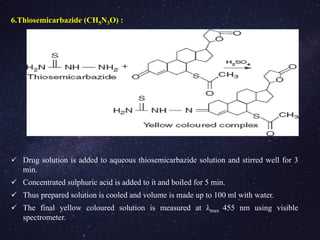
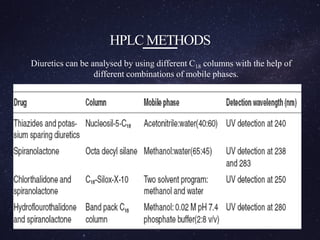
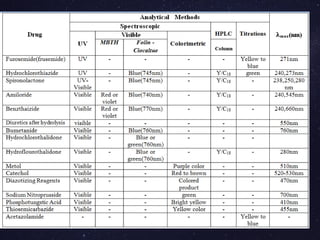
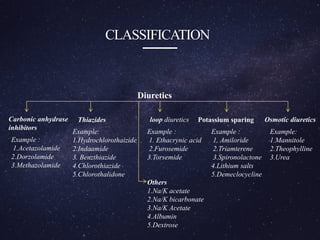
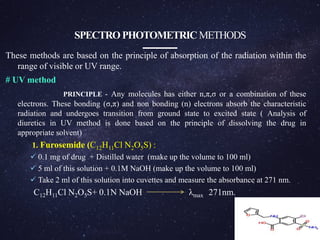
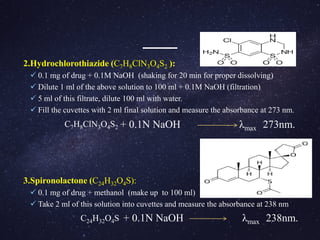
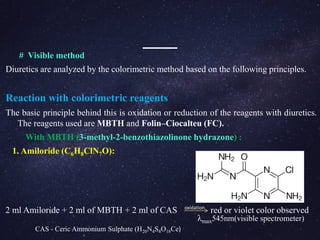
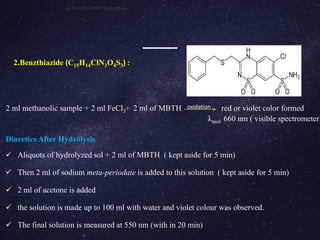
The document is a comprehensive analysis of diuretics, detailing their classification, analytical methods for assessment (including spectrophotometric, HPLC, and titrimetric), and various applications in medical treatments such as high blood pressure and fluid retention. It covers specific examples of diuretics, their mechanisms of action, and experimental methodologies for their analysis using different reagents and solvents. References and methodologies are well-documented, providing a thorough resource for understanding the role of diuretics in pharmacology.




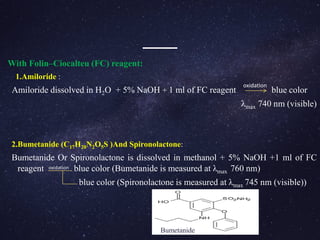
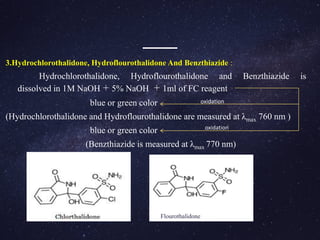
![# Colorimetric Methods
1.Metol (p-N-methyl amino phenol sulphate) [(C7H10NO)2SO4 ]:
p-N-methyl benzoquinoneimine is resulted from the reaction between metol and
sodium meta- periodate
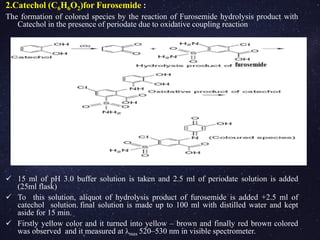
15 ml of pH 3.0 buffer solution is taken and 2.5 ml of periodate solution is added (25 ml
flask).
To this solution, aliquot of hydrolysis product of furosemide is added along with 2.5 ml
of catechol solution.
The final solution is made up to 100 ml with distilled water and kept aside for 15 min.
finally purple coloured charge transfer complex was formed.
The purple colour solution is measured at λmax 510 nm using visible spectrometer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analysisofdiuretics-180420094219/85/Analysis-of-diuretics-12-320.jpg)
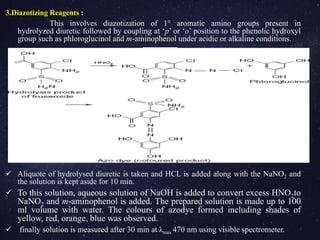
![4. Sodium nitroprusside(Na2[Fe(CN)5NO]) For Spiranolactone:
Sodium nitroprusside is also called penta cyano nitrosyl ferrate
dihydrate or sodium nitro ferric cyanide.
To the drug solution, aqueous solution of NaOH is added along with
CH3COOH and alkaline sodium nitroprusside.
The prepared solution is made up to 100 ml with distilled water within 12
min.
The obtained green solution is measured at λmax 700 nm(visible)
5. Phosphotungstic acid (24WO3.2H3PO4.48H2O):
Phosphotungstic acid + chloroform, acetic anhydride and Phosphotungstic
acid (mixed well)
Concentrated sulphuric acid is added to the above solution after 3 min
( made up to 100 ml with methanol). Bright yellow colored solution
measured at λmax 410 nm (visible spectrometer)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analysisofdiuretics-180420094219/85/Analysis-of-diuretics-15-320.jpg)