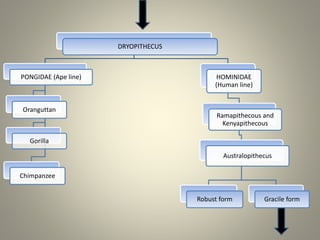
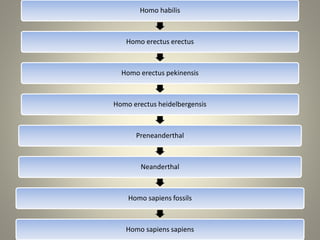
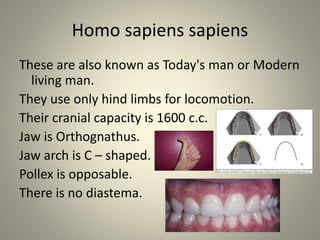
Human evolution is a gradual process that has occurred over a long period of time. Key stages included Dryopithecus, which is considered the common ancestor of apes and humans around 25 million years ago. Ramapithecus and Kenyapithecus, dated to between 12-5 million years ago, displayed traits that were ancestral to humans. Australopithecus, the first upright walking species around 4 million years ago, had a brain capacity of around 500cc. Homo habilis began making tools around 2.4 million years ago. Later species such as Homo erectus had larger brains and used fire. Homo sapiens emerged around 200,000 years ago, with modern humans