Embed presentation
Downloaded 136 times




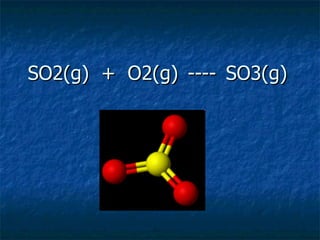




Sulfur dioxide is the main gas responsible for reducing smog. It reduces other gases in the atmosphere while also oxidizing to sulfur trioxide, which dissolves in water to form an acidic mist or smog. There are two ways this can happen - through heterolytic catalysts like unburnt hydrocarbons that weaken bonds, or through free radical catalysts produced when nitrogen dioxide molecules split due to UV light. Both catalysts can help sulfur dioxide and other gases convert to sulfur trioxide and ultimately sulfuric acid smog.








