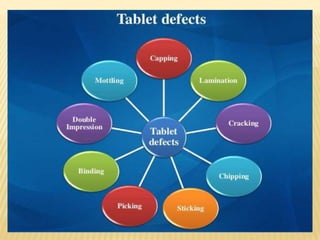
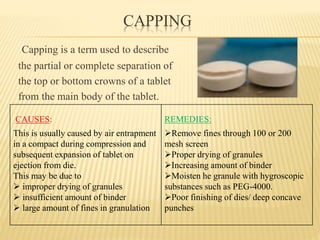
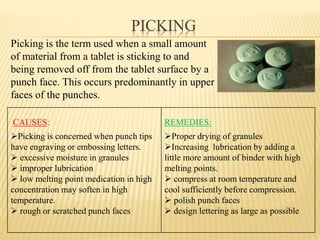
This document discusses common processing problems that can occur during tablet manufacturing and their causes and remedies. Major problems discussed include capping, lamination, picking, sticking, mottling, chipping, and cracking. Capping is caused by air entrapment during compression and can be prevented by proper drying, sufficient binder, and removing fines. Lamination is caused by oily or waxy materials and too much lubricant, and can be addressed by modifying the mixing process and using minimal lubricant. Sticking occurs due to moisture, excess binder, or improper lubrication and drying. Remedies involve drying, lubrication, and modifying granulation.