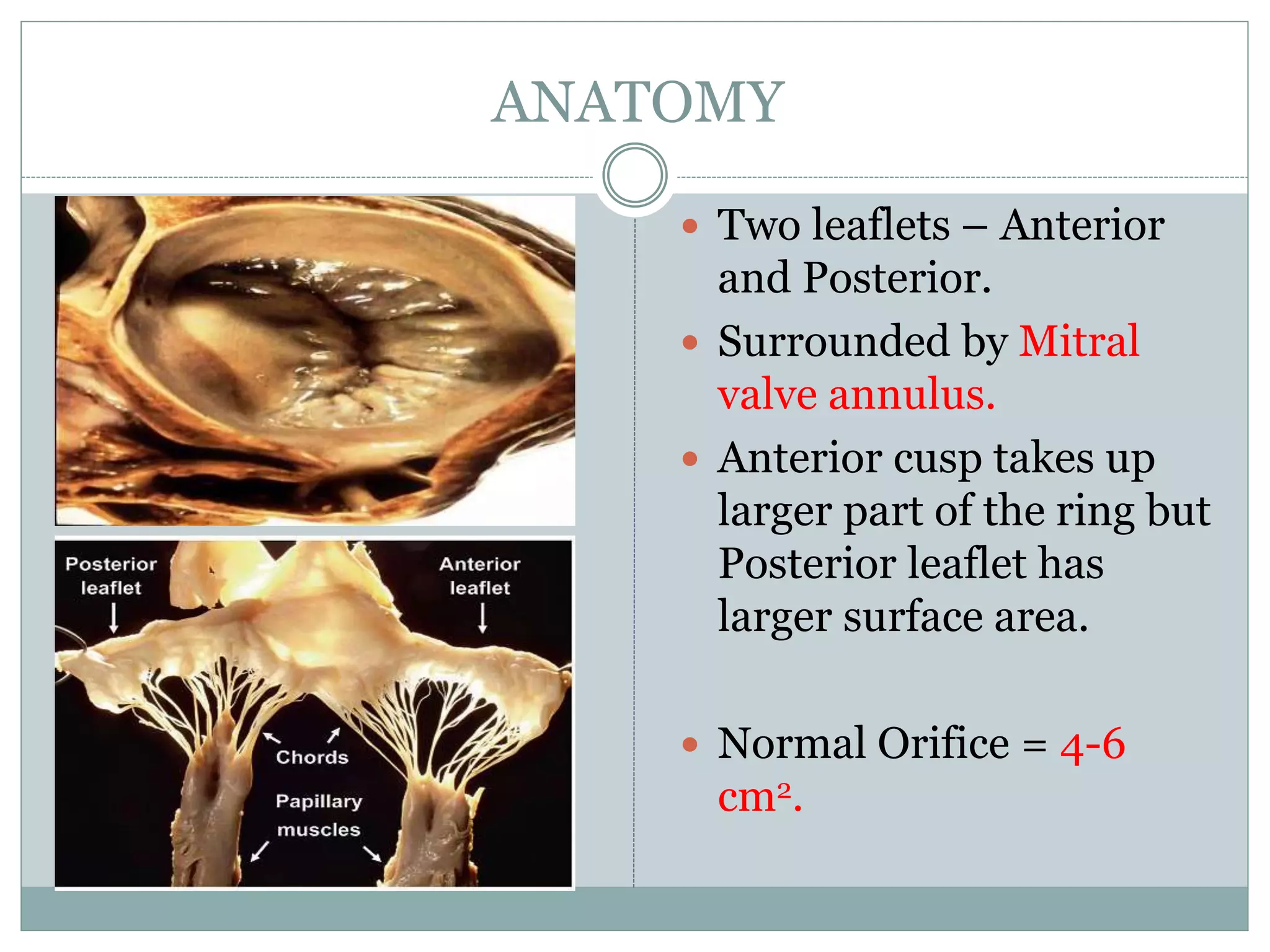
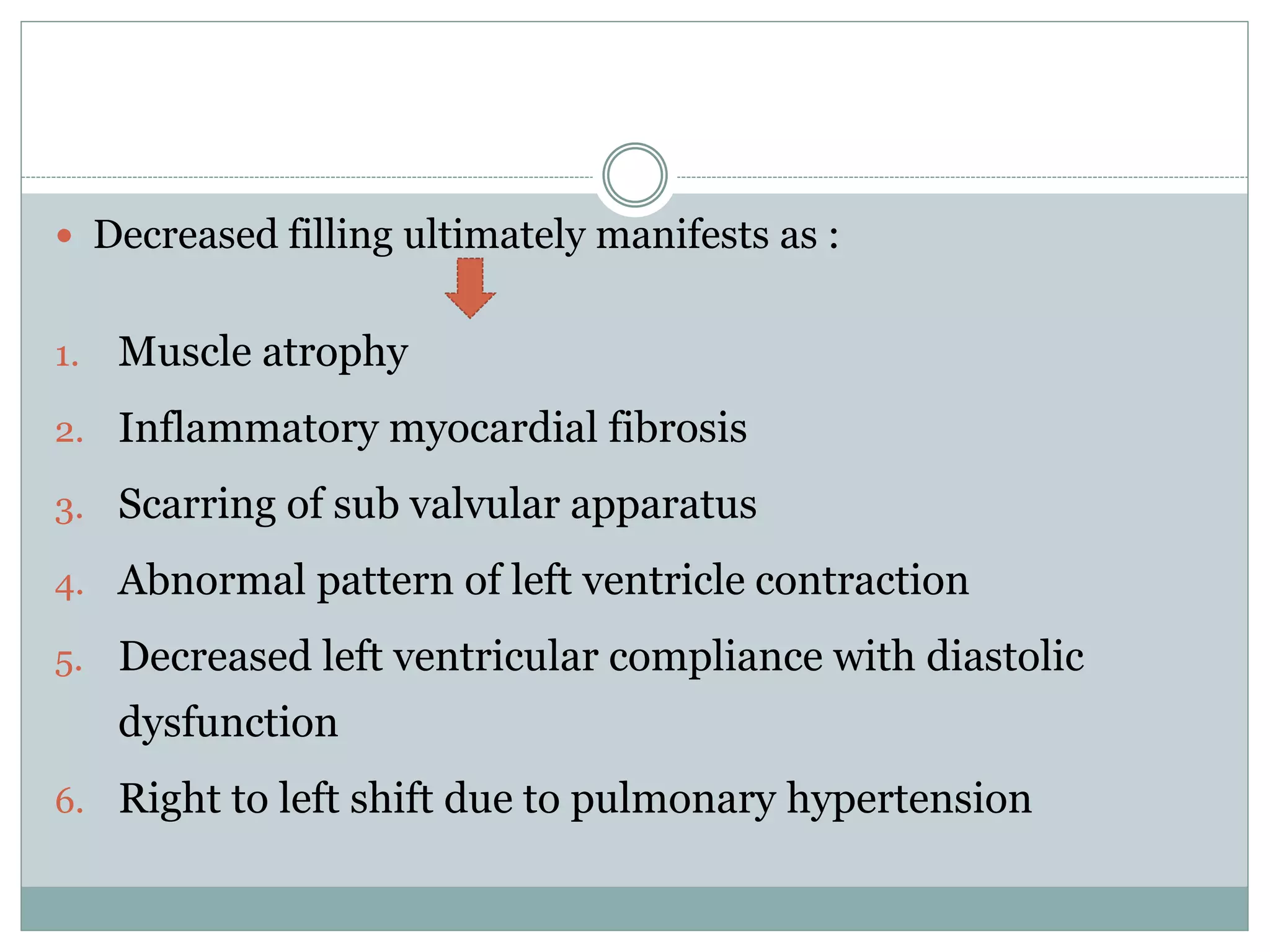
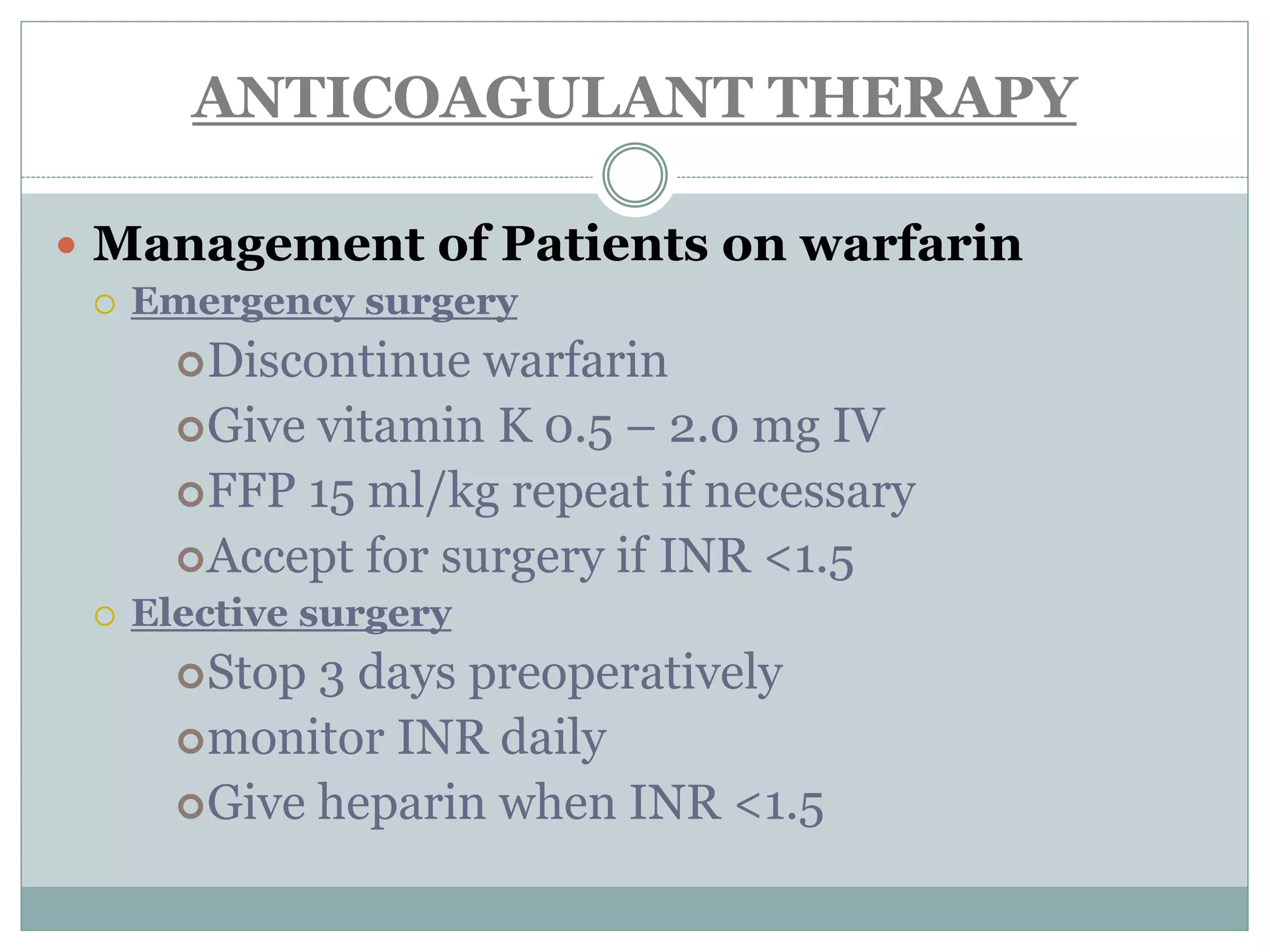
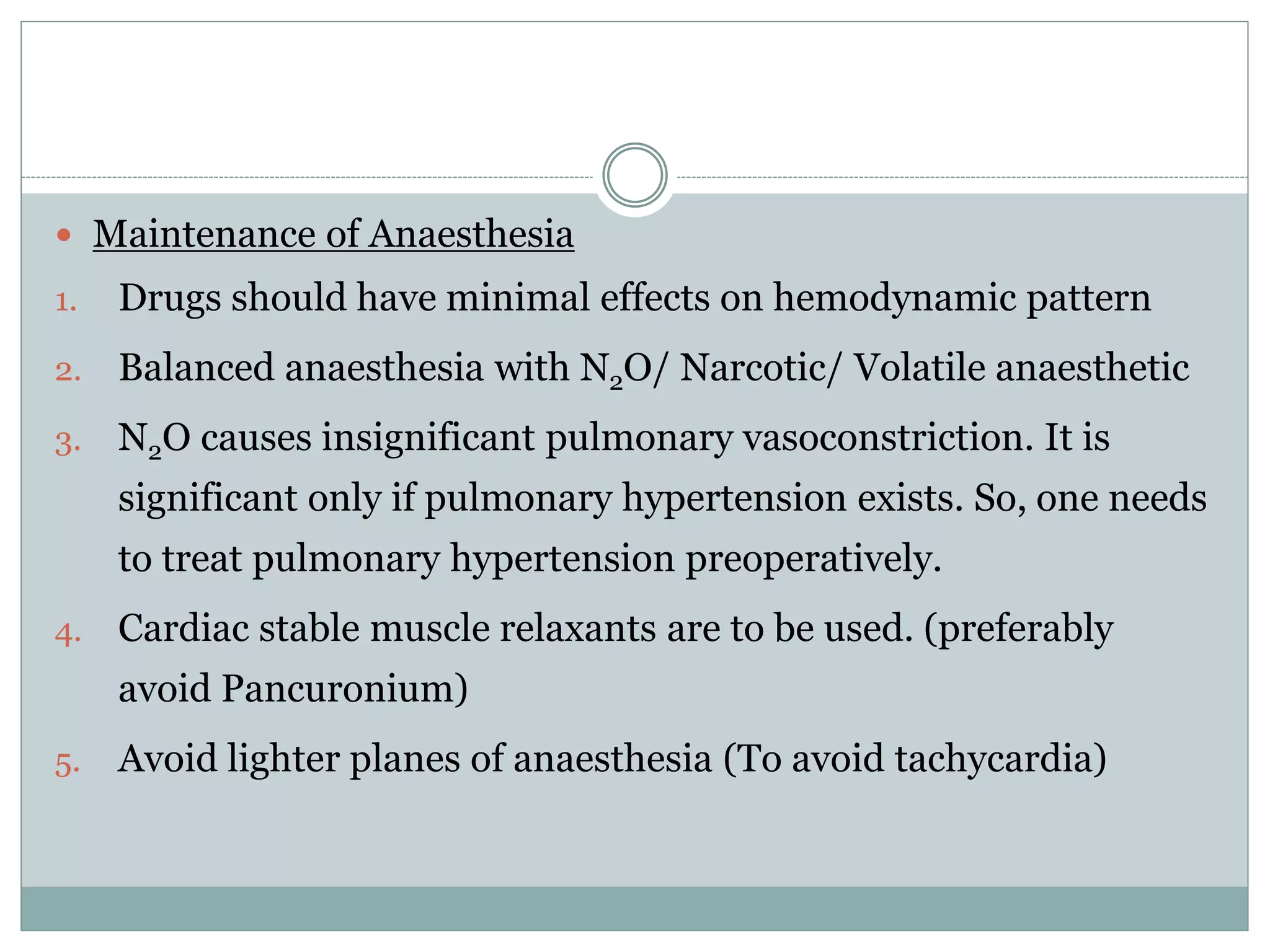
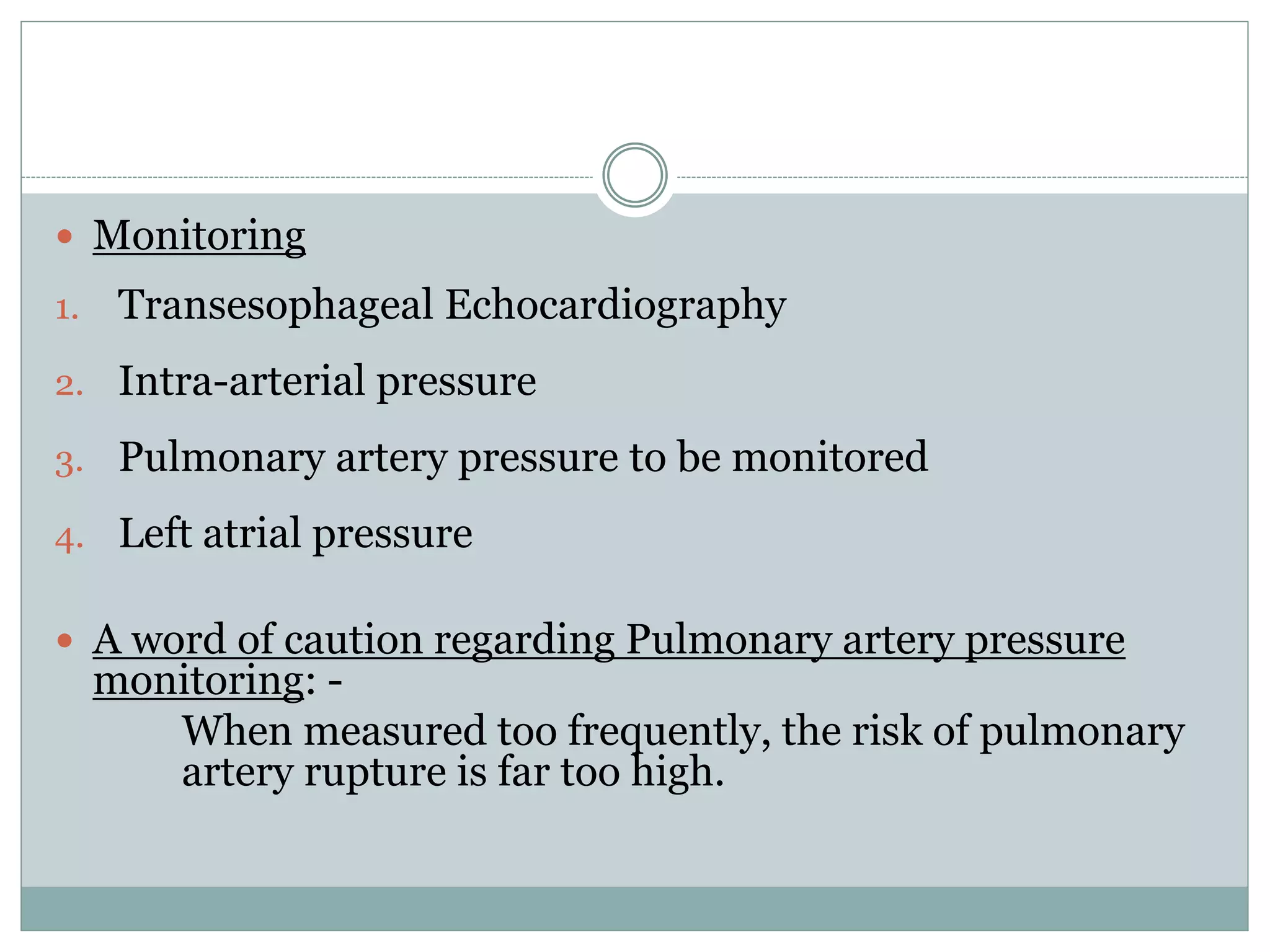
This document discusses the anaesthetic management of closed mitral valvotomy. It begins with the anatomy and pathophysiology of mitral stenosis. It then discusses the indications for closed mitral valvotomy and the pre-anaesthetic assessment. The key aspects of anaesthetic management are maintaining haemodynamic stability, avoiding tachycardia and hypotension, and careful fluid management. Etomidate is recommended for induction due to hemodynamic stability. Post-operatively, risks of pulmonary edema and right heart failure must be assessed and managed.