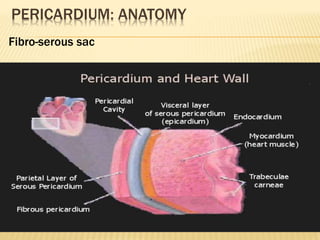
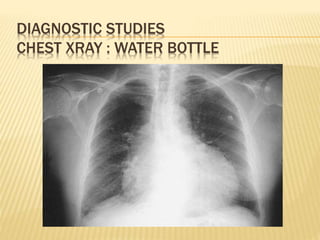
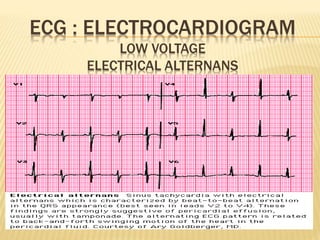
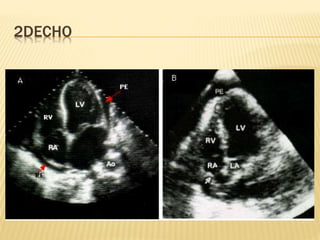
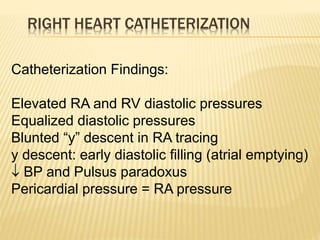
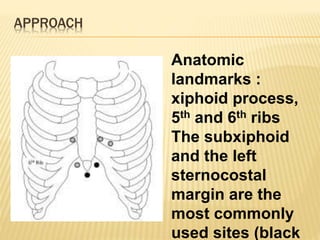
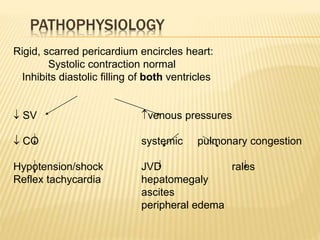
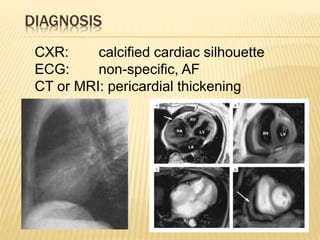
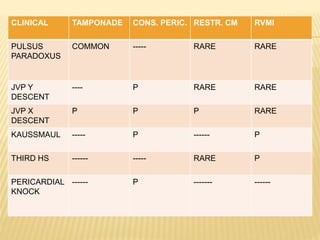
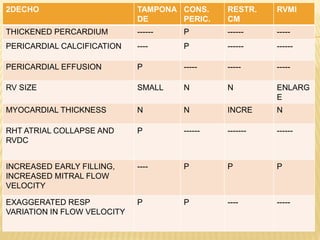
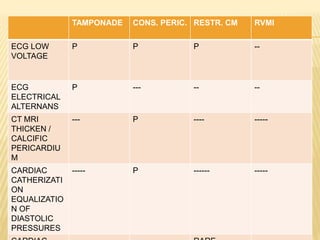
This document discusses pericardial diseases, focusing on pericarditis, pericardial effusion, and cardiac tamponade. It defines the pericardium and its functions. It describes the symptoms, signs, and diagnostic criteria for acute pericarditis. Causes of pericarditis include infections, autoimmune disorders, neoplasms, radiation, renal failure, and trauma. Treatment involves NSAIDs, colchicine, or steroids depending on severity and recurrence risk. Pericardial effusion and tamponade can develop as complications, requiring drainage procedures or surgery.