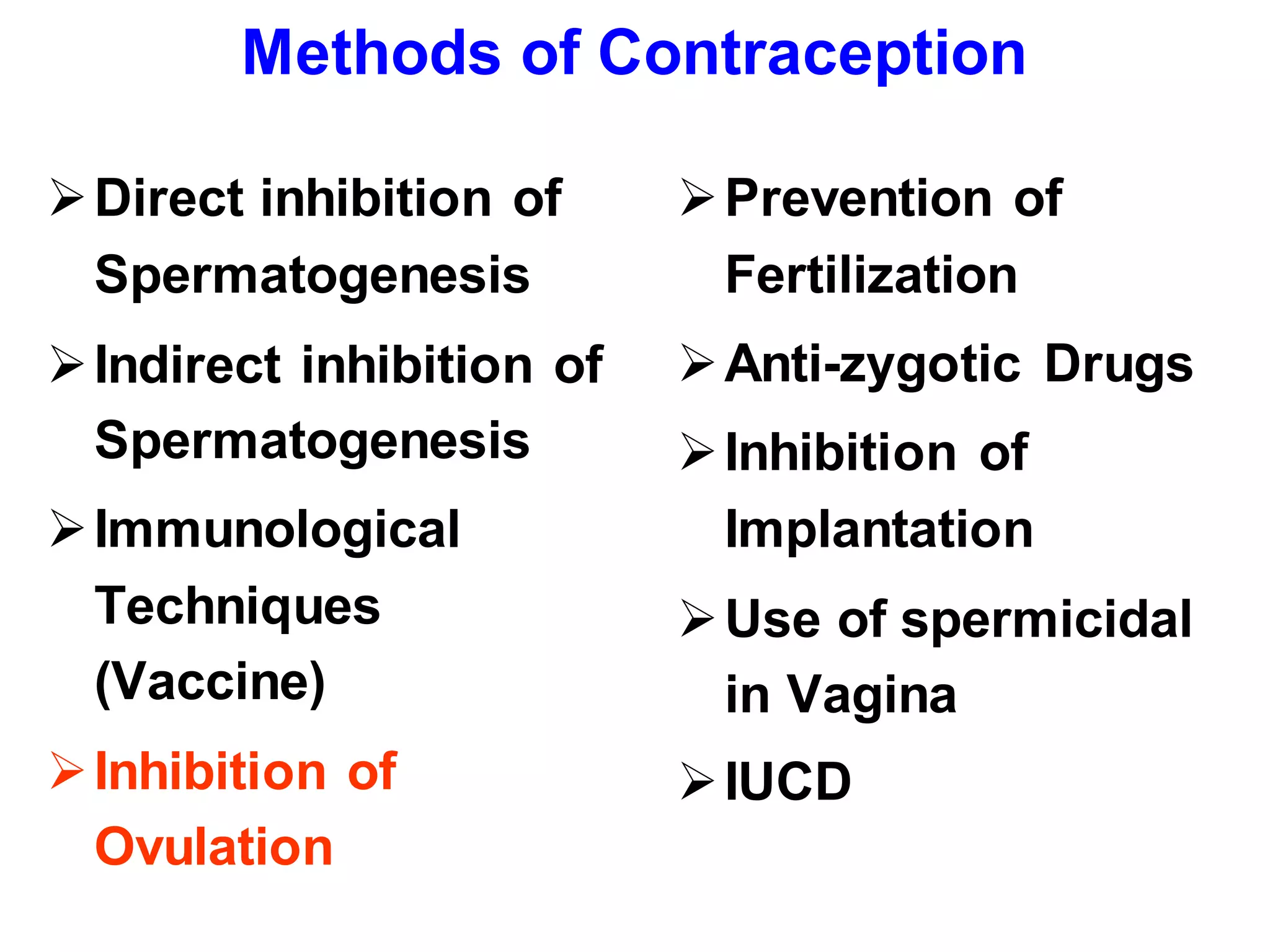
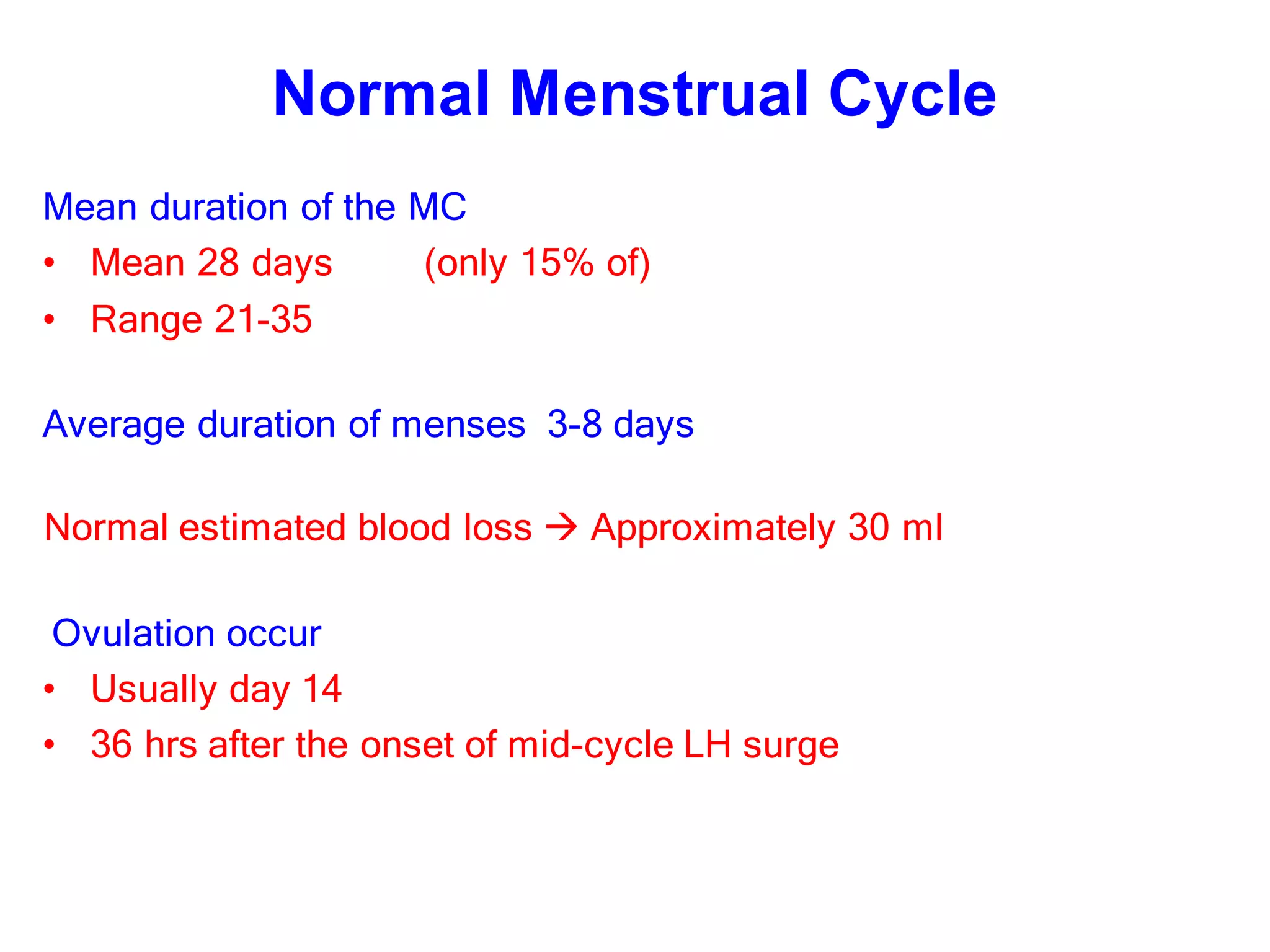
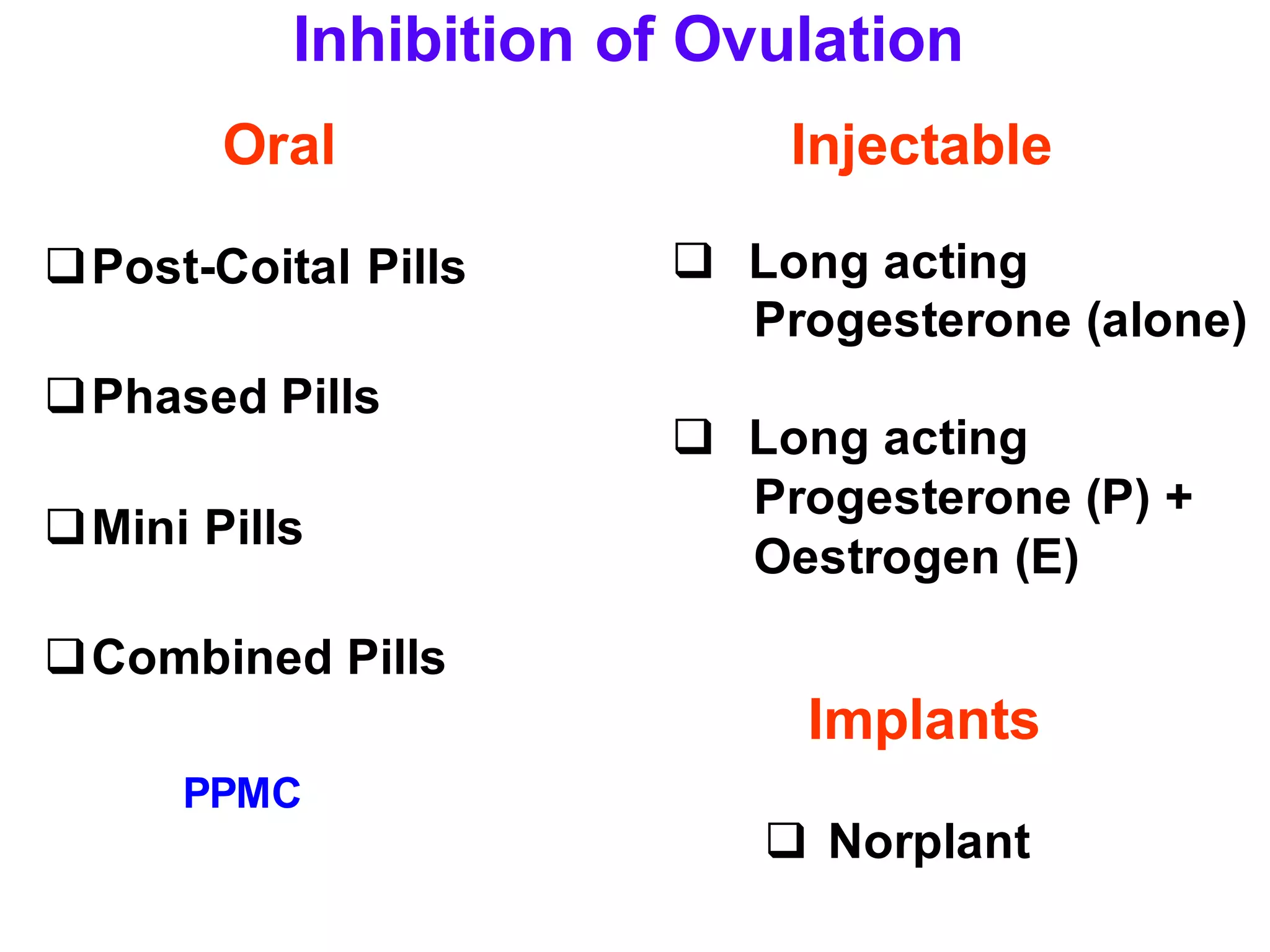
This document discusses various methods of contraception including oral and injectable contraceptive steroids. It provides details on the history, mechanisms of action, types (combined pills, mini pills, emergency contraception), administration, effects and side effects of oral contraceptive steroids. It also discusses injectable contraceptives including long acting progestogen injections and implants, and their effectiveness.