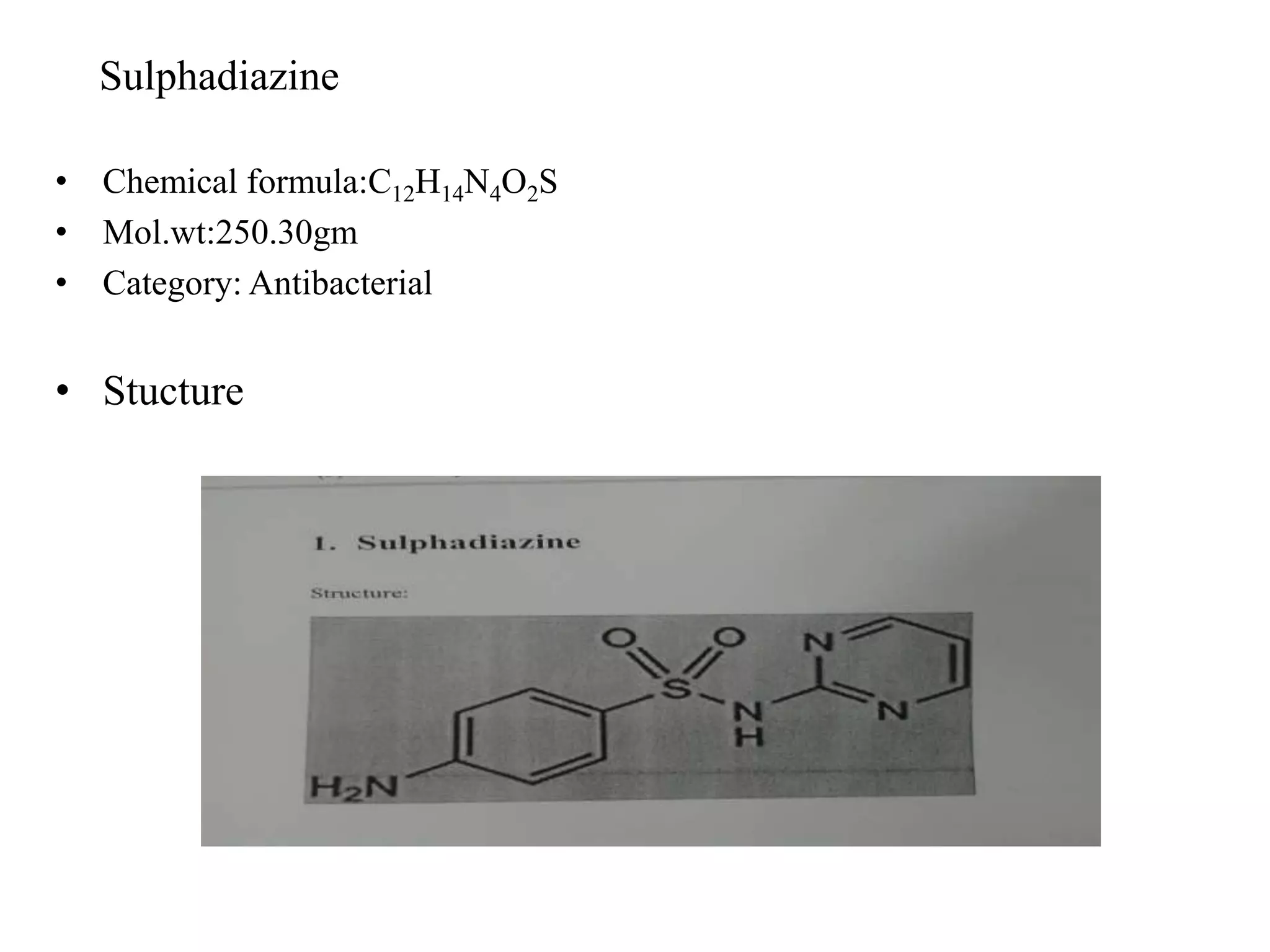
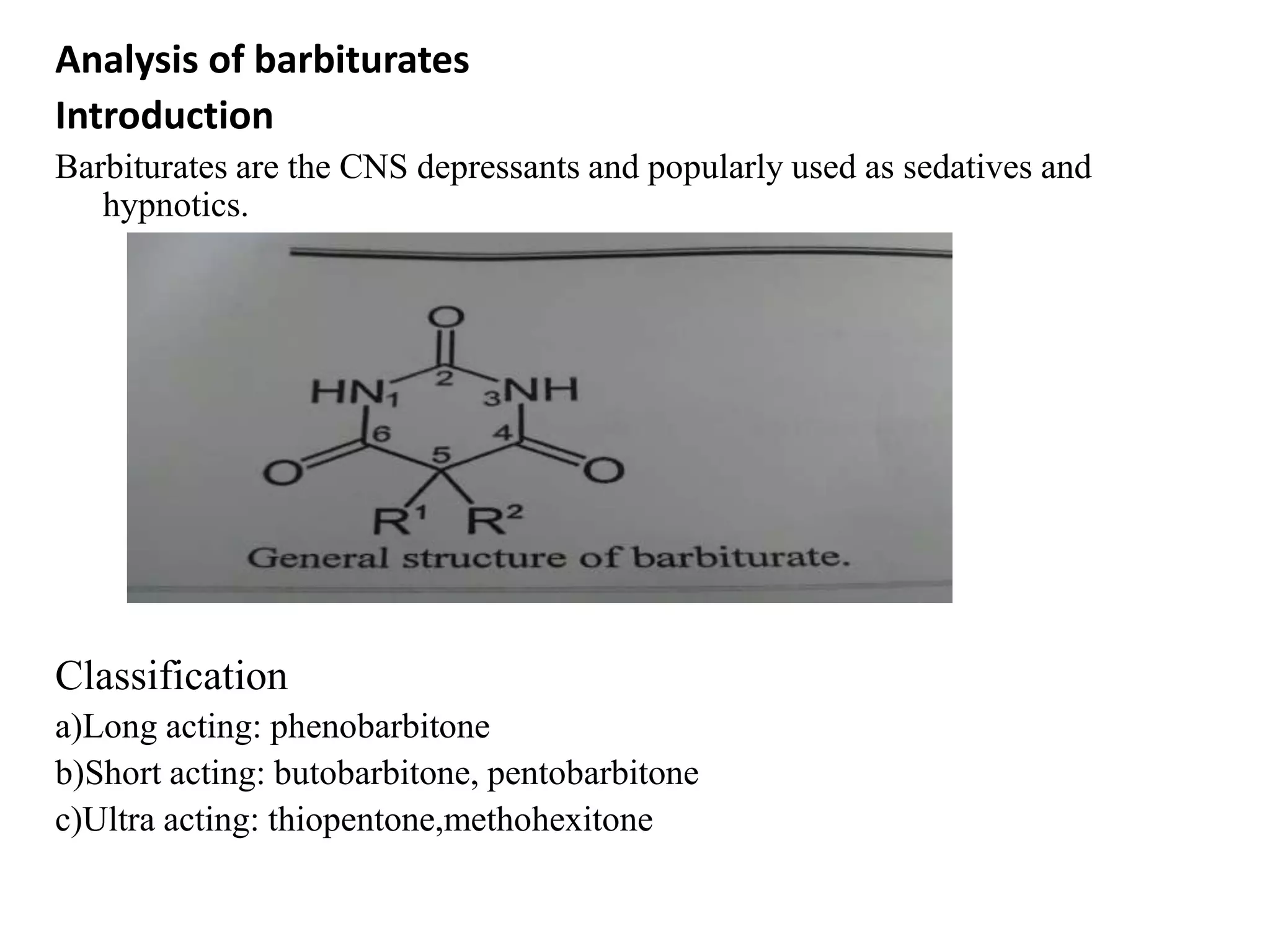
This document summarizes analytical methods for various drug classes including sulphonamides, barbiturates, adrenergic drugs, antitubercular drugs, and diuretics. It discusses physico-chemical properties and describes specific analytical techniques for several drugs including sulfadiazine, phenobarbital, xylometazoline hydrochloride, isoniazid, and furosemide. Methods include titrimetry, spectroscopy, chromatography, and colorimetry. The document serves as a reference for analytical techniques to identify and quantify pharmaceutical compounds.
















![Mixed action sympathomimetics
They act directly as well as indirectly
Eg: ephedrine, amphetamine etc.
XYLOMETAZOLINE HYDROCHLORIDE:
Molecular formula:C16H24N2.HCl
Chemical name:2[4-tert-butyl 2,6- dimethylbenzyl]- 2-
imidazoline monohydrochloride.
Molecular weight:280.84
Appearance: white crystaline and odourless substance.
Solubility: soluble in methanol& ethanol in 3% in water.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ima2ndinternals-160401071114/75/physicochemical-and-instrumental-method-analysis-of-pharmaceutical-dosage-forms-19-2048.jpg)









