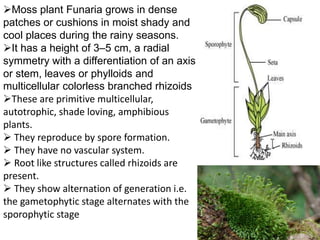
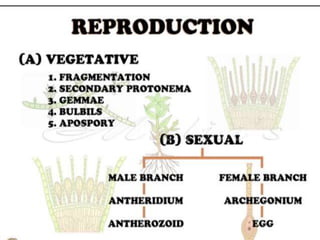
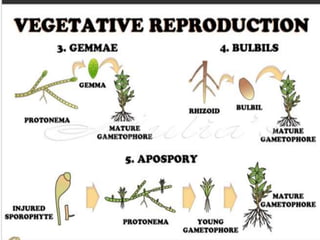
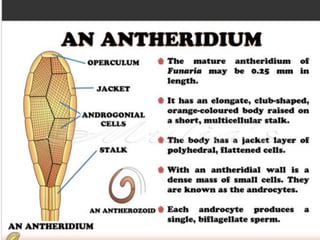
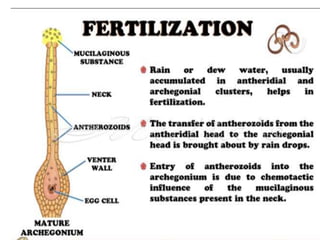
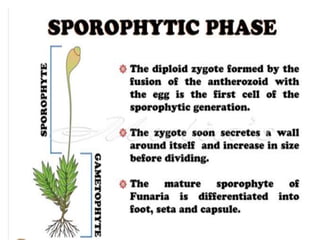
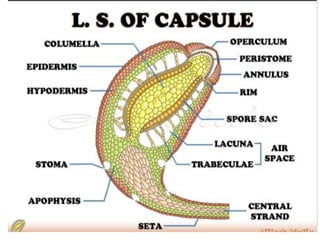
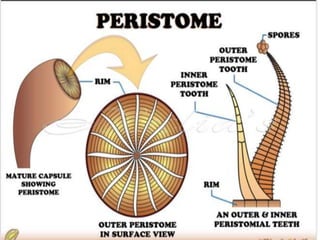
Funaria is a genus of approximately 210 moss species, with 18 found in India. Funaria hygrometrica, or "cord moss", is the most common. It grows in dense patches in moist, shady areas during rainy seasons. The gametophyte stage is dominant and produces an erect, branched structure up to 3 cm tall with flat, spirally arranged leaves. It reproduces via spores and alternates between gametophyte and sporophyte generations. Internally, the stem has an epidermis, cortex and central cylinder providing structure and transport, while the leaves are one cell thick except for the midrib.