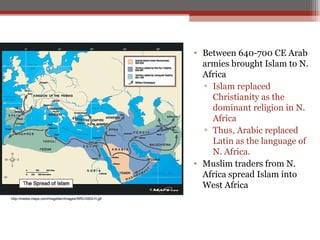
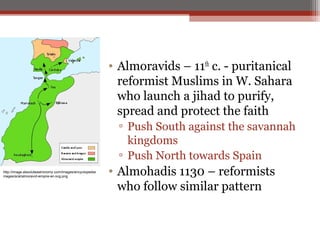
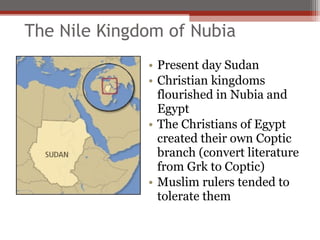
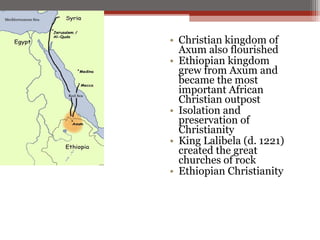
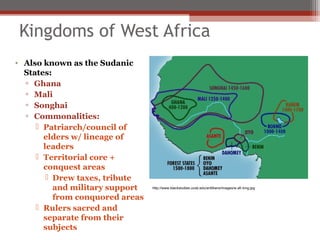
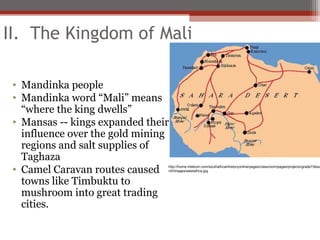
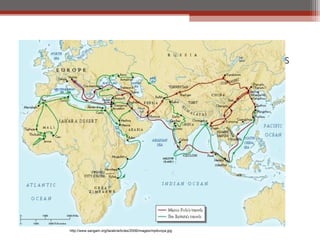
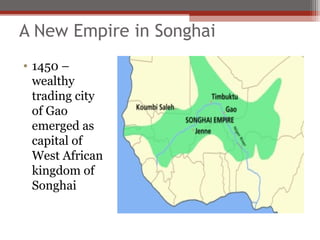
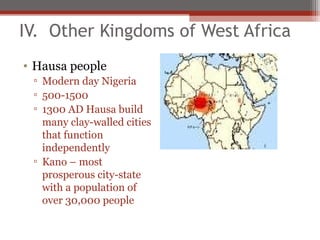
African civilizations were typically organized around kinship groups with decentralized political authority. Common elements included use of Bantu languages, animistic religions, and veneration of ancestors. North Africa was influenced by Mediterranean traders and later the Romans, and Christianity spread. The arrival of camels enabled trans-Saharan trade networks, through which Islam spread south, replacing Latin and Christianity as dominant. Major West African kingdoms like Ghana, Mali, and Songhai controlled gold and salt trade routes across the Sahara and grew wealthy. Other notable states included the Christian kingdoms of Nubia, Axum, the Hausa city-states, and the Benin Kingdom known for its bronze art.