Anatomy of Human Heart
- 1. Anatomy of Human Heart BY ANJALI SINGH
- 2. Definition of Heart The upper part of the chest contains the muscular organ known as the heart. It circulates blood throughout the body by pumping blood. The cardiovascular system is made up of the blood vessels and the blood itself, in addition to the heart.
- 3. INTRODUCTION TO THE HUMAN HEART Among the most crucial organs necessary for maintaining life is the human heart. It has four chambers and is a muscular organ. The heart is roughly the size of a clenched hand. One of the strongest and most active muscles in an individual's body, the heart continues to beat throughout a person's lifetime. The majority of animals, excluding humans, have hearts that circulate blood throughout their bodies. Even invertebrates like grasshoppers have a pumping organ that resembles a heart, though it does not work in the same manner that the heart of humans does. The human heart is situated in the thoracic cavity, just to the left of the sternum (breastbone), between the lungs. It comes from the germ layer of the mesoderm of the embryo.
- 4. FUNCTION OF HUMAN HEART The heart of a human being performs an essential job in the body as a strong pump that pumps blood throughout the entire circulatory system. All of the body's cells depend on it to remove wastes like carbon dioxide while also providing oxygen, nutrition, and hormones. The heart's four primary jobs are as follows: • Blood Circulation: Through systemic circulation, the heart distributes oxygen-rich blood from the respiratory system to the rest of the body. This makes sure that every tissue and organ gets the oxygen and nutrients they need to function properly. • Pulmonary Circulation: The heart helps the lungs circulate blood that has been deoxygenated from the body and returns oxygenated blood to the heart through the pulmonary system. As a result, the blood supply is replenished in the lungs, where carbon dioxide can be exchanged for oxygen. • Contraction and Relaxation: The heart regulates the blood's flow with a series of rhythmic contractions and relaxations. In order to pump blood out of the heart chambers, the heart contracts (systole), then relaxes (diastole), allowing blood to return to the chambers. • Blood Pressure and Regulation: Controlling blood pressure is a crucial function of the heart. Blood is forced into the blood vessels when the heart contracts, creating pressure. The proper blood pressure levels are maintained by the coordinated relaxation and contraction of the heart's chambers.
- 5. • Electrical Conduction: The electrical conduction system inside the heart regulates the heartbeat. Electrical impulses are started by the sinoatrial (SA) node, which causes the cardiovascular system's muscles to contract in unison. By ensuring that both ventricles and atria contract in the appropriate order, effective blood flow is made possible. • Thermoregulation: The heart plays a role in maintaining body temperature. During physical activity or exposure to cold, the heart rate can increase to pump more blood and distribute heat throughout the body. • Removal of waste products: As the heart circulates blood, it also helps in removing waste products, such as carbon dioxide and metabolic byproducts, which are then eliminated from the body through exhalation, urine, and other waste elimination processes.
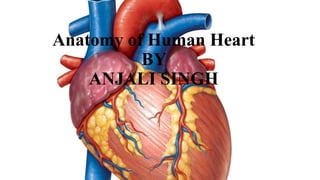
- 6. ANATOMY OF HEART The heart's structure and internal organization are described in terms of its anatomy. Located in the chest cavity and slightly skewed to the left, the human heart is a muscular organ. It weighs between 250 and 350 grammes and has a size similar to that of a clinched fist. The heart has four chambers, each of which plays a particular role in blood flow. The top chambers are known as atria (plural: atrium), and the lower chambers are known as ventricles. These chambers are separated into two pairs. • Atria: There are four chambers in the heart, and each one contributes differently to blood flow. The upper chambers are called atria, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. There are two pairs of these chambers.
- 7. • Ventricles: The right and left ventricles and the other two ventricles make up the heart. The heart's ventricles are in charge of pumping blood away. Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery, which connects to the lungs. The largest artery in the body, known as the aorta, is used by the left ventricle to pump blood and oxygen to the rest of the body. There are septa, which are muscular walls that divide the heart's chambers. In contrast to the interventricular septum, which divides the ventricles, the interatrial septum separates the atria. The heart's valves guarantee one-way blood flow. The atrioventricular (AV) valves divide the ventricles and atria. In contrast to the mitral (bicuspid) valve, which is situated between the left atrium and left ventricle, the tricuspid valve is found between the right atrium and right ventricle. The pulmonary valve and aortic valve, two semilunar valves, protect the ventricles' entry points into the arteries. The pulmonary veins and superior and inferior vena cava, which transport oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium and deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium, respectively, are connected to the heart. The pericardium, the protective double-layered membrane that surrounds the heart and aids in stabilising it and lubricating its motions, helps maintain the heart in place. Understanding the heart's structure is essential to understanding how the body circulates blood and how the heart works.
- 8. BLOOD CIRCULATION • The circulatory system is a complicated network of blood vessels that circulates blood throughout the body. Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart and reaches the right atrium via the superior and inferior vena cava. It then enters the right ventricle via the tricuspid valve. When the right ventricle contracts, deoxygenated blood is forced via the pulmonary valve and into the pulmonary artery, where it is sent to the lungs. • The lungs oxygenate the blood by absorbing oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide. The pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the heart and enter the left atrium. After going through the mitral valve, the left ventricle is reached. The aorta, the body's biggest artery, receives oxygenated blood as a result of the left ventricle's contractions. The aorta's split into smaller arteries allows oxygenated blood to reach all organs and tissues.
- 9. BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE HEART • Regardless of its role in blood circulation, the heart requires a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients to function properly. The coronary arteries play an important part in this. The left coronary artery and its branches supply the left side of the heart, whereas the right coronary artery and its branches supply the right side of the heart. • Coronary artery disease develops when the coronary arteries constrict or become occluded as a result of plaque buildup. This condition restricts blood supply to the heart muscle, resulting in symptoms such as angina (chest discomfort) or, in extreme cases, a heart attack (myocardial infarction). Timely intervention, such as medication, lifestyle changes, or surgical procedures such as angioplasty or coronary bypass surgery, can help restore blood flow while avoiding further complications.
- 10. COMMON DISORDERS OF HEART The human heart is prone to a variety of illnesses that can impair its structure and function. Among the most frequent heart conditions are: • Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): This condition develops when the coronary arteries constrict or obstruct, resulting in less blood reaching the heart muscle. • Heart Failure: Chronic illness known as heart failure affects the heart's ability to pump blood effectively. Numerous underlying conditions, such as coronary artery disease, excessive blood pressure, or past heart attacks, may be the cause. • Arrythmias: Heart rhythm irregularities are known as arrhythmias. A fast heartbeat (tachycardia), a slow heartbeat (bradycardia), or an irregular heartbeat (atrial fibrillation) are some of their symptoms. • Valvular Heart Disease: Valvular heart disease is caused by defective or damaged heart valves, which impair the heart's capacity to regulate blood flow adequately. • Congenital Heart Defects: These are structural heart defects that are present at birth. They can range from simple flaws that have no effect on health to severe disorders that necessitate surgical intervention.