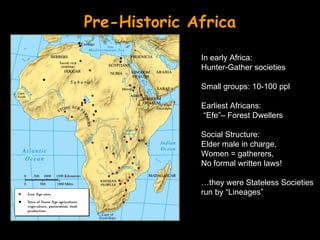
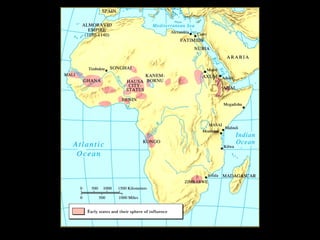
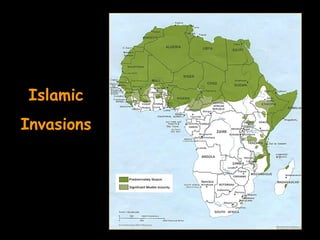
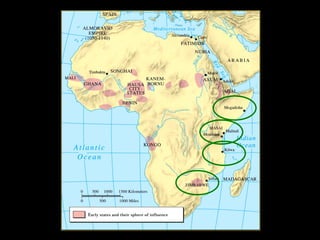
The document summarizes the effects of Islam on North Africa in three sections. Section 1 explains how Muslim states like the Almoravids and Almohads brought Islam to North Africa and established Islamic rule. Section 2 discusses the Islamic invasions and the rise of empires like Ghana, Mali, and Songhai due to the gold-salt trade. Section 3 explains how Islam influenced East African peoples like the Swahili who blended Bantu and Arabic languages and cultures.













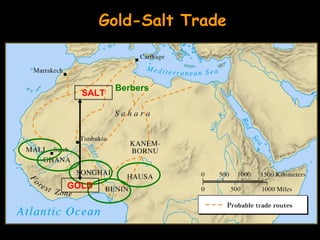




![2. Mali Empire [13c-15c]
SALT
GOLD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-22-320.jpg)


![#1. Sundiata [1210-1255]
“Lion Prince”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-25-320.jpg)

![#2. Mansa Musa [r. 1312-1332]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-27-320.jpg)







![3. Songhai Empire [15c-16c]
SALT
GOLD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-35-320.jpg)
![Sunni Ali [r.1464-1492]
• Aggressive Muslim
ruler of Songhai
• Built a vast empire
through Military
conquest
• Captured Timbuktu
from Mali
• Created centralized
gov’t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-36-320.jpg)
![Askia Mohammed [r.1493-1529]
• Muslim rebel that took
over Sunni Ali’s son
• Excellent
administrator:
• Set up tax system
• Put officials in charge
of treasury, military,
agriculture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-37-320.jpg)
![Askia Mohammed’s Tomb [1443-1538]
Gao, Mali](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-38-320.jpg)


![Benin Empire [15c-19c]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-41-320.jpg)






![Swahili-Speaking Areas of E. Africa
SWAHILI [“the coast’] = Bantu + some Arabic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-50-320.jpg)

![Great Zimbabwe [1200-1450]
“Zimbabwe” = “stone enclosure”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-52-320.jpg)

![Manamotopa Empire [1450-1630]
Who: Founded by Mutota from Great Zimbabwe
What: new empire that replaced Great Zim
in power; military dominated
Why: conquered all of Zimbabwe; control of
Eastern Africa; forced conquered areas
to mine gold for them; Portuguese
took over = European POWER!!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-54-320.jpg)

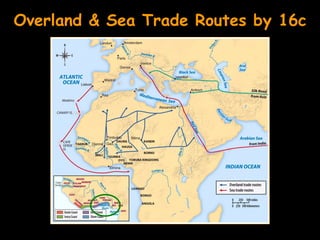
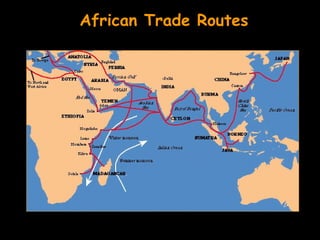
![African Trade [15c-17c]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch15africanhistory-120311185239-phpapp01/85/Ch-15-african-h-istory-57-320.jpg)