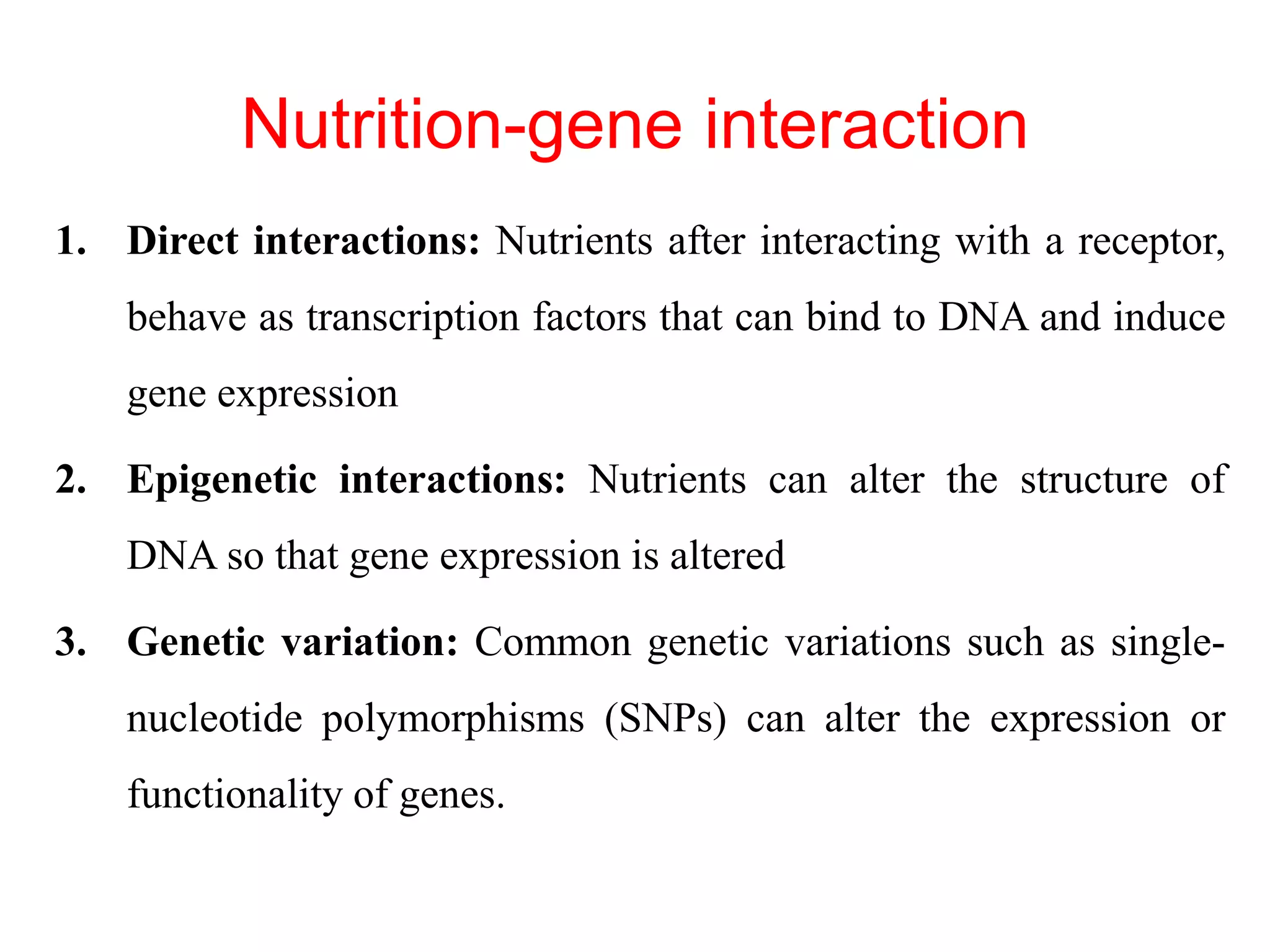
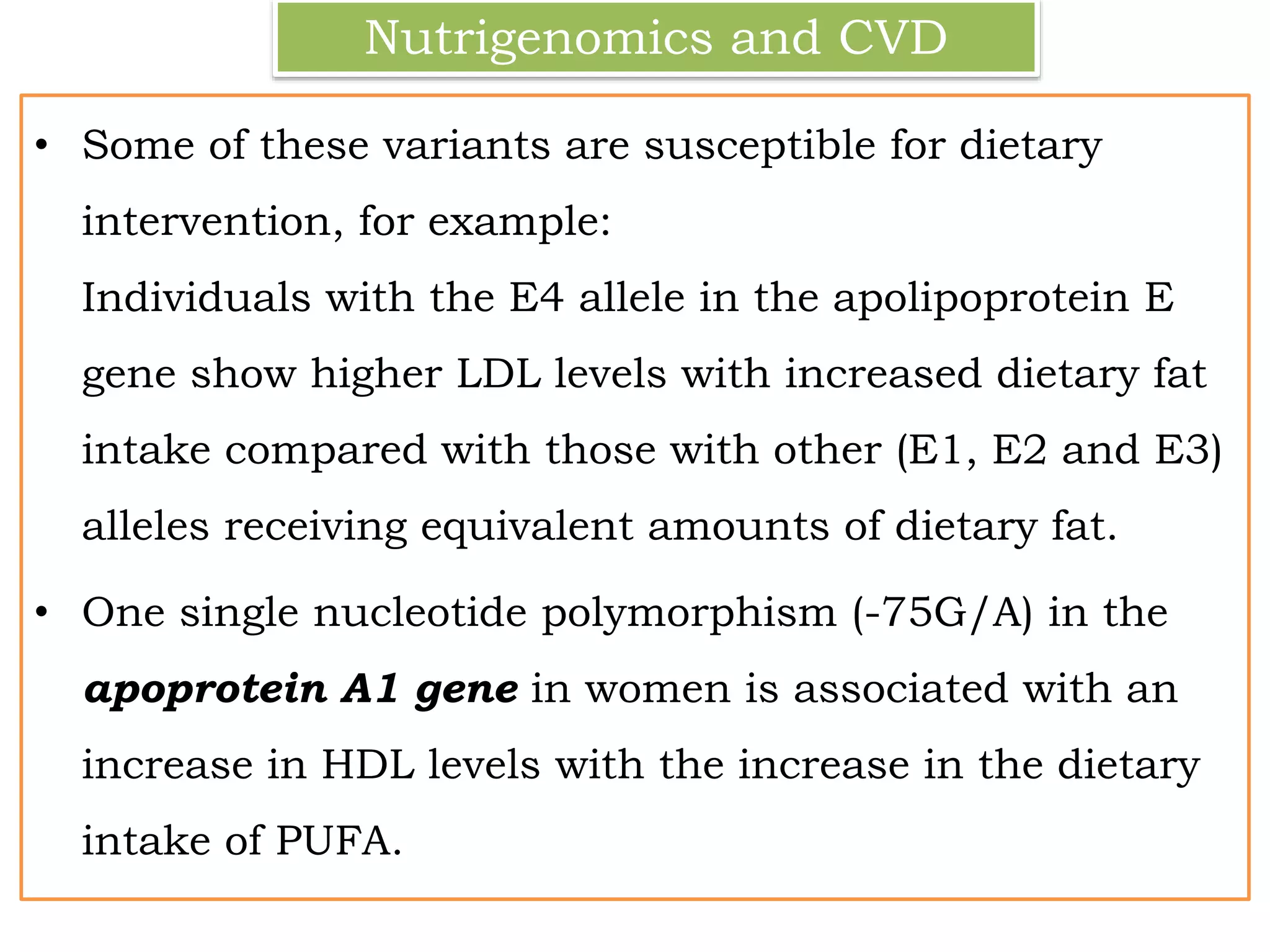
Nutrigenomics is the study of how nutrients and other food components interact with an individual's genome to affect gene expression. It examines how diet influences cellular processes and looks at individual variability in responses to foods based on genetic makeup. The main concepts are that specific diets can modulate health and disease by impacting gene expression, genetic polymorphisms influence disease risk and diet response, and personalized diets may help reduce risk for genetically predisposed individuals. Key applications of nutrigenomics include understanding how diet relates to obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other chronic health conditions by studying gene-diet interactions and genetic variations.