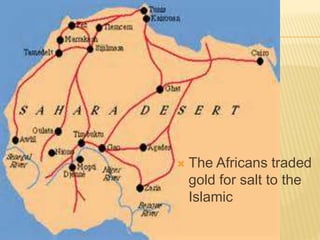
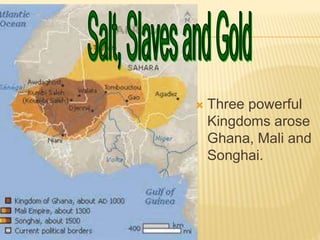
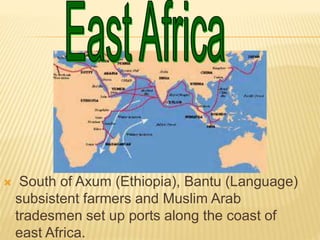
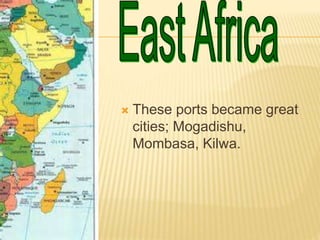
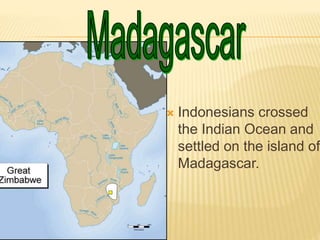
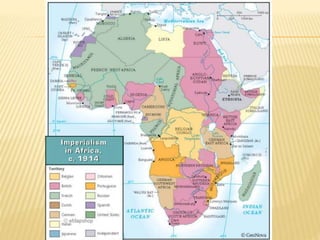
Great states arose in West, East, and South Africa as a result of the spread of Islamic trade and culture. In West Africa, Islam spread through cultural diffusion while East African port cities were colonized. This introduced new religions, literacy, trade practices, and arts to African kingdoms. Powerful states like Ghana, Mali, and Songhai emerged along the Niger River, benefiting from the trans-Saharan gold and salt trade with North Africa. Wealthy city-states also developed in East Africa along trade routes to India and China, introducing Arabic and African cultures. Eventually, European powers began colonizing the African coasts in the 15th-16th centuries to gain control of the lucrative trade networks.