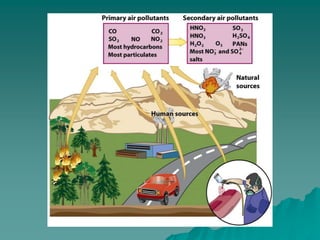
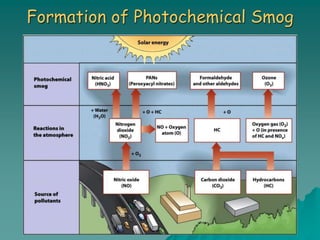
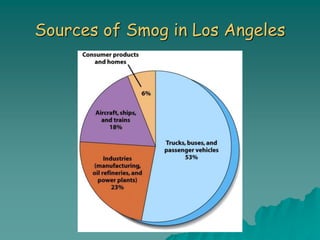
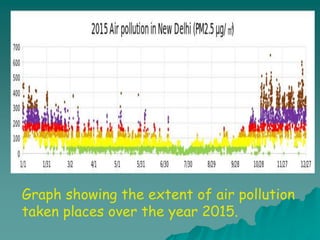
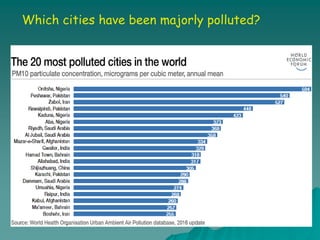
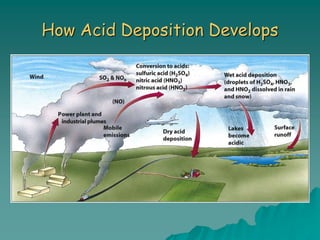
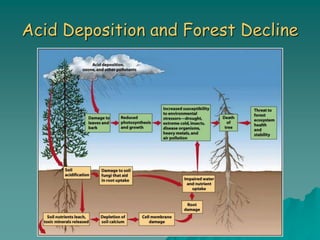
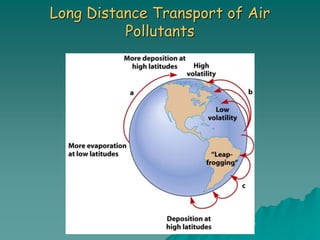
The document discusses air pollution, outlining its sources, types, and effects on health and the environment. It covers major classes of air pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, and highlights issues like ozone depletion and urban smog. Additionally, it emphasizes controlling measures for air pollution and the importance of regulations such as the Clean Air Act.