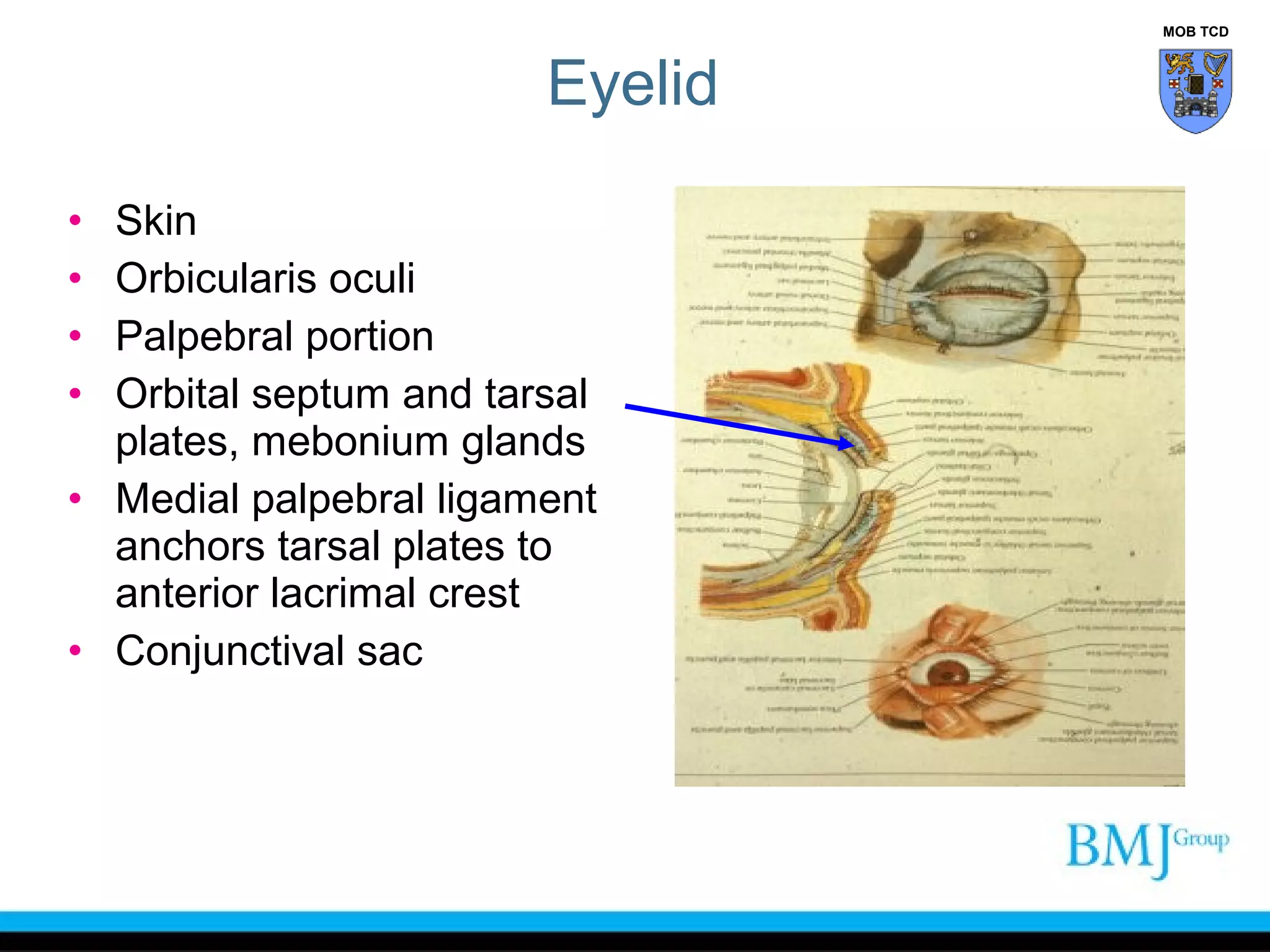
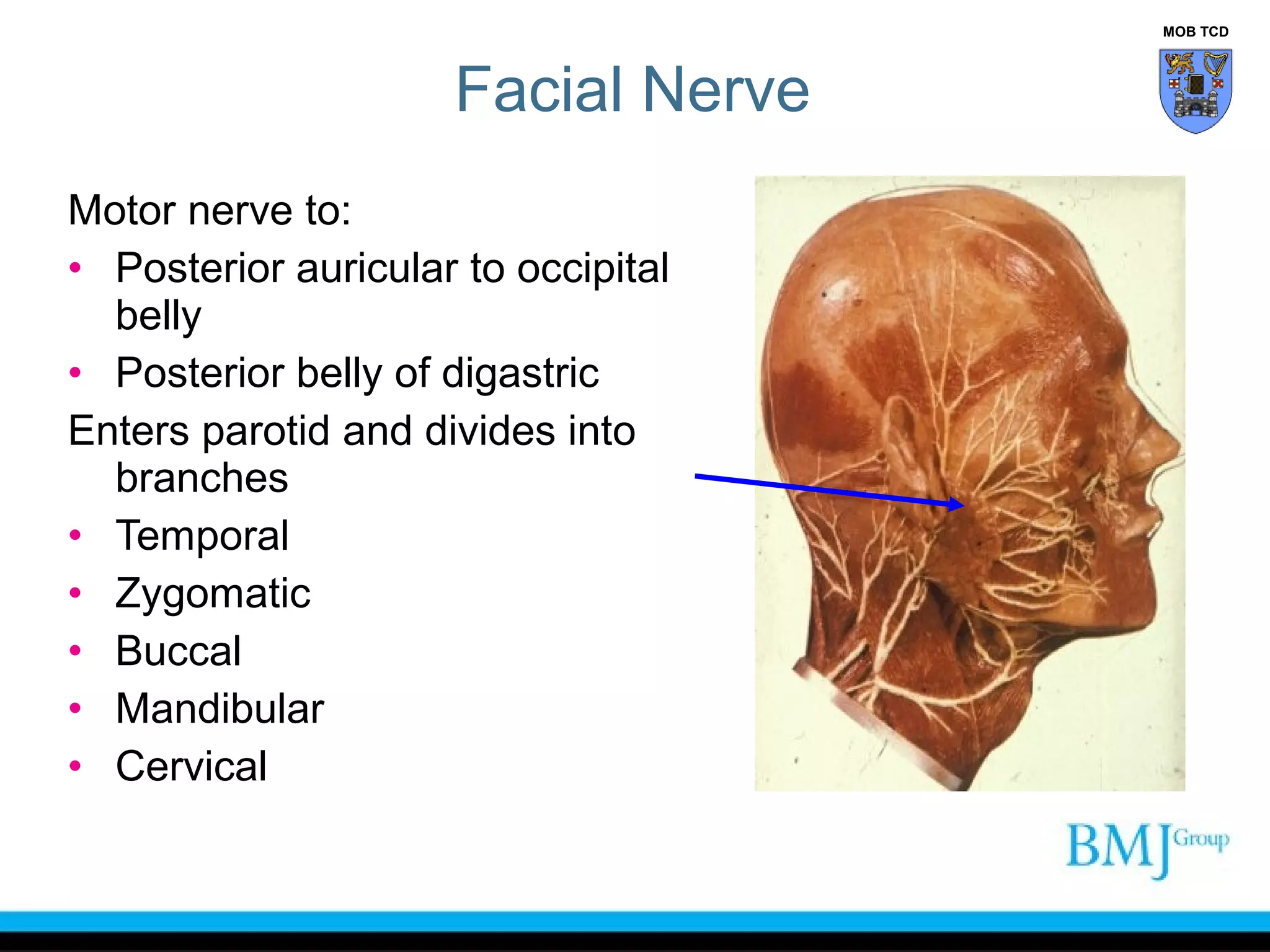
The document outlines the anatomy of the face, detailing the sensory and motor nerve supplies, primarily the trigeminal and facial nerves. It describes various structures including muscles of facial expression, blood supply, and lymphatic drainage, as well as conditions such as Bell's palsy and Horner's syndrome. Additionally, it provides insights into the anatomy of the eyelid and scalp, and highlights the implications of injuries and surgical approaches to the face.