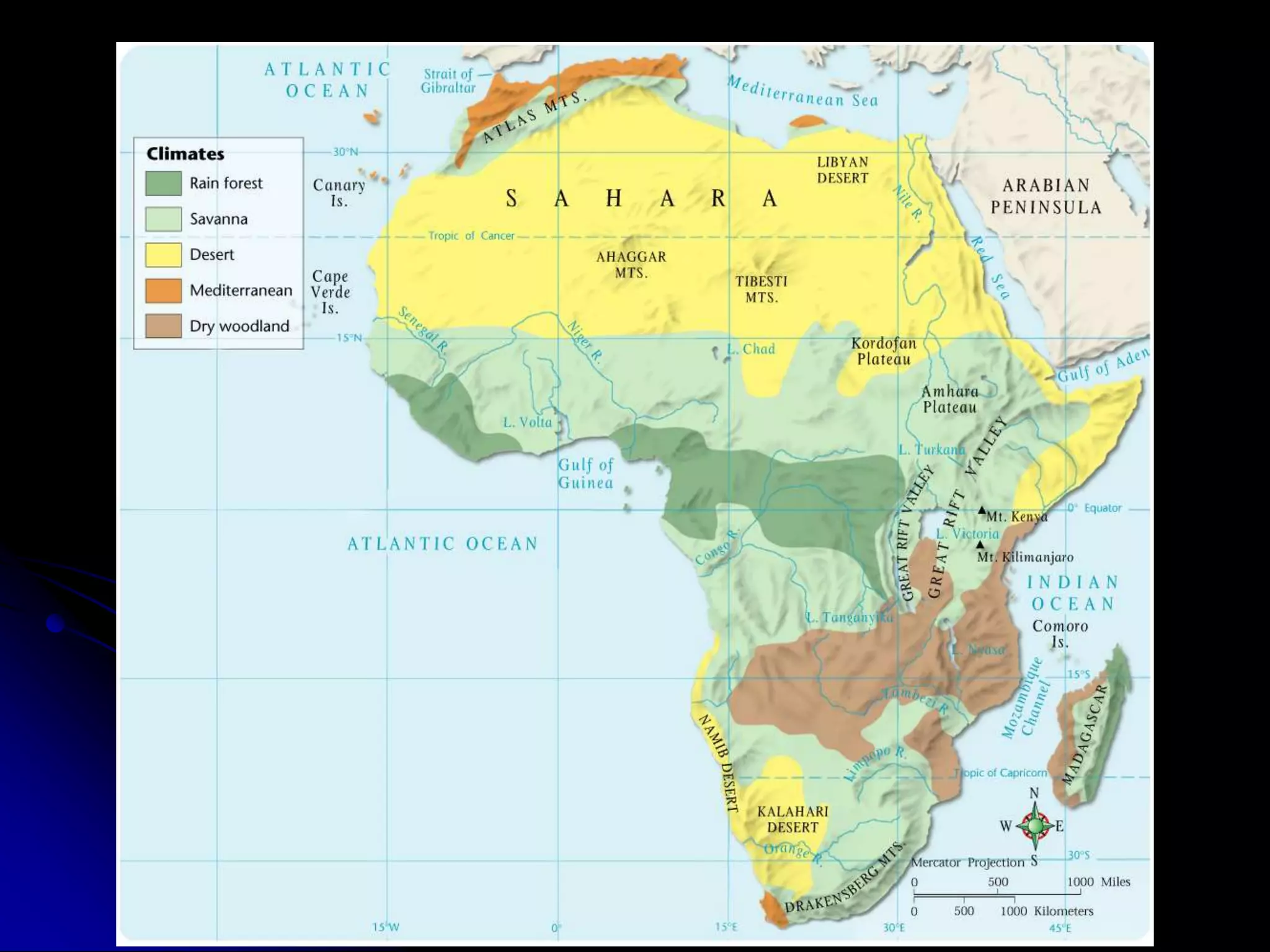
The document provides an overview of kingdoms and trading states in Africa from 730 BC to 1591 AD. It discusses the influence of geography on trade and resources, including the Sahara Desert acting as a barrier. Major kingdoms discussed include Nubia, Ghana, Mali, and Songhai in West Africa, which prospered through trade of gold and salt. In East Africa, it describes the kingdoms of Axum and city-states along the Swahili coast that engaged in trade. Family structures, political systems, religions, arts and oral traditions of medieval African societies are also summarized.