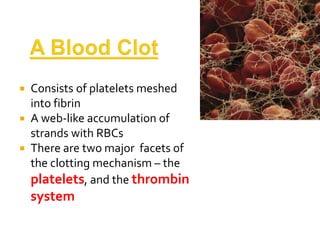
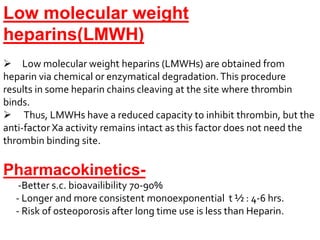
Platelets and thrombin systems work together to form blood clots. Platelets become activated when bleeding occurs and begin sticking together. Activated clotting proteins engage in chemical reactions producing fibrin strands that stick to vessel walls, trapping red blood cells and forming clots. Anticoagulants prevent clotting by inhibiting factors in the coagulation cascade like thrombin and factor Xa. Heparin is a commonly used anticoagulant that activates antithrombin to inhibit coagulation factors. Newer direct thrombin and factor Xa inhibitors offer more consistent anticoagulation than warfarin with less drug interactions and monitoring requirements.