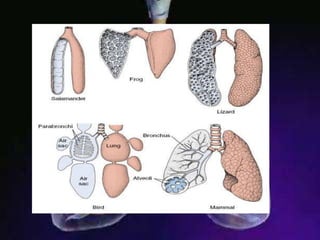
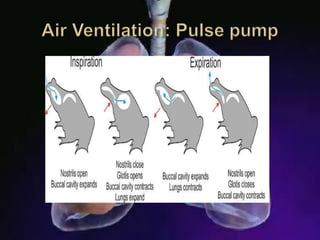
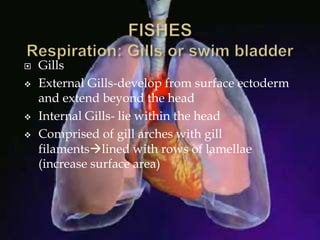
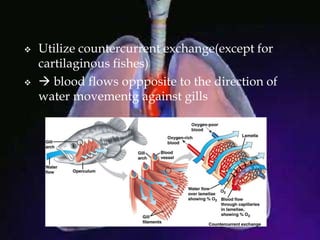
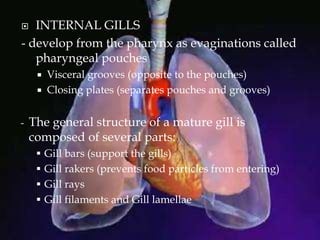
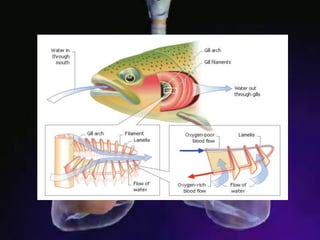
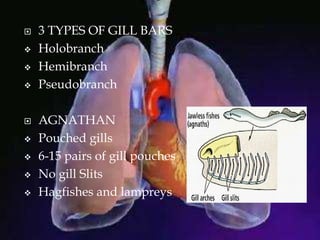
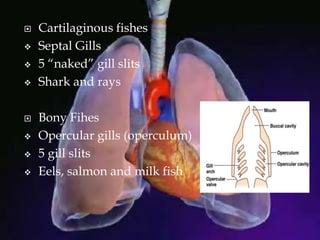
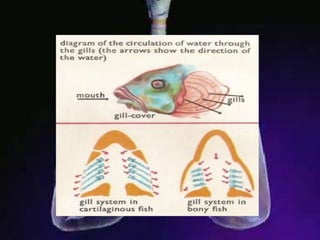
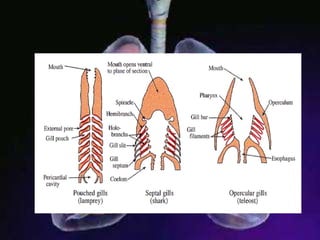
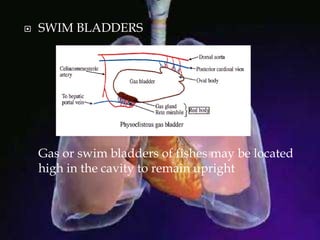
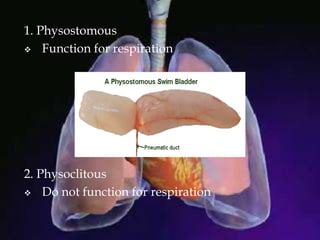
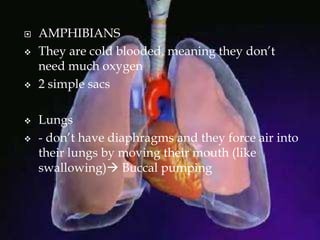
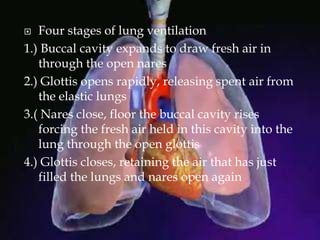
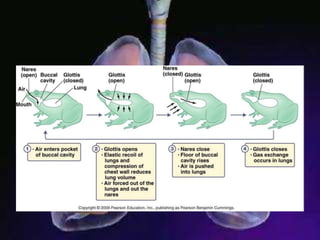
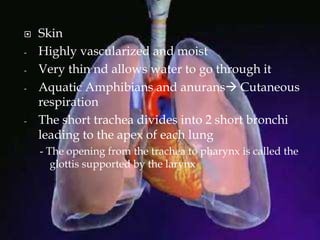
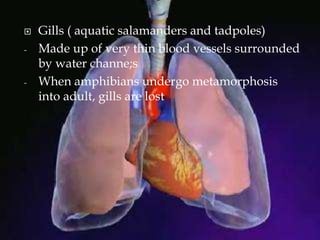
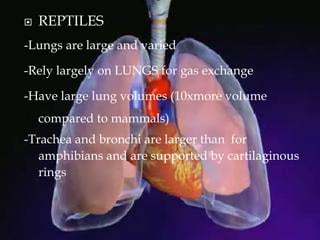
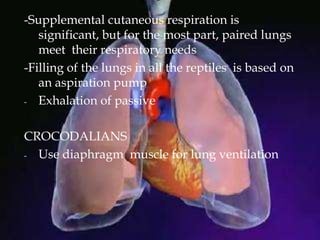
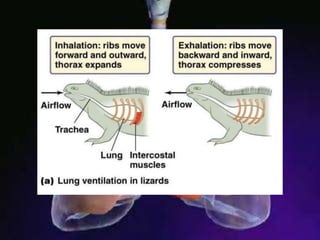
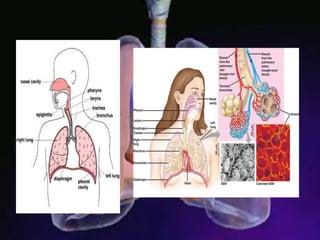
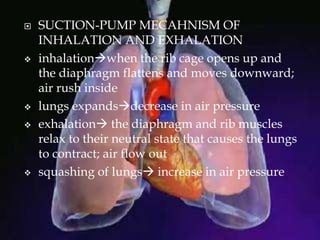
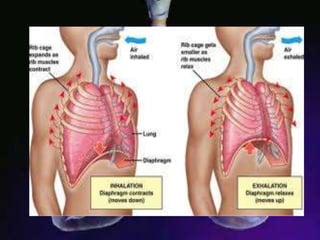
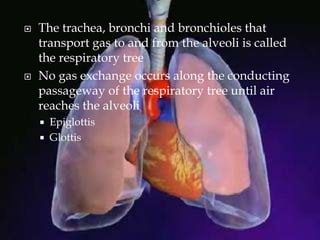
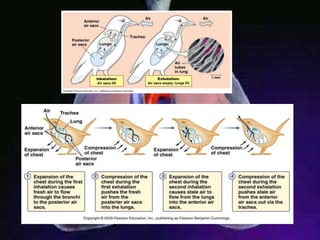
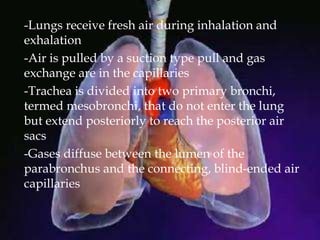
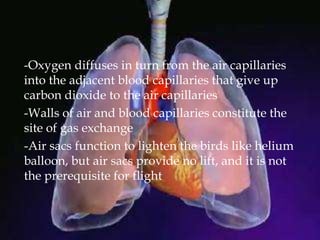
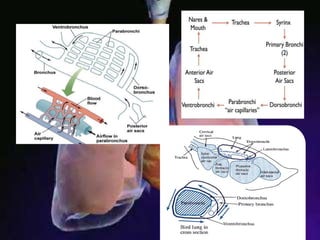
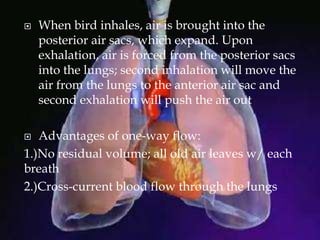
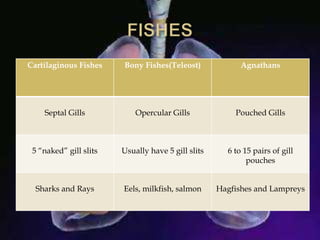
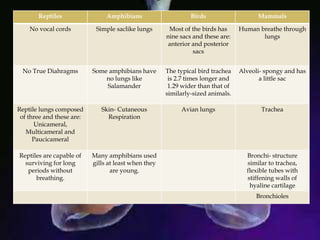
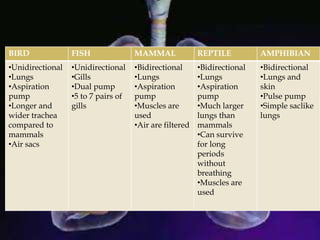
The respiratory system allows organisms to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide through the process of respiration. Respiration includes ventilation, external respiration where gases are exchanged with the environment, and internal respiration where gases are exchanged at the tissue level. The main respiratory organs are lungs, gills, and in some cases skin or gas bladders. Lungs are found in air-breathing vertebrates like mammals and birds, using an aspiration pump for ventilation. Gills are found in fish and some aquatic amphibians and function via various water pumping mechanisms. Skin respiration also occurs in some amphibians.