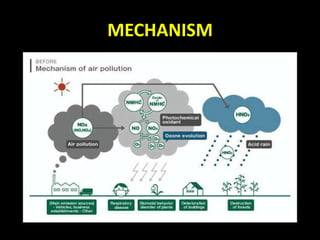
This document defines air pollution as occurring when air contains harmful amounts of gases, dust, fumes or odors. It discusses outdoor sources like smog and indoor sources like burning wood. Natural sources include wildfires and volcanoes, while human sources are things like vehicles, power plants, and burning wood. Air pollution can cause health issues for humans and environmental effects like acid rain. The document recommends mitigating air pollution through sustainable development, international agreements, and new technologies.