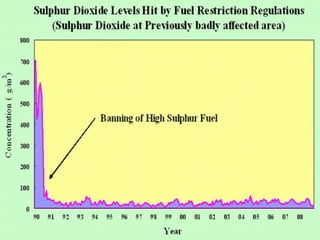
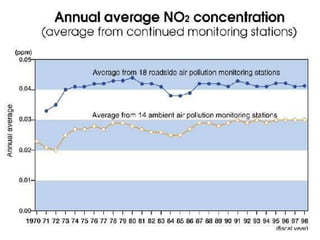
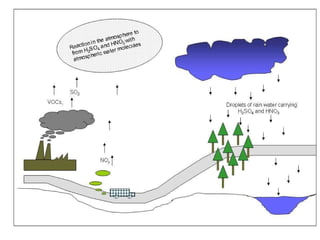
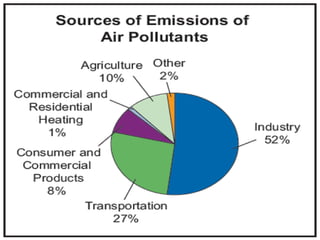
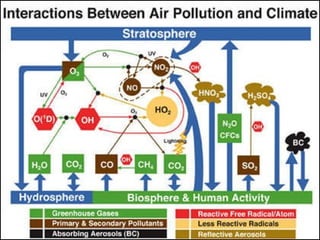
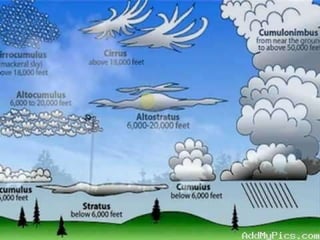
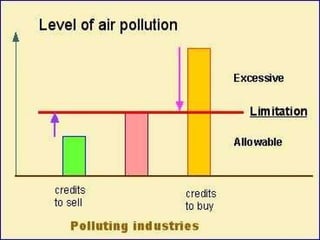
The document discusses air pollution, its causes and effects. It outlines the primary air pollutants such as particulate matter, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and fluorides. Secondary pollutants like photochemical smog and acid rain are also mentioned. Control methods for air pollution include the use of scrubbers, cyclonic separators and electrostatic precipitators to capture particulate matter, and combustion, absorption and adsorption techniques to control gaseous pollutants. The role of Central Pollution Control Board in regulating air pollution in India is highlighted.