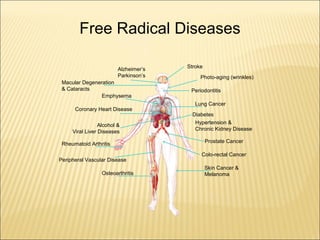
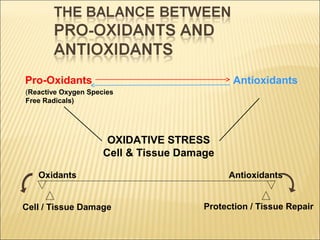
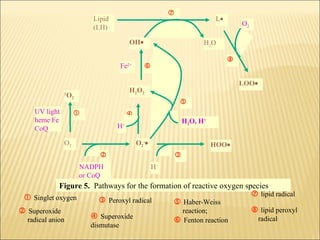
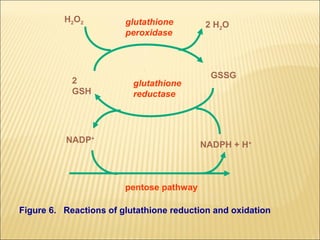
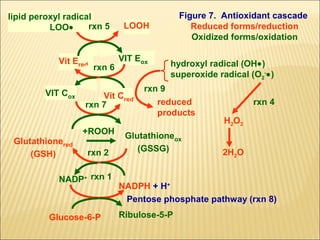
The document discusses how antioxidants like vitamins C and E, carotenoids, and enzymes like superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase protect the body from free radical damage by neutralizing reactive oxygen species. It explains that oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body's antioxidant defenses, leading to cell and tissue damage if left unchecked. Maintaining adequate intake of antioxidants from foods and proper functioning of the body's endogenous antioxidant systems is important for preventing diseases linked to oxidative stress.