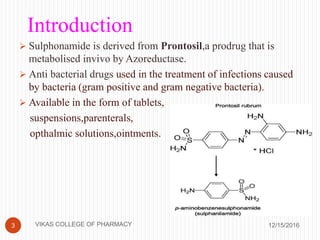
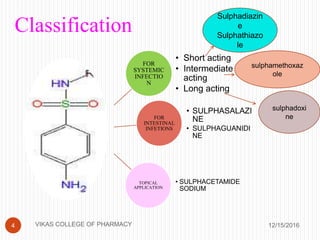
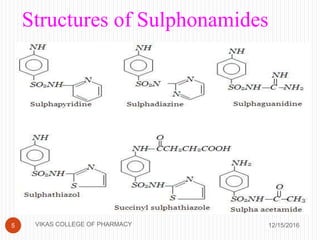
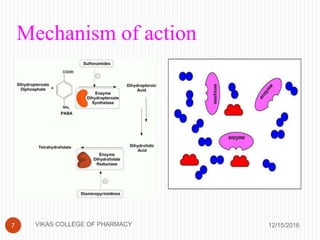
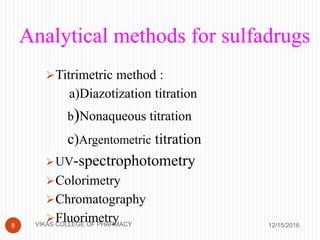
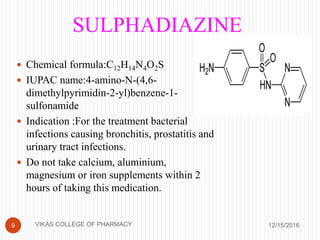
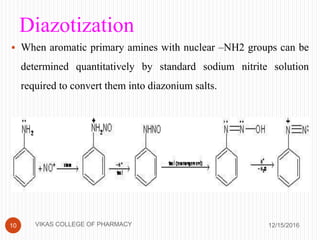
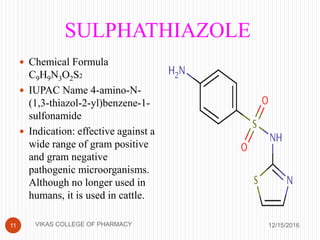
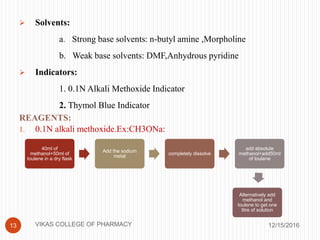
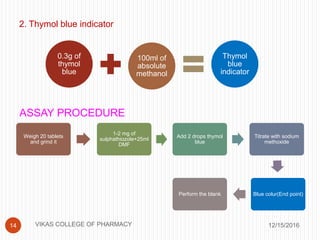
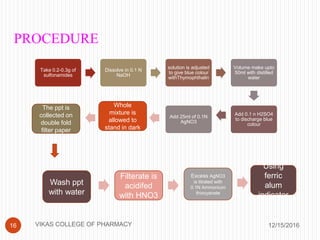
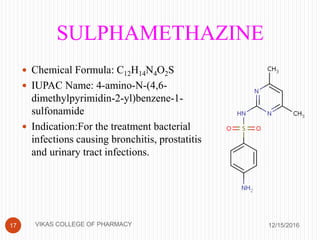
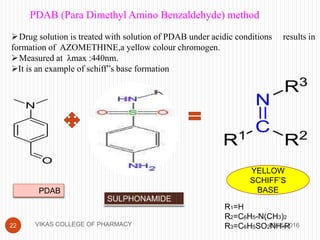
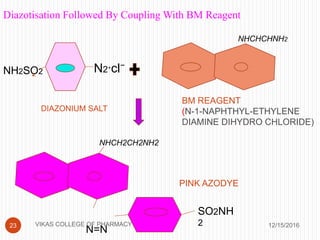
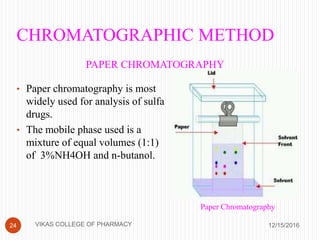
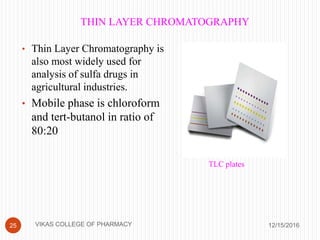
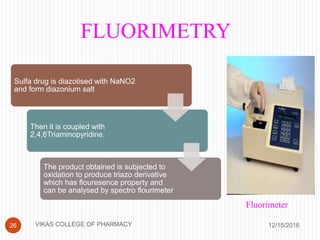
This document analyzes and summarizes various analytical methods for sulfonamides. It discusses the classification, mechanism of action, and common analytical techniques for sulfonamides including titrimetric methods, UV-spectrophotometry, colorimetry, chromatography, and fluorimetry. The document provides examples of specific sulfonamides and how different analytical techniques can be applied to identify and quantify these drugs.