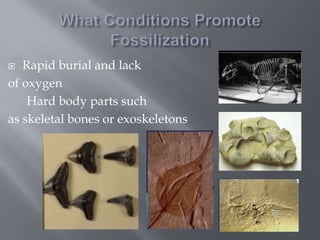
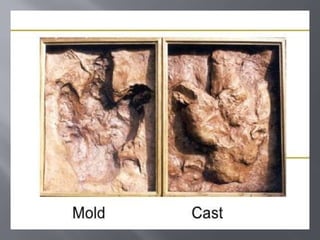
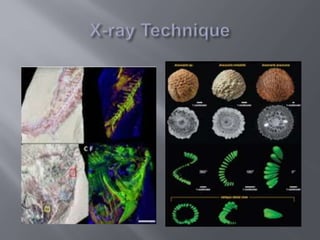
This document discusses several techniques used to prepare and analyze fossils, including thin sectioning, peeling, transferring, maceration, x-ray imaging, and microtoming. It explains that thin sectioning involves slicing rock or other samples very thin for microscopic study. Peeling and transferring techniques are used to stabilize and prepare fossil specimens for analysis. Maceration uses acids to separate fossilized plant parts. X-rays and microtoming can also be used to image internal fossil structures at the microscopic level. The document also briefly discusses how fossils provide evidence of evolution by showing changes in life over time.