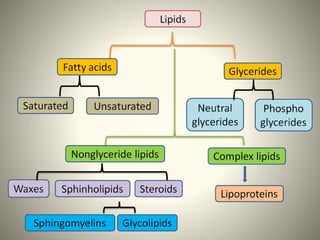
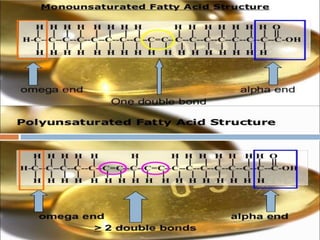
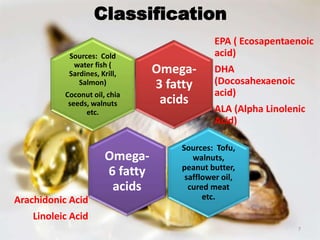
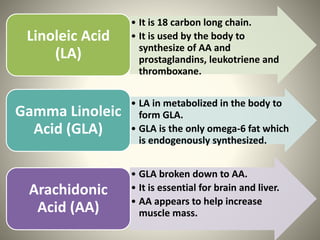
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are beneficial for health, found in sources like nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, and are essential for reducing cholesterol and risk of heart disease. However, they can become harmful when oxidized, leading to inflammation and other health issues. Various studies highlight both the health benefits of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs and the potential risks associated with their oxidation.