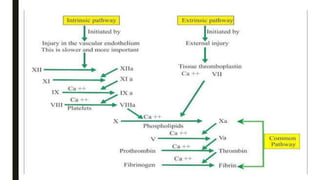
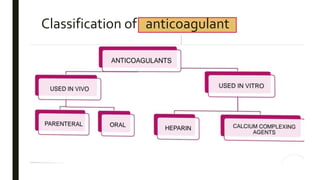
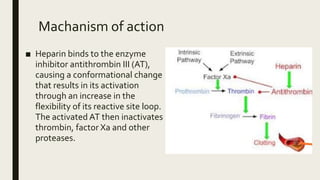
This document discusses coagulants and anticoagulants. It defines coagulants as substances that promote coagulation and are used to treat hemorrhagic states. Anticoagulants delay blood clotting and are given to prevent conditions like strokes and heart attacks. Specific coagulants and anticoagulants discussed include heparin, warfarin, vitamin K, and factors I-XIII involved in coagulation. The mechanisms, uses, and side effects of heparin and warfarin are summarized.