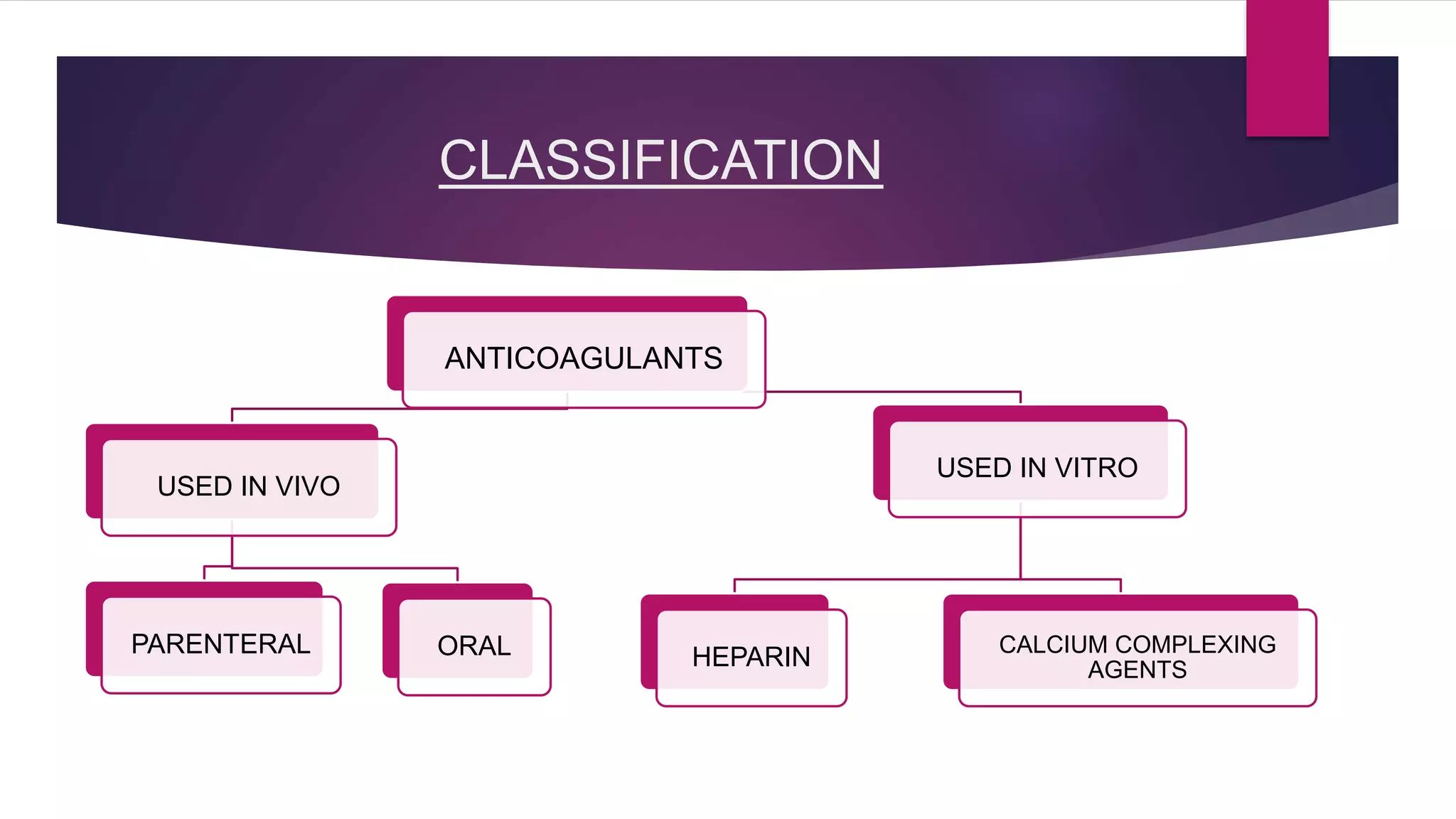
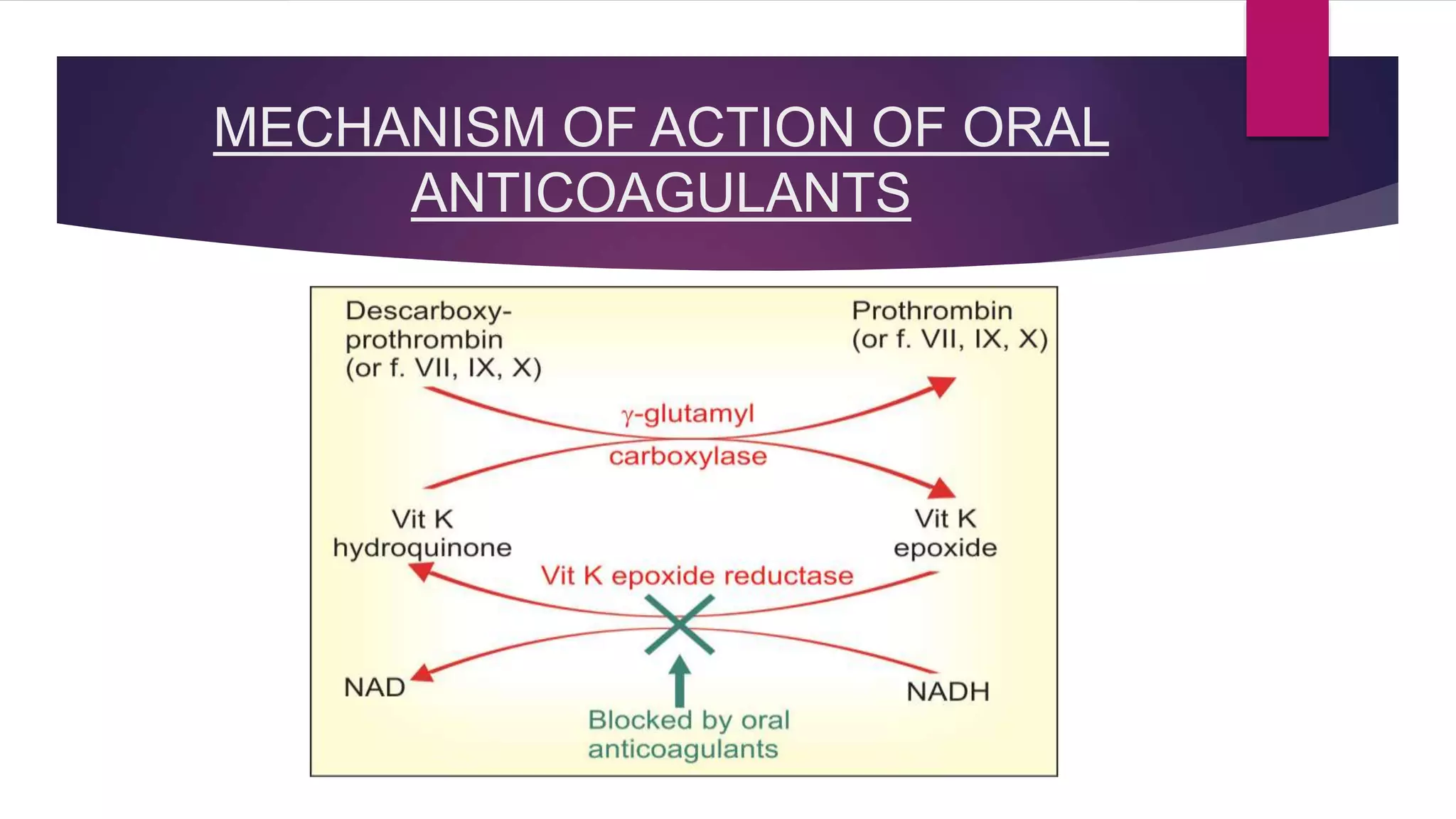
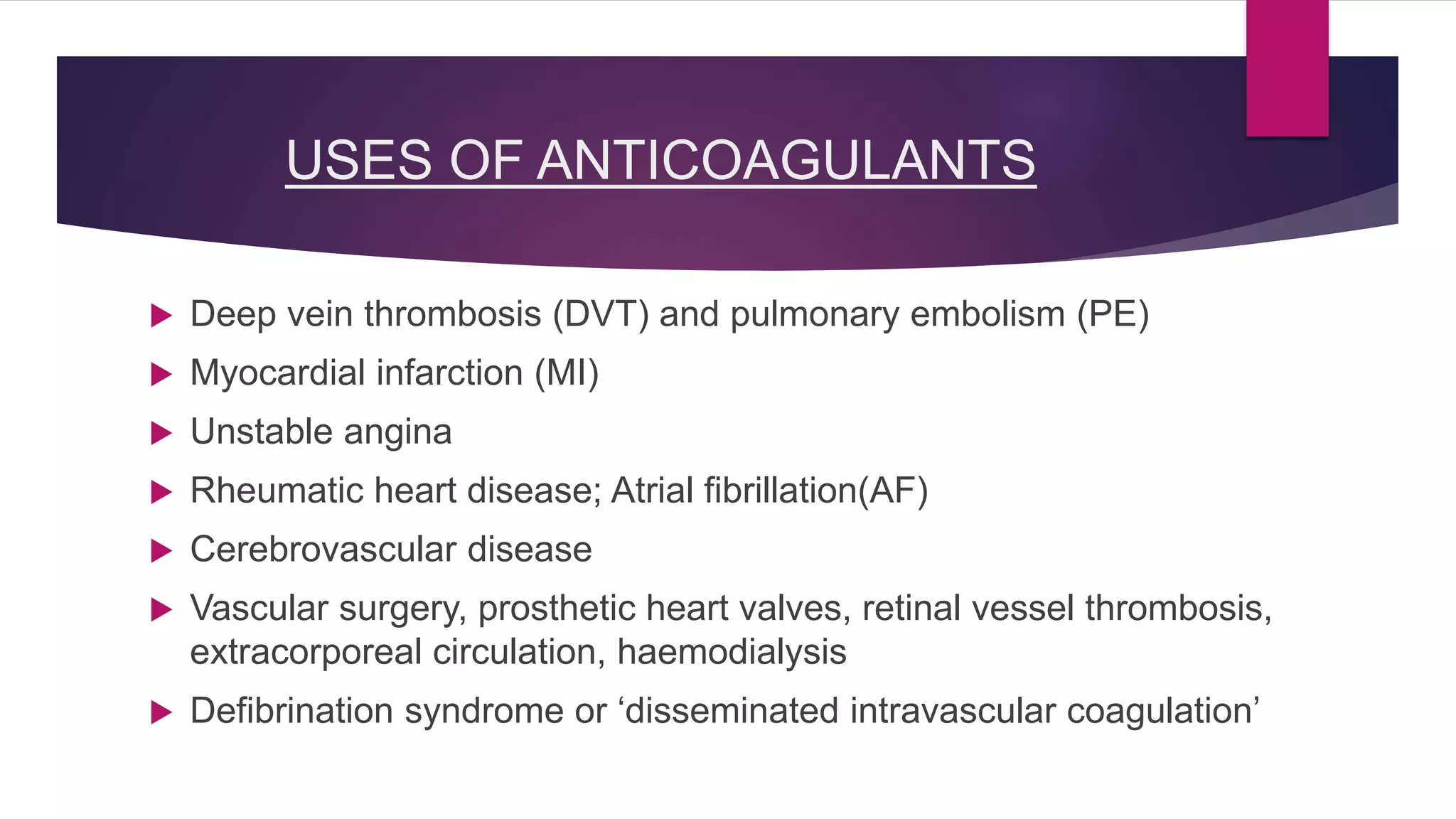
Anticoagulants help prevent blood clotting. They are classified as those used in vivo (parenteral or oral) and those used in vitro. Parenteral anticoagulants include indirect and direct thrombin inhibitors like heparin and direct factor Xa inhibitors like fondaparinux. Oral anticoagulants include coumarin derivatives like warfarin and newer direct thrombin and factor Xa inhibitors. Anticoagulants are used to treat conditions involving blood clots like deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and atrial fibrillation. Newer anticoagulants have advantages over warfarin like fewer drug and food interactions and less monitoring requirements.