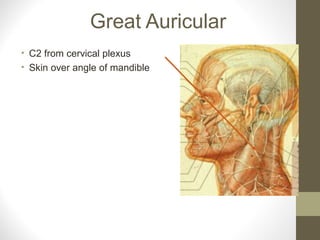
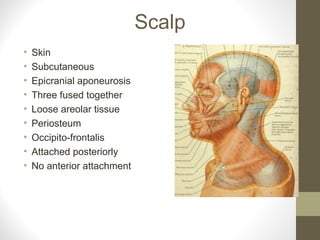
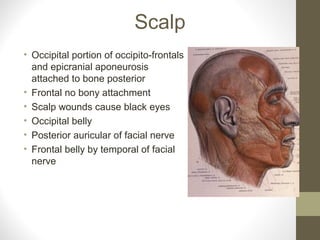
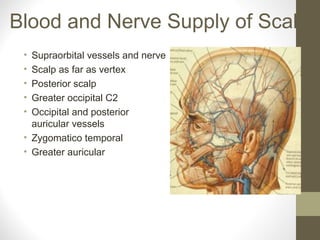
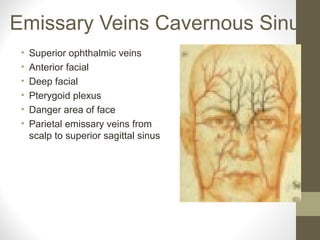
The document provides an anatomy overview of the face, including:
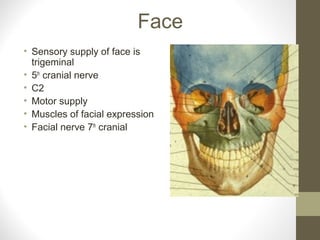
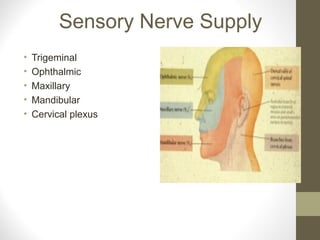
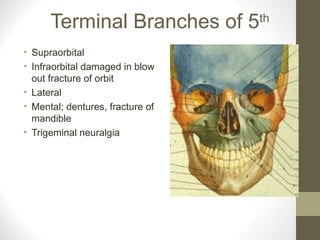
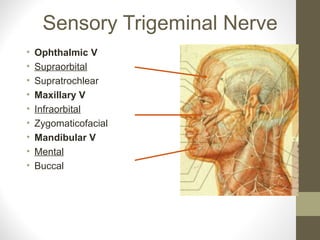
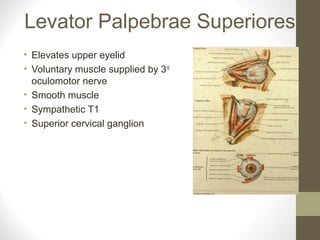
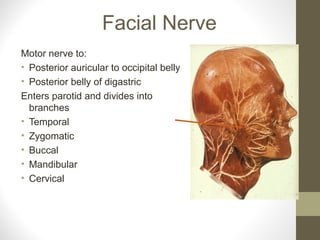
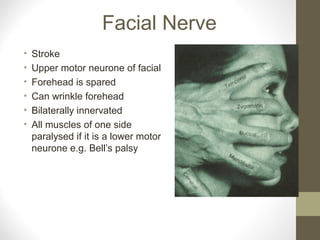
- The sensory supply is the trigeminal nerve (5th cranial nerve) and the motor supply includes the facial nerve (7th cranial nerve) for muscles of facial expression.
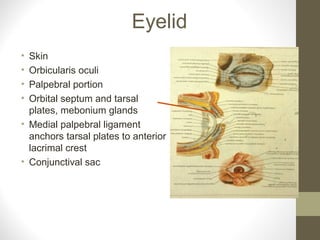
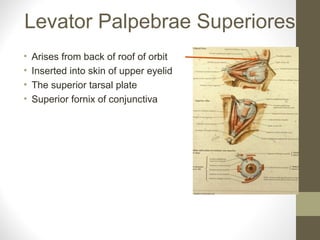
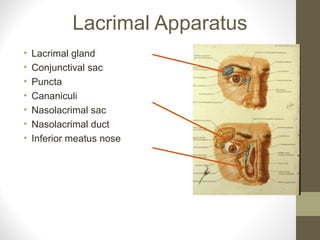
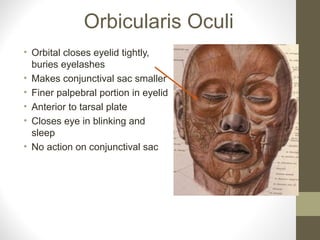
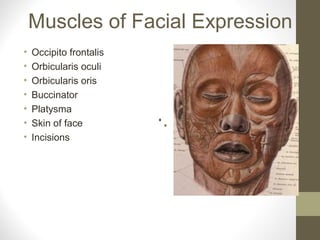
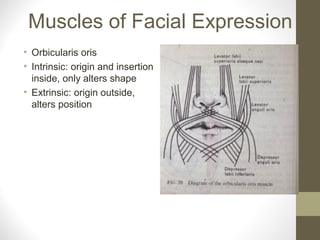
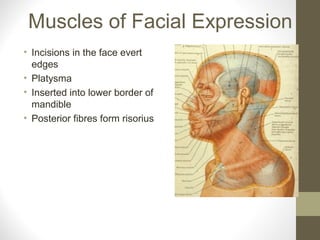
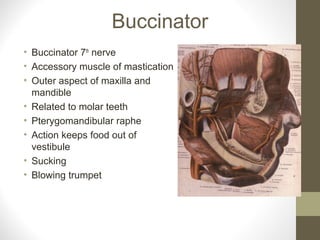
- Key structures discussed include the eyelid, lacrimal apparatus, muscles of facial expression like the orbicularis oculi and orbicularis oris, and the buccinator muscle.
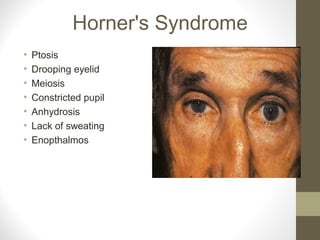
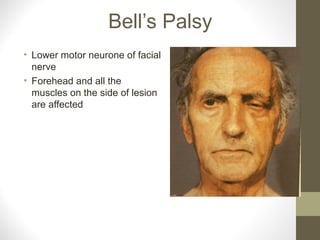
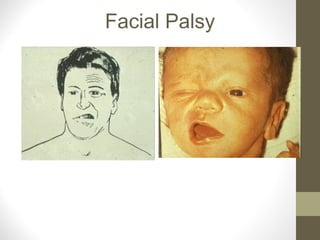
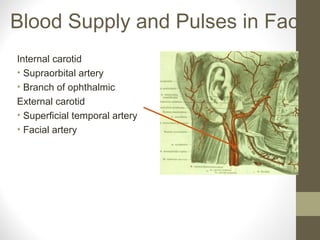
- Conditions like Bell's palsy and Horner's syndrome are mentioned. Blood supply and venous drainage routes to structures like the cavernous sinus are also summarized.