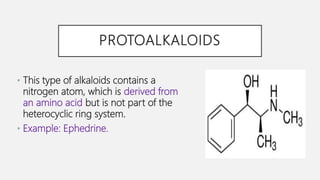
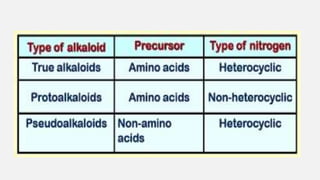
This document discusses alkaloids, which are nitrogen-containing organic compounds that have pharmacological effects on humans and animals. It defines three types of alkaloids - true alkaloids, protoalkaloids, and pseudoalkaloids - and provides examples of each type. The document also examines two specific alkaloid-containing plants - vinca and belladonna - describing their macroscopic characteristics, chemical constituents, and medicinal uses.